Chapter: Business Science : Financial Management : Working Capital Management
Factoring - Working Capital Management
FACTORING
1History
2Modus of Operations
3Mechanics of Factoring
4 Types Of Factoring
5 Difference between Factoring And Forfeiting
Factoring
Factoring is a service of financial nature involving the
conversion of credit bills into cash. Accounts receivables, bills recoverables
and other credit dues resulting from credit sales appear, in the books of
accounts as book credits. Here the risk of credit, risk of credit worthiness of
the debtor and as number of incidental and consequential risks are involved.
These risks are taken by the factor which purchase these credit receivables
without recourse and collects the m when due. These balance-sheet items are
replaced by cash received from the factoring agent.
1History
Roman
Factoring
has not been documented as having been used by the Romans. However, the word
‗factoring‘ has a Roman root. It is derived from the Latin verb ‘facio‘ which
can be translated as ―he who does things‖. In Roman times this referred to
agent of a property owner, i.e., his business manager. Though the root word has
nothing to do with the industry, as they attempt to help their clients thro ugh
their financial problem.
Factoring in United States
Factoring
arose in the United States during 19th century, as direct result of the
inability of manufacturers to ma intain consta nt and timely communications
with their sales forces in the field. At that time, as the case today, the
sales force was paid by communications. If all sales were at the risk of the
manufacturer, the salesman had no incentive to exercise prudence in connection
with whom to sell to on credit.
On the
other hand, the distant manufacturer was not in the position to make the credit
risk on sales. The risk of defective or non-conforming merchandise remained
with the manufacturer. The credit risk was now separated from disputes as to quality,
work mans hip and conformity of goods. Soon after, the salesman began to act as
independent sales agencies. It was common for them to act for more than one
manufacturer. Still later the sales function was separated from the credit
function and ―Traditional Factoring‖ as the people know, it had, at that point,
developed in the United States.
History Factoring in India
Banks
provide generally bill collection and bill discounting and with recourse. They
provide working capital finance based on these bills classified by a mounts
maturity wise. Such bills if accumulated in large quantities will burden the
liquidity and solvency position of the company and reduces the credit limits
from the banks. It is therefore felt necessary that the company assigns these
book debts to a factor for taking them off from the balance sheet. This reduces
the workload, increases the solvency and improves the liquidity position of the
company.
Vaghul
Committee report on money market reforms has confirmed the need for factoring
services to be developed in India as part of the money market instruments. Many
new instruments were already introduced like Participation certificates,
Commercial papers, Certificate of deposits etc., but the factoring service has
not developed to any significant extent in India.
The
Reserve Bank allowed some banks to set up subsidiaries on a zonal basis to take
care of the require me nts of companies in need of such service. Thus Canara
Bank, State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank and a few other banks have been
permitted to set up jointly some factor, for Eastern, Western, Northern, and
Southern Zones. The progress of the activity did not show any worth while dime
ns ion, so far.
2Modus of Operations
If a
company wants to factor its receivables it submits a list of customers, their
credit rating, a mount involved in maturity and other terms. If the factor
scrutinizes the list of buyers and they are in the approved list, the factor
gives its decision of the clients and the a mounts they may take all
receivables on wholesale discounting basis. The factor the n takes all the
documents in respect of approved list and pays up to 80% to 90% of the a mount
due less commission to the company which in turn removes these instruments,
from base of accounts and shows cash flow as against bills receivables written
off.
Factoring services
re nde re d the following services:
Purchase of book debts and receivables.
Ad ministration of sales ledger of the
clients.
Prepayments of debts
partially or fully.
Collection of book
debts or receivables
or with or
without documents.
Covering the credit risk of the
suppliers.
Dealing in book
debts of customers without recourse.
Why Factoring?
Factoring is one of the most important and
unavoidable part of the business concern which meets the short-term financial
requirement of the concern. Factoring is favorable to the industrial concern
for the following reasons.
1
.Quickest response–Customer oriented timely decisions and decision on sanction
within a week.
2. Low
cost.
3. Low
service charges (0.1% to 0.3%).
4. Low
margin (20% onwards).
5.
Instant finance–against each invoice.
6.
Generous grace period.
7.
Improves cashflow.
8.
Substitutes sundry creditors.
9.
Increases sales through better terms on sales.
10. More
operating cycles and more profits.
11. No
upfront recovery of charges.
12.
Interest on daily products.
13. Very
easy to operate.
14.
Flexible credit periods.
15. No
penal interest up to grace period.
16.
Empowers cash purchase.
17.
Improves credit reputation.
18.
