Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Library : Networking
InetAddress - Java
InetAddress
The InetAddress class is used to
encapsulate both the numerical IP address and the domain name for that address.
You interact with this class by using the name of an IP host, which is more
convenient and understandable than its IP address. The InetAddress class hides the number inside. InetAddress can handle both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
Factory Methods
The InetAddress class has no visible
constructors. To create an InetAddress
object, you have to use one of the available factory methods. Factory methods are merely a convention
whereby static methods in a class return an instance of that class. This is
done in lieu of overloading a constructor with various parameter lists when
having unique method names makes the results much clearer. Three commonly used InetAddress factory methods are shown
here:
static
InetAddress getLocalHost( ) throws UnknownHostException
static
InetAddress getByName(String hostName)
throws UnknownHostException
static
InetAddress[ ] getAllByName(String hostName)
throws UnknownHostException
The getLocalHost( ) method simply returns
the InetAddress object that
represents the local host. The getByName(
) method returns an InetAddress
for a host name passed to it. If these methods are unable to resolve the host
name, they throw an UnknownHostException.
On the
Internet, it is common for a single name to be used to represent several
machines. In the world of web servers, this is one way to provide some degree
of scaling. The getAllByName( ) factory
method returns an array of InetAddresses
that represent all of the addresses
that a particular name resolves to. It will also throw an UnknownHostException if it can’t resolve the name to at least one
address.
InetAddress also includes the factory method getByAddress( ), which takes an IP address and returns an InetAddress object. Either an IPv4 or
an IPv6 address can be used.
The following
example prints the addresses and names of the local machine and two Internet
web sites:
// Demonstrate InetAddress.
import java.net.*;
class InetAddressTest
{
public static void
main(String args[]) throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress Address =
InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(Address);
Address =
InetAddress.getByName("www.HerbSchildt.com");
System.out.println(Address);
InetAddress SW[] =
InetAddress.getAllByName("www.nba.com"); for (int i=0;
i<SW.length; i++)
System.out.println(SW[i]);
}
}
Here is
the output produced by this program. (Of course, the output you see may be
slightly different.)
default/166.203.115.212
www.HerbSchildt.com/216.92.65.4
www.nba.com/216.66.31.161
www.nba.com/216.66.31.179
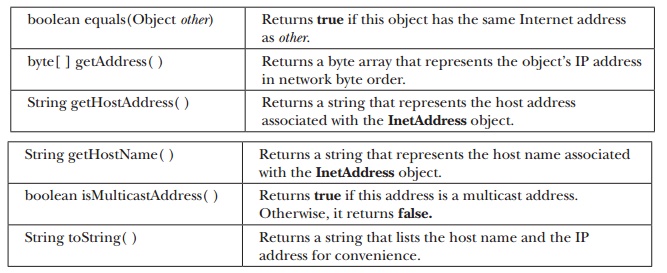
Instance Methods
The InetAddress class has several other
methods, which can be used on the objects returned by the methods just
discussed. Here are some of the more commonly used methods:
boolean equals(Object other)
: Returns true if this object has the same Internet address as other.
byte[ ] getAddress( ) :
Returns a byte array that represents the object’s IP address in network byte
order.
String getHostAddress( ) :
Returns a string that represents the host address associated with the
InetAddress object.
String getHostName( ) :
Returns a string that represents the host name associated with the InetAddress
object.
boolean isMulticastAddress( )
: Returns true if this address is a multicast address. Otherwise, it returns
false.
String toString( ) : Returns
a string that lists the host name and the IP address for convenience.
Internet
addresses are looked up in a series of hierarchically cached servers. That
means that your local computer might know a particular name-to-IP-address
mapping automatically, such as for itself and nearby servers. For other names,
it may ask a local DNS server for IP address information. If that server
doesn’t have a particular address, it can go to a remote site and ask for it.
This can continue all the way up to the root server. This process might take a
long time, so it is wise to structure your code so that you cache IP address
information locally rather than look it up repeatedly.
Related Topics