Chapter: Mechanical and Electrical : Thermal Engineering : Steam Nozzles and Turbines
Steam Nozzles
STEAM NOZZLE
Introduction
A steam turbine converts the energy of high-pressure, high temperature steam produced by a steam generator into shaft work. The energy conversion is brought about in the following ways:
1. The high-pressure, high-temperature steam first expands in the nozzles emanates as a high velocity fluid stream.
2. The high velocity steam coming out of the nozzles impinges on the blades mounted on a wheel. The fluid stream suffers a loss of momentum while flowing past the blades that is absorbed by the rotating wheel entailing production of torque.
3. The moving blades move as a result of the impulse of steam (caused by the change of momentum) and also as a result of expansion and acceleration of the steam relative to them. In other words they also act as the nozzles.
Flow Through Nozzles
Ø A nozzle is a duct that increases the velocity of the flowing fluid at the expense of pressure drop.
Ø A duct which decreases the velocity of a fluid and causes a corresponding increase in pressure is a diffuser .
Ø The same duct may be either a nozzle or a diffuser depending upon the end conditions across it. If the cross-section of a duct decreases gradually from inlet to exit, the duct is said to be convergent.
Ø Conversely if the cross section increases gradually from the inlet to exit, the duct is said to be divergent.
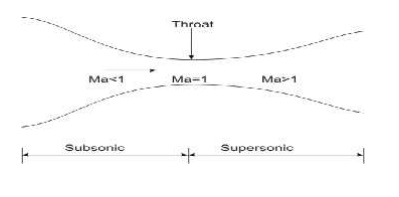
Ø If the cross-section initially decreases and then increases, the duct is called a convergent-divergent nozzle.
Ø The minimum cross-section of such ducts is known as throat.
Ø A fluid is said to be compressible if its density changes with the change in pressure brought about by the flow.
Ø If the density does not changes or changes very little, the fluid is said to be incompressible. Usually the gases and vapors are compressible, whereas liquids are incompressible .
Shapes of nozzles
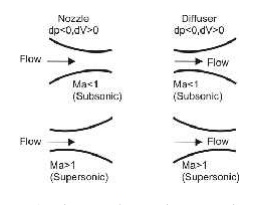
1. At subsonic speeds (Ma<1) a decrease in area increases the speed of flow.
2. In supersonic flows (Ma>1), the effect of area changes are different.
Convergent divergent nozzles
SIGNIFICANCE OF STEAM TURBINES
Ø Large scale electrical energy production largely depends on the use of turbines. Nearly all of the world's power that is supplied to a major grid is produced by turbines.
Ø From steam turbines used at coal-burning electricity plants to liquid water turbines used at hydro-electric plants, turbines are versatile and can be used in a number of applications.
Ø There are also gas turbines that combust natural gas or diesel fuel for use in remote locations or where a large backup power supply is required. Most power plants use turbines to produce energy by burning coal or natural gas.
Ø The heat produced from combustion is used to heat water in boiler. The liquid water is converted to steam upon heating and is exhausted through a pipe which feeds the steam to the turbine.
Ø The pressurized steam flow imparts energy on the blades and shaft of the turbine causing it to rotate.
Ø The rotational mechanical energy is then converted to electrical energy using a generator.
Related Topics