Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Indian Economy Economic status Higher secondary school College
Exceptions to the Law of Demand
Exceptions to the Law of Demand
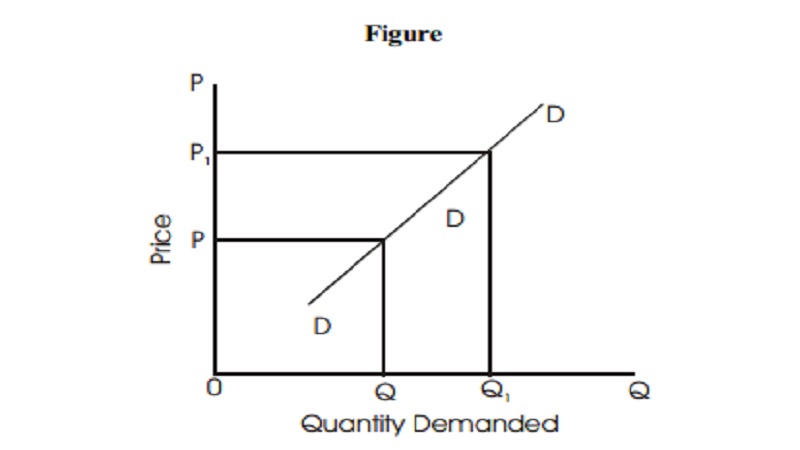
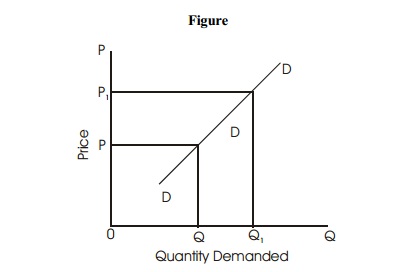
The Law of demand is a general statement telling that prices and quantities of a commodity are inversely related. There are certain peculiar cases in which the law of demand will not hold good. In those cases, more will be demanded at a higher price and less will be demanded at a lower price. The demand curves in those cases slope upwards showing a positive relationship between price and quantity demanded as shown in figure.
When the price increases from OP to OP1, quantity demanded also increases from OQ to OQ1 and vice versa. DD is the exceptional or abnormal demand curve. The following is the list of few exceptions to the law of demand.
(1) Veblen Effect
Veblen has pointed out that there are some goods demanded by very rich people for their social prestige. When price of such goods rise, their use becomes more attractive and they are purchased in larger quantities. Demand for diamonds from the richer class will go up if there is increase in price. If such goods were cheaper, the rich would not even purchase.
(2) Giffen Paradox
Sir Robert Giffen discovered that the poor people will demand more of inferior goods if their prices rise and demand less if their prices fall. Inferior goods are those goods which people buy in large quantities when they are poor and in small quantities when they become rich. For
When the price of a good is OP, demand is OQ. If the price of good falls to OP2, demand expands to OQ1. Thus extension in demand is QQ1. On the other hand, when the price of good rises to OP1 demand contracts to OQ2. Thus contraction in demand is QQ2.
Shifts in demand or Increase and decrease in demand
One of the basic assumptions of economic theory is 'other things being equal'. Other things are income, tastes, population, government policy, technology, price of related goods etc. Change in such factors will bring about increase or decrease in demand. In figure, the increase in demand is shown by the shifts of the demand curve to the right from DD to D2 D2. The decrease in demand is shown by the shift to the left from DD to D1 D1. The increase and decrease in demand are shifts in the demand curves.
example, poor people spend the major part of their income on coarse grains (e.g. ragi, cholam ) and only a small part on rice. When the price of coarse grains rises, they will buy less rice. To fill up the resulting gap, more of coarse grains have to be purchased. Thus, rise in the price of coarse grains results in the increase in quantity of coarse grains purchased. This is called 'Giffen Paradox'. In these cases, the law of demand has an exception.
Related Topics