Accountancy - Profit and loss account | 11th Accountancy : Chapter 12 : Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors - I
Chapter: 11th Accountancy : Chapter 12 : Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors - I
Profit and loss account
Profit and loss account
Profit and loss account is the
second part of income statement. It is a nominal account in nature. A business
entity is interested in knowing not only the gross profit or loss but also the
net profit earned or net loss incurred during the year. Hence, profit and loss
account is prepared to ascertain the net profit or net loss during the year.
Profit and loss account contains all the items of indirect expenses and losses
and indirect incomes and gains in addition to gross profit or gross loss
pertaining to the accounting period. The difference is net profit or net loss.
According to Prof. Carter, “A Profit and Loss Account is an account into which
all gains and losses are collected, in order to ascertain the excess of gains
over the losses or vice-versa”.
Need for preparing profit and loss account
Profit and loss account is
prepared for the following purposes:
(i) Ascertainment of net profit or net loss
The profit and loss account discloses the net profit available to the
proprietor or net loss to be borne by him. Ascertainment of profitability helps
in planning for the growth and efficiency of a business enterprise. Inter-firm
comparison and intra-firm comparison of profit and loss account items help in
assessing efficiency in comparison with other enterprises and other departments
of the same enterprise respectively.
(ii) Comparison of profit
The net profit of the current year can be compared with the profit of the previous years. It helps to know whether the business is conducted efficiently or not.
(iii) Control on expenses
Profit and loss account helps in comparing various expenses with the expenses of the previous years. The percentage of individual expenses to net sales can be calculated and compared with the similar ratios of previous years. Such a comparison will be helpful in taking effective steps for controlling unnecessary expenses.
(iv) Helpful in the preparation of balance sheet
A balance sheet can be prepared only after ascertaining the net profit
or loss through profit and loss account. Net profit or loss is shown in the
balance sheet. Thus, it facilitates preparation of balance sheet.
Preparation of profit and loss account
The amount of gross profit or gross loss brought down from the trading
account is the first item in the profit and loss account. All the indirect
expenses and losses are debited to profit and loss account. Indirect expenses
include office and administrative expenses, selling expenses, distribution
expenses, etc. As the profit and loss account is a nominal account, all the
indirect expenses and losses are shown on the debit side and all the indirect
incomes and gains are shown on the credit side.
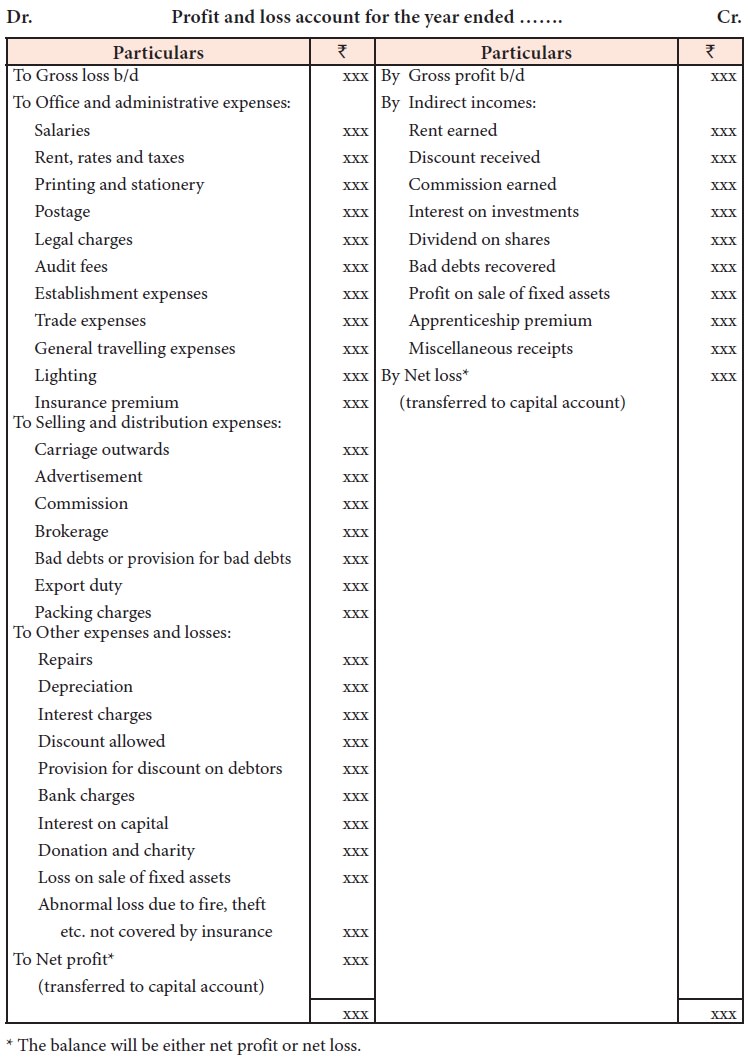
Items shown on the debit side of profit and loss
account are as follows:
(i) Gross loss
If trading account discloses gross loss, it is shown on the debit side
of the profit and loss account.
