Python - Introduction to Tuples | 12th Computer Science : Chapter 9 : Python Modularity and OOPS : Lists, Tuples, Sets And Dictionary
Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 9 : Python Modularity and OOPS : Lists, Tuples, Sets And Dictionary
Introduction to Tuples
Tuples
Introduction to Tuples
Tuples consists of a number of values separated
by comma and enclosed within parentheses. Tuple is similar to list, values in a
list can be changed but not in a tuple.
1. Advantages of Tuples over list
1. The elements of a list are changeable
(mutable) whereas the elements of a tuple are unchangeable (immutable), this is
the key difference between tuples and list.
2. The elements of a list are enclosed within
square brackets. But, the elements of a tuple are enclosed by paranthesis.
3. Iterating tuples is faster than list.
2. Creating Tuples
Creating tuples is similar to list. In a list,
elements are defined within square brackets, whereas in tuples, they may be
enclosed by parenthesis. The elements of a tuple can be even defined without
parenthesis. Whether the elements defined within parenthesis or without
parenthesis, there is no differente in it's function.
Syntax:
Empty tuple
Tuple_Name = ( )
Tuple with n
number elements
Tuple_Name = (E1, E2, E2 ……. En)
Elements of a
tuple without parenthesis
Tuple_Name = E1, E2, E3 ….. En
Example
>>>MyTup1 = (23, 56, 89,
'A', 'E', 'I', "Tamil")
>>>print(MyTup1)
(23, 56, 89, 'A', 'E', 'I',
'Tamil')
>>>MyTup2 = 23, 56, 89, 'A', 'E',
'I', "Tamil"
>>>print (MyTup2)
(23, 56, 89, 'A', 'E', 'I',
'Tamil')
(i) Creating tuples using tuple( ) function
The tuple( ) function is used to create Tuples
from a list. When you create a tuple, from a list, the elements should be
enclosed within square brackets.
Syntax:
Tuple_Name = tuple( [list elements] )
Example
>>>MyTup3 = tuple( [23, 45, 90] )
>>>print(MyTup3)
(23, 45, 90)
>>>type (MyTup3)
<class ‘tuple’>
(ii) Creating Single element tuple
While creating a tuple with a single element,
add a comma at the end of the element. In the absence of a comma, Python will
consider the element as an ordinary data type; not a tuple. Creating a Tuple
with one element is called “Singleton” tuple.
Example
>>>MyTup4 = (10)
>>>type(MyTup4)
<class 'int'>
>>>MyTup5 = (10,)
>>>type(MyTup5)
<class 'tuple'>
3. Accessing values in a Tuple
Like list, each element of tuple has an index
number starting from zero. The elements of a tuple can be easily accessed by
using index number.
Example
>>>Tup1 = (12, 78, 91,
“Tamil”, “Telugu”, 3.14, 69.48)
# to access all the elements of a tuple
print(Tup1)
(12, 78, 91, 'Tamil', 'Telugu',
3.14, 69.48)
#accessing selected elements using indices
>>> print(Tup1[2:5])
(91, 'Tamil', 'Telugu')
#accessing from the first element up to the specified
index value
>>> print(Tup1[:5])
(12, 78, 91, 'Tamil', 'Telugu')
#accessing from
the specified element up to the last element.
>>> print(Tup1[4:])
('Telugu', 3.14, 69.48)
#accessing from
the first element to the last element
>>> print(Tup1[:])
(12, 78, 91, 'Tamil', 'Telugu',
3.14, 69.48)
4. Update and Delete Tuple
As you know a tuple is immutable, the elements
in a tuple cannot be changed. Instead of altering values in a tuple, joining
two tuples or deleting the entire tuple is possible.
Example
Program to join two tuples
Tup1 = (2,4,6,8,10)
Tup2 = (1,3,5,7,9)
Tup3 = Tup1 + Tup2
print(Tup3)
Output
(2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 1, 3, 5, 7, 9)
To delete an entire tuple, the del command can
be used.
