Chapter: 11th 12th Standard Higher secondary School student
Gene transfer in plants
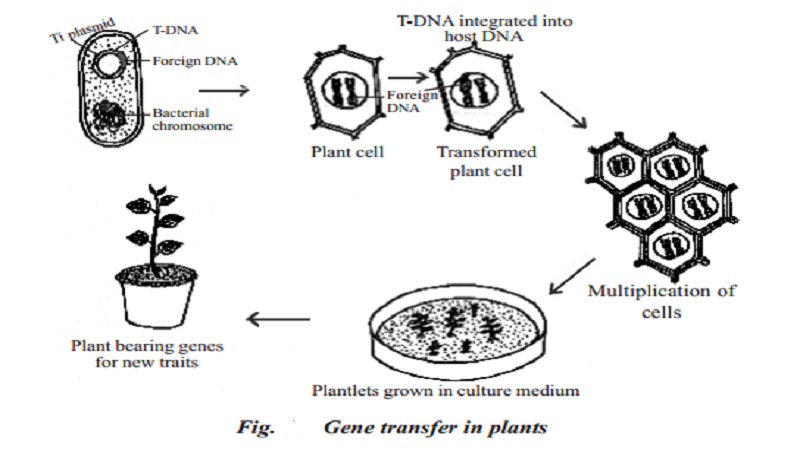
Gene transfer in plants
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a soil inhabiting bacterium and has Ti (tumor inducing) plasmid. This bacterium invades crops such as tomato, sunflower, brinjal and cotton and causes crown gall disease which is in the form of tumerous growth. The Ti plasmid carried by the pathogenic bacterium causes tumours. For effective cloning of foreign genes by the plant cells, and for introduction of genes into plant system, Agrobacterium strains are modified by the removal of tumour - inducing genes from the bacterium. T-DNA is the part of Ti plasmid transferred into plant cell DNA. The T-DNA which holds the desired foreign gene after splicing is introduced into the plant cell. The bacterial plasmid do not produce tumerous growth since the gene had been deleted. Once the T-DNA along with the spliced gene is introduced, it combines with the chromosome of the donor cell where it produces copies of itself, by migrating from one chromosomal position to another. Through tissue culture methods, such plant cells are cultured, induced to multiply and differentiate to form into plantlets. The plantlets are transplanted to soil, where they are allowed to express the foreign gene introduced into them when they multiply and grow in larger population.
Related Topics