Chapter: Essentials of Psychiatry: Couples Therapy
Individual, Couple, or Sex Therapy for Sexual Problems
Individual,
Couple, or Sex Therapy for Sexual Problems
This
distinction was clearer 10 years ago when sex therapy was primarily focused on
a specific and highly detailed behavioral protocol. Sex therapy in the last few
years has moved in the di-rection of further understanding of the physiologic
causes of sex dysfunction on one hand, and cognitive–behavioral issues on the
other. It is clear at this point that, in general, sexual problems do not
disappear with couple therapy unless specific attention is paid to the nature
and quality of the sexual problems. Usu-ally, it is most effective to deal with
severe couple conflict before beginning to deal with sexual issues directly
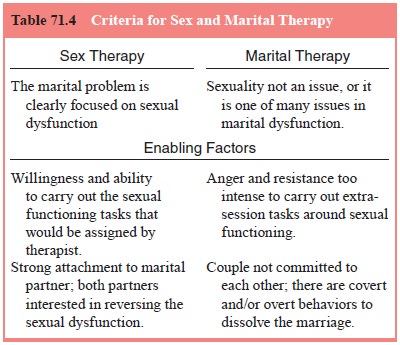
(Table 71.4). Sex therapy includes education, a focus on the intimacy and power
aspects of sex, and often homework assignments that in some way deal with
sexual anxiety and expansion of sexual options. Individual therapy is indicated
if the problems are clearly related to the partner’s history (sexual abuse,
hatred of women), have occurred in multiple relationships, and are not amenable
to being worked on in the couple. Individual therapy is the most inefficient
way of dealing with most couple centered sexual problems. It is
also
important to consider the possible role of organic problems in any dysfunction.
Contraindications for Couples Therapy
Couples
therapy is not indicated for every couple in distress. In fact, at times, it
may even be contraindicated. If one mem-ber is keeping an important secret, an
attempt to work with them as a pair may fail and the therapist often has to
take a strong stand and refuse to treat the couple, as in the case of an HIV
positive male who refused to share this information with his wife. At times,
one member of a couple may be too ill to benefit from couples therapy. This may
be the case when one partner has a bipolar disorder or schizophrenia and is
acutely psychotic.
Other
couples feel more comfortable when each partner has his or her own therapist.
At times it can be more effective to have each member in individual therapy
with good coordination between the two therapists. Finally, cases may arise
where seeing a couple together may put one member of the couple in physical
danger. When one member has a history of violence toward the partner, the
therapist must often see each party alone to ensure the safety of a partner.
Discussing areas of conflict together may risk increasing the violent behavior
of one partner.
Sex
therapy may be contraindicated in the same situations as above. In addition,
many couples do not feel comfortable in a therapy exclusively focusing on sex.
These couples may make more progress if the sex therapy is carefully included
in the over-all treatment of the couple. When referring to a sex therapist, it
is particularly important to be familiar with the skill and creden-tials of the
therapist.
Related Topics