(ii) Indirect expenses
Expenses which are not connected with purchase of goods are indirect
expenses, i.e., expenses incurred in administration, office, selling and
distribution of goods are indirect expenses.
(a) Office and administrative expenses
Expenses incurred for office and administration such as salary of office
employees, office rent, lighting, postage, printing, legal charges, audit fee,
depreciation and maintenance of office equipment, etc. are classified as office
and administrative expenses.
(b) Selling and distribution expenses
Expenses incurred for selling, promotion of sales and distribution of
goods such as advertisement charges, commission to salesmen, carriage outwards,
bad debts, godown rent, packing charges, etc., are classified as selling and
distribution expenses.
(c) Other indirect expenses and losses
The expenses such as interest on loan, repair charges, depreciation,
charity, loss on sale of fixed assets and abnormal losses such as loss due to
fire, theft, etc. not covered by insurance are shown under this category.![]()
Items shown on the credit side of profit and loss account are as follows:
(i) Gross profit
The first item on the credit side of profit and loss account is the
gross profit brought down from the trading account if there is gross profit.
(ii) Other incomes and gains
All items of indirect incomes and gains are shown on the credit side of
the profit and loss account. Income from investments, rent earned, discount
received, commission earned, interest earned and dividend received are indirect
incomes. Profit on sale of fixed assets and investments are examples of gains.
Closing of profit and loss account
After debiting indirect expenses and losses and crediting all indirect
incomes and gains, if the total of the credit side of the profit and loss
account exceeds the debit side, the difference is termed as net profit. On the other
hand, if the total in the debit side exceeds the credit side, the difference is
termed as net loss. Net profit or net loss is transferred to the capital
account.
Format of profit and loss account
Tutorial note
The expenses which are not related to the business are not shown in the
profit and loss account. Examples are personal expenses of the proprietor such
as domestic and household expenses of the proprietor, income-tax and life
insurance premium of the proprietor, etc. These expenses are classified as
drawings by the proprietor and are deducted from capital on the liabilities
side of the balance sheet if they are paid out of business funds
Only revenue receipts and revenue expenses are shown in the trading and
profit and loss account. Capital receipts, capital gains, capital expenditure
and capital losses are not shown in trading and profit and loss account. That
part of capital items that relate to that accounting period only are shown. For
example, depreciation on fixed assets. Purchase of fixed asset is a capital
expenditure. But depreciation is a revenue item which relates to the use of the
fixed asset in the current accounting period.
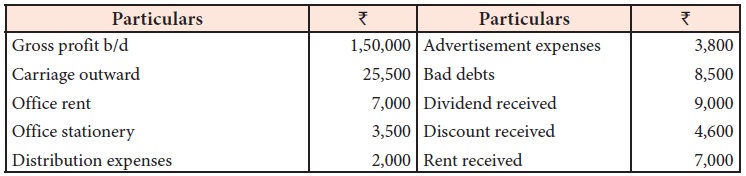
Illustration 8
From the following information, prepare profit and loss account for the
year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution
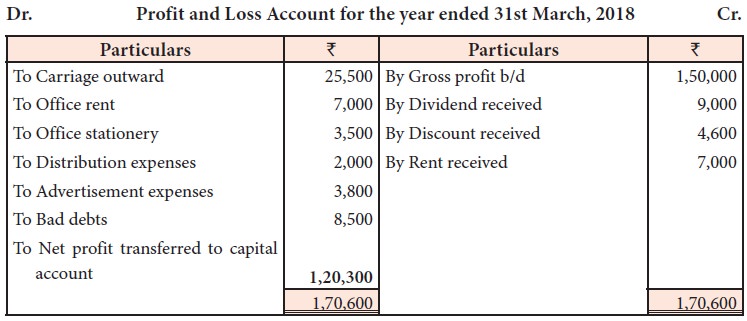
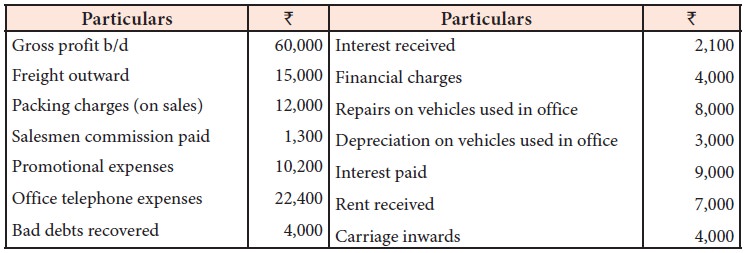
Illustration 9
From the following information,
prepare profit and loss account for the year ended 31st December, 2017.
