Types, Manufacturing Process, Finishing Process, Properties, Uses of Rayon | Man-Made Fibres - Rayon Fibre | 11th Textiles and Dress Designing : Chapter 3 : Man-Made Fibres
Chapter: 11th Textiles and Dress Designing : Chapter 3 : Man-Made Fibres
Rayon Fibre
RAYON:
The rayon fibre is made with pure cellulose.
Cellulose is the substance which is obtained from the cell walls of the woody
part of trees and cotton plant. Cellulose is commonly used for making products
such as paper. The rayon fibre that has been formed with regenerated or
re-formed cellulose substance is called as regener-ated cellulose fibres.
Rayon is the first man -made fibre and its
production has been prophesied as long ago as 1664 by Robert Hooke, an English
naturalist. He believed that it is possible to make an “artificial glutinous”
composition which can resemble the silk-worm fibre. Man-made textile fibres
were officially recognized in 1925 when the Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
per-mitted the use of the name “rayon” from yarns obtained from cellulose or
its deriv-atives. With the increase in production of man -made fibres, FTC
ruled again in 1937 that any fibre or yarn produced chemi-cally from cellulose
must be designated as rayon.
Types of Rayon
Based on the method of manufacture, at present
there are two principal types of rayon.
1.
Rayon or Viscose
2.
High Wet Modulus Rayon (regener-ated rayon)
In High Wet Modulus Rayon (HWM), the original
material (cellulose) is changed chemically into another form, which is then
changed or regenerated into cellulose again. These changes produce the final
product that is purified cellulose in the fibre form.
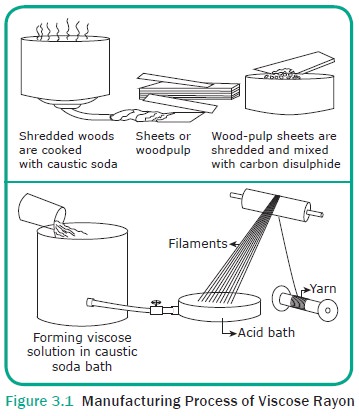
Manufacturing Process of Viscose Rayon
For making viscose rayon, wood chips or cotton
linters are treated with chemicals to produce sheets of purified cellulose that
resembles white blotters. This purified cellulose is soaked in caustic soda
which produces sheets of alkali cellulose. These sheets are then broken up into
fluffy white flakes or grains called cellulose crumbs. The crumbs are aged for
2-3 days under controlled temperature and humidity.
Liquid carbon disulphide is then added to these
cellulose crumbs which turn it into a light orange substance called cellulose
xanthate. The cellulose xanthate crumbs are then dissolved in a weak solution
of caustic soda, which turns it to a thick vis-cous solution resembling honey
in colour and consistency. This thick solution is called viscose. The viscose
is aged, fil-tered and vacuum treated to remove the air bubbles present, as
they may cause the filament to break. This treated viscose solution is then
forced through the holes of a spinneret into sulphuric acid which coagulates
the cellulose of the cellulose xanthate to form pure regenerated cellu-lose
filaments (Figure 3.1).
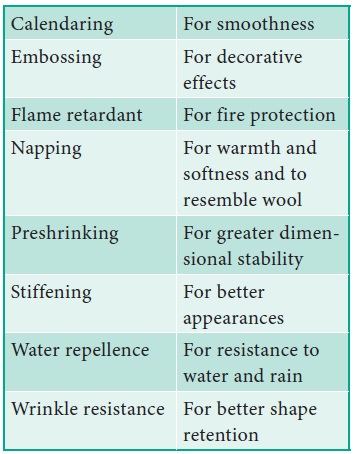
Finishing Process
A wide variety of fabrics can be produced by
viscose rayon. Spun rayon fabrics can be used for making fabrics that resem-ble
cotton, linen or wool. Rayon filament yarns can be used for making fabric that
resemble silk. Various finishes can be applied to these rayon fabrics to
improve their serviceability and to enhance their appearance. The most common
finishes given to rayon fabrics are as follows :
Properties of Rayon
Shape : Thin long filament
Size : Diameter varies from 12 to 40
microns (controlled by manufacturer)
Luster : Varies from brightness to
dullness
Strength : 2.4 – 3.0 Pa m3/kg
Elongation : 19 –
24%
Elasticity : 82%
Density : 1.5 g/cm3 for all rayon types
Moisture : Upto 10.7%
Dimensional stability : Poor
Resistance to acids : Not
good, but can be improved in special conditions
Resistance to alkalies : Not
good, but can be improved in special conditions
Sunlight : Can withstand sunlight to an
extent
Insects : Silver fish damages all type of
cellulose fibres
Reaction to heat : Can
withstand heat, but longer exposure will eventually degrade the fibre
Uses of Rayon
·
The uses of Rayon are:
·
The rayon is used to create clothing such as
blouse, jackets, sportswear and dresses.
·
It is used in textile industry for mak-ing
textile belts.
·
Rayon is used for making tyre.
·
It is also used for making carpets and surgical
dressings.
·
Rayon is used for a wide range of fabrics for
household.
Related Topics