Syntax:
del tuple_name
Example
Tup1 = (2,4,6,8,10)
print("The elements of Tup1
is ", Tup1)
del Tup1
print (Tup1)
Output:
The elements of Tup1 is (2, 4, 6,
8, 10)
Traceback (most recent call
last):
File "D:/Python/Tuple Examp
1.py", line 4, in <module> print (Tup1)
NameError: name 'Tup1' is not defined
Note that, the print statement in the above
code prints the elements. Then, the del statement deletes the entire tuple.
When you try to print the deleted tuple, Python shows the error.
5. Tuple Assignment
Tuple assignment is a powerful feature in
Python. It allows a tuple variable on the left of the assignment operator to be
assigned to the values on the right side of the assignment operator. Each value
is assigned to its respective variable.
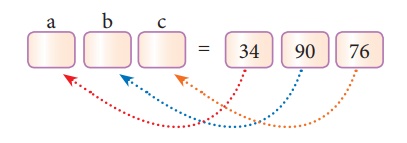
Example
>>> (a, b, c) = (34, 90,
76)
>>>print(a,b,c)
34 90 76
#expression are
evaluated before assignment
>>> (x, y, z, p) =
(2**2, 5/3+4, 15%2, 34>65)
>>> print(x,y,z,p)
4 5.666666666666667 1 False
Note that, when you assign values to a tuple,
ensure that the number of values on both sides of the assignment operator are
same; otherwise, an error is generated by Python.
6. Returning multiple values in Tuples
A function can return only one value at a time,
but Python returns more than one value from a function. Python groups multiple
values and returns them together.
Example : Program to return the maximum as well as
minimum values in a list
def Min_Max(n):
a = max(n)
b = min(n)
return(a, b)
Num = (12, 65, 84, 1, 18, 85, 99)
(Max_Num, Min_Num) = Min_Max(Num)
print("Maximum value =
", Max_Num)
print("Minimum value =
", Min_Num)
Output:
Maximum value = 99
Minimum value = 1
7. Nested Tuples
In Python, a tuple can be defined inside
another tuple; called Nested tuple. In a nested tuple, each tuple is considered
as an element. The for loop will be useful to access all the elements in a
nested tuple.
Example
Toppers = (("Vinodini",
"XII-F", 98.7), ("Soundarya", "XII-H", 97.5),
("Tharani", "XII-F", 95.3), ("Saisri",
"XII-G", 93.8))
for i in Toppers:
print(i)
Output:
('Vinodini', 'XII-F', 98.7)
('Soundarya', 'XII-H', 97.5)
('Tharani', 'XII-F', 95.3)
('Saisri', 'XII-G', 93.8)
8. Programs using Tuples
Program 1: Write a program to swap two values using
tuple assignment
a = int(input("Enter value
of A: "))
b = int(input("Enter value
of B: "))
print("Value of A = ",
a, "\n Value of B = ", b)
(a, b) = (b, a)
print("Value of A = ",
a, "\n Value of B = ", b)
Output:
Enter value of A: 54
Enter value of B: 38
Value of A = 54
Value of B = 38
Value of A = 38
Value of B = 54
Program 2: Write a program using a function that
returns the area and circumference of a circle whose radius is passed as an
argument.two values using tuple assignment
pi = 3.14
def Circle(r):
return (pi*r*r, 2*pi*r)
radius = float(input("Enter
the Radius: "))
(area, circum) = Circle(radius)
print ("Area of the circle =
", area)
print ("Circumference of the
circle = ", circum)
Output:
Enter the Radius: 5
Area of the circle = 78.5
Circumference of the circle =
31.400000000000002
Program 3: Write a program that has a list of
positive and negative numbers. Create a new tuple that has only positive
numbers from the list
Numbers = (5, -8, 6, 8, -4, 3, 1)
Positive = ( )
for i in Numbers:
if i > 0:
Positive += (i, )
print("Positive Numbers:
", Positive)
Output:
Positive Numbers: (5, 6, 8, 3, 1)
Related Topics