Solution
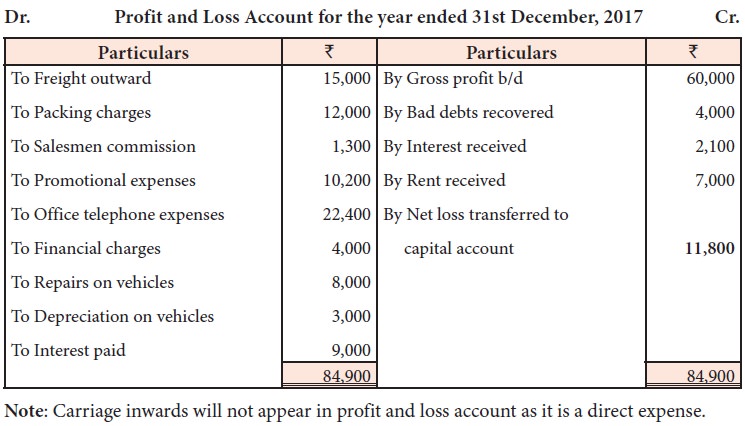
Illustration 10
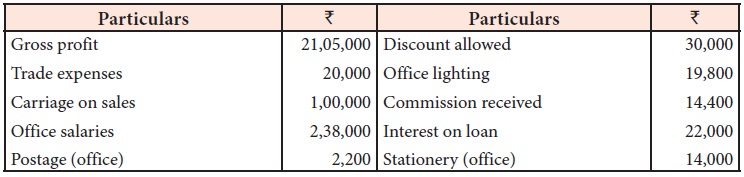
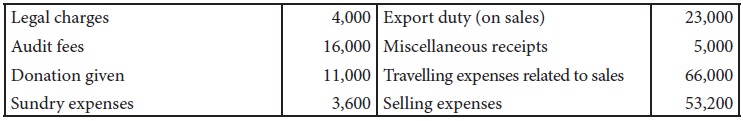
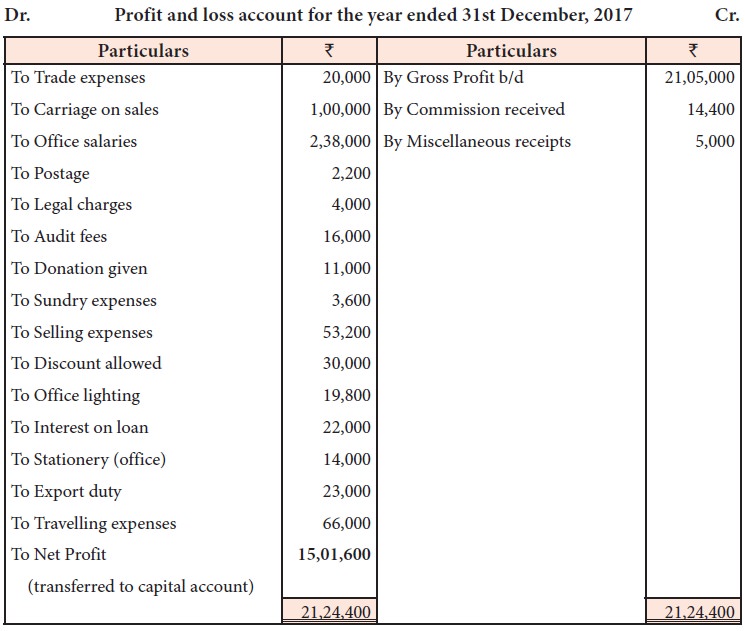
From the following particulars,
prepare profit and loss account for the year ended 31st December, 2017.

Related Topics