Health and Hygiene-Food for Living - Adulteration | 9th Science : Health and Hygiene-Food for Living
Chapter: 9th Science : Health and Hygiene-Food for Living
Adulteration
Adulteration
Observe the picture

What do you think the man in the picture is doing?
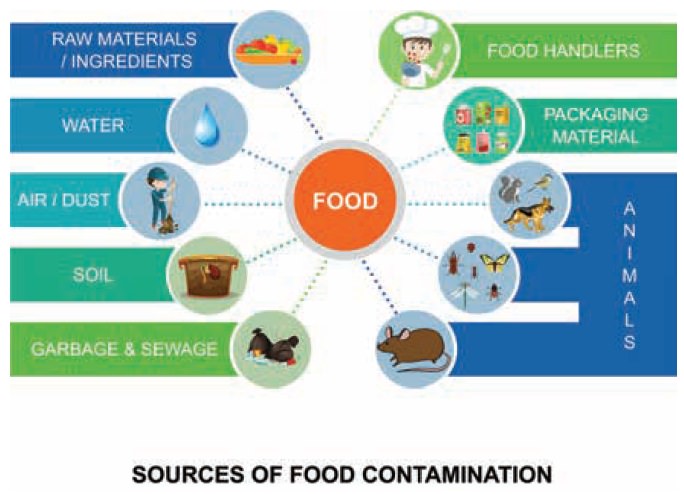
Food safety is becoming a major concern in these
days. Food is contaminated or adulterated from production to consumption for
financial gain or due to ignorance, carelessness and poor hygienic conditions
during processing, storing and marketing. Adulteration is defined as “the
addition or subtraction of any substance to or from food, so that the natural
composition and the quality of food substance is affected.”
Some of the common adulterated foods are milk and
milk products, cereals, pulses, co ee powder, tea powder, turmeric powder, sa
ron, confectionary, non-alcoholic beverages, spices, edible oils, meat, poultry
products etc. The adulterants in food can be classi ed in three categories
based on whether they occur naturally in food, or added intentionally or
unintentionally.
Types of adulterants
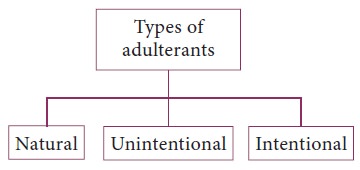
1. Natural adulterants
Natural adulterants are those chemicals, organic
compounds or radicals that are naturally present in food. They include,
a. Naturally
occurring toxic substances in certain poisonous mushrooms, Prussic acid in
seeds of apples, cherry and peach pits, marine toxins, fish oil poisoning etc.,
b. Environmental
contaminants like pollutants in air, water and land.
2. Incidental/ unintentionally added adulterants
These types of adulterants are added unknowingly
due to ignorance or carelessness during food handling and packaging. It
includes
a. Pesticide residues

b. Droppings of rodents, insects, rodent bites and
larva in food during its storage

c. Microbial contamination due to the presence of
pathogens like Escherichia coli, Salmonella in fruits, vegetables, ready-to-eat meat and
poultry products
3. Intentionally added adulterants
These adulterants are added intentionally for
financial gain and have serious impact on the health of the consumers. These
types of adulterants include:
a. Additives
and preservatives like vinegar, citric acid, sodium bicarbonate (baking soda),
hydrogen peroxide in milk, modified food starch, food flavours, synthetic
preservatives and artificial sweeteners.

b. Chemicals
like calcium carbide to ripen bananas and mangoes.
c. Non
certified food colours containing chemicals like metallic lead are used to give
colours to vegetables like green leafy vegetables, bitter gourd, green peas
etc. These colours are added to give a fresh look to the vegetables.

d. Edible
synthetic wax like shellac or carnauba wax is coated on fruits like apple, pear
to give a shining appearance.

e. Growth hormones, steroids and antibiotics are administered as adulterants to vegetables, cattle, sheep and poultry for faster growth and to increase milk production in dairy cows.
·
How these apples are different in their appearance?
·
Why is it so?
·
Which one is safe for consumption?
Consumption of these adulterated foods may lead to
serious health issues like fever, diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal
disorders, asthma, allergy, neurological disorder, skin allergies, immune
suppression, kidney and liver failure, colon cancer and even birth defects.
Fruit flies are more attracted towards fruits that
are naturally ripened.
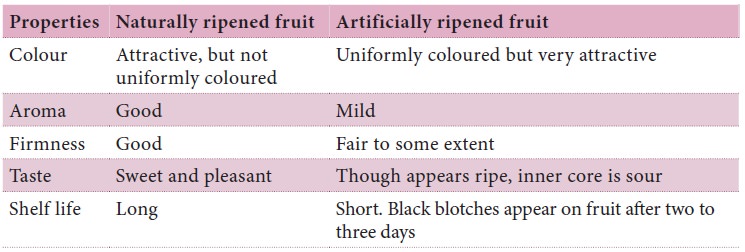
Difference between naturally ripened fruit and artificially ripened fruit
Some simple techniques used to detect adulterants at home

Project
Project: Collect information on the methods of
organic or non-chemical farming and its role in maintaining food quality.
Food quality control agencies of our Country

Food should be pure, nutritious and free from any
adulteration for proper maintenance of human health.
It is the duty of every government to make pure and
safe food available to public in sufficient quantities. In 1954, the Indian
government enacted the food law known as Prevention of Food Adulteration Act
and the Prevention of Food Adulteration Rules in 1955 with the objective of
ensuring pure and wholesome food to the consumers and protect them from
fraudulent trade practices.
Minimum standards of quality for food and strict
hygienic conditions for its sale are clearly outlined in the Act. Any food that
does not conform to the minimum standards laid down in the Act is said to be
adulterated. The Act also intends to penalise the dealers who are engaged in
the production and sale of contaminated food substances. is Act is periodically
amended based on requirements.
Quality control agencies such as
·
ISI, AGMARK, FPO, FCI and other health departments enforce minimum standards for the consumer
products.
FCI (Food
Corporation of India) was set
up in the year 1965 with the following objectives:
· Effective price support operations for safeguarding the interest of farmers.
·
Distributing food grains throughout the country.

Food control agencies, their standardized mark and their role in food safety

·
Maintaining satisfactory levels of operational and
buffer stock of food grains to ensure national security.
·
Regulate the market price to provide food grains to
consumers at reliable price.
A Case Study
Siddanth came back from school. He was feeling very
hungry. His mother sent him to buy a packet of biscuits from a nearby shop.
When his mother opened the packet, she realized that it was not fresh. So she
asked him to return the packet for a new one.
What do you think Siddanth should have observed
before buying the biscuit packet?


Related Topics