Chapter: Signals and Systems : Linear Time Invariant –Continuous Time Systems
Important Short Questions and Answers: Linear Time Invariant, Continuous Time Systems
1. What is the overall impulse
response h(t) when two systems with impulse response h1(t) and h2(t)
are in parallel and in series?
(or)
State the properties needed for
interconnecting LTI systems.
For parallel connection, h(t)=ℎ1(t)+ℎ2 (t)
For series connection, h(t)= ℎ1(t)
∗ℎ2(t).
2. Write convolution integral of
x(t) (or) Define convolution integral of continuous time systems.
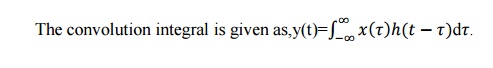
3. Check whether the causal system
with transfer function H(s) = 1/(s-2) is stable
Here
the pole lies at s = 2. Since the pole of causal system does not lie on the
left side of jω axis, the system is not stable.
4. The impulse response of the LTI
– CT system is giv en as h(t)=e-tu(t). Determine transfer function
and check whether the system is causal and stable.
h(t) = e-tu(t)
Taking
laplace transform,
H(s)
= 1/(s+1)
Here
the pole lies at s = -1, i.e. located in left half of s-plane. Hence this
system is causal and stable.
5. What are the conditions for a
system to be LTI system?
Input and output of an LTI system are related
by,
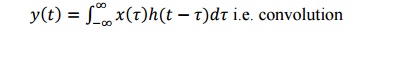
6. What is the impulse response of
two LTI systems connected in parallel?
If the system are connected in parallel,
having responses h1(t) and h2(t),
then their
overall response is given as,
h(t)
= h1(t) + h2(t)
7. Write Nth order
differential equation.
The Nth order differential equation
can be written as,
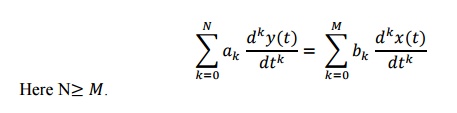
8. What is the condition for LTI
system to be stable?
An
LTI system is stable if the impulse response is absolutely integrable.
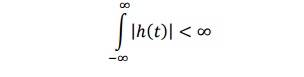
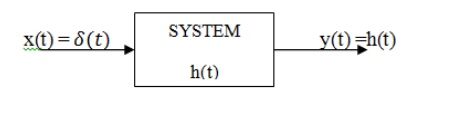
9. What is meant by impulse
response of any system?
When
the unit impulse function is applied as input to the system, the output is
nothing but impulse response h(t). The impulse response is used to study
various properties of the system such as causality, stability, dynamicity etc.
10. Determine the response of the system with
impulse response h(t)= t u(t) for the input x(t)= u(t)
The
response is given as,

11. State the properties of convolution.
1)
Commutative property:x(t)*h(t) = h(t)*x(t)
2)
Associative property: [x(t)*h1(t)]*h2(t) = x(t)*[h1(t)*h2(t)]
3)
Distributive property:x(t)*h1(t)+x(t)*h2(t) =
x(t)*[h1(t)+h2(t)]
12.
What are
the three elementary
operations in block
diagram representation of
continuous time system?
· Scalar multiplication
X(t) --- > y(t) = ax(t)
Related Topics