Follow up of each invoice.
19.
Collection of receivables.
20. MIS reports
like customers overdue invoices enabling constant evaluation of customers.
21.
Outstation payments at nominal rates.
3 Mechanics of
Factoring
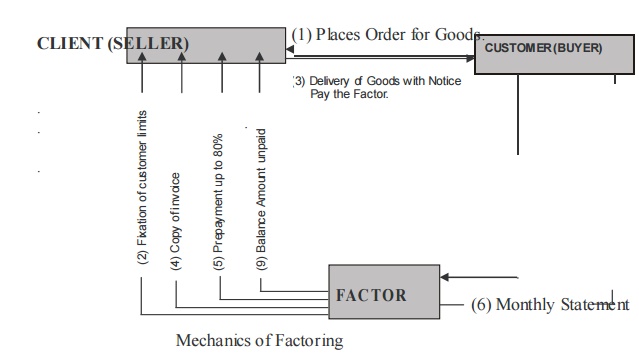
The
following are the steps for factoring:
The customer places an order with
the seller (client).
The factor and the seller enter into
a factoring agreement about the various terms of factoring.
Sale contract is entered into with
the buyer and the goods are delivered.
The
invoice with the notice to pay the factor is sent alongwith.
The copy of invoice covering the
above sale to
the factor, who maintains the sale ledger.
The factor prepays 80% of the
invoice value.
The monthly statement are sent by
the factor to the buyer.
Follow up action is initiated if
there are any unpaid invoices.
The buyer settles the invoices on the
expiry of the credit period allowed.
The balance 20% less the cost of
factoring is paid by the factor to the client.
4 Types Of Factoring
Notified factoring
Here, the
customer is intimated about the assignment of debt to a factor, also directed
to make payments to the factor instead of to the fir m. This is invariably done
by a legend and the invoice has been assigned to or sold to the factor.
Non-notified or confidential factoring
Under
this facility, the supplier/factor arrangement is not declared to the customer
unless or until there is a breach of the agreement on the part of the client,
or exceptionally, where the factor considers himself to be at risk.
With re course or without re course factoring
Under
recourse arrangements, the client will carry the credit risk in respect of
debts sold to the factor. In without recourse factoring, the bad debts are
borne by the factor.
Bank Participation Factoring
The
client creates a floating charge on the factoring reserves in favour of banks
and borrow against these reserves.
Ex port Facto ring
There is
usually the presence of two factors: an export factor and an import factor. The
former buys the invoices of a client exporter and assumes the risk in case of
default by the overseas customers. Because of distance, different condition or
lake of information, the export factor usually forms out to an agent, known as
the import factor, the administrative job of servicing the debts owed to its
exporting clients.
5 Difference between Factoring And Forfeiting
The
following are differences between factoring and forfeiting
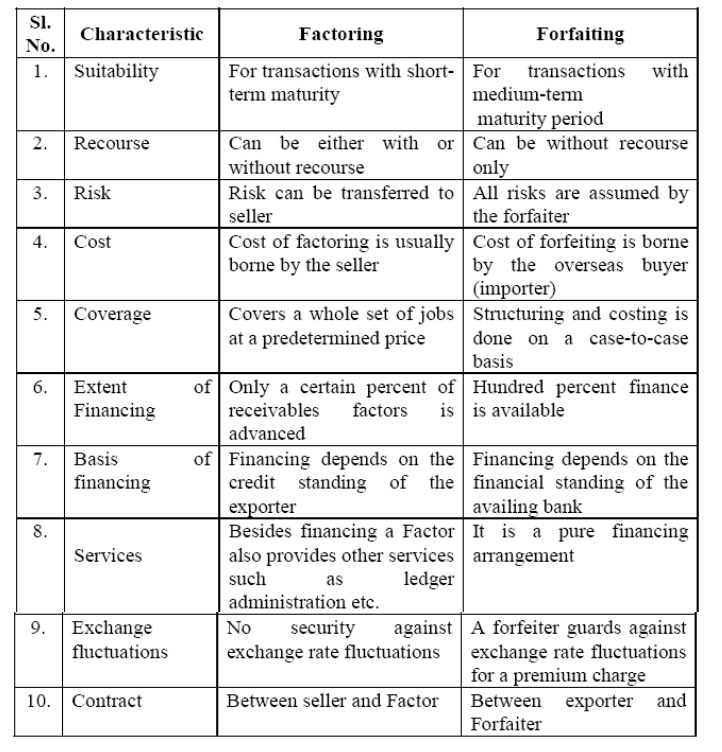
Related Topics