Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Anaphylaxis
What treatment should be administered to this patient? What else should be checked on physical examination?
What
treatment should be administered to this patient? What else should be checked
on physical examination?
The A and B of the ABCs are already addressed
in this case, since the patient is intubated and mechanically ventilated.
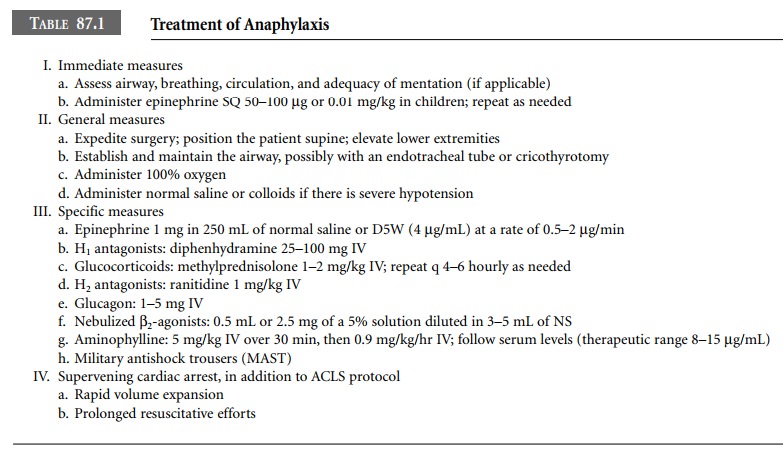
Epinephrine 50–100 μg (0.5–1 mL of a 1:10,000 solu-tion found in
pre-filled syringes, or 0.05–0.1 mL of the more commonly used 1:1,000
solution), or 0.01 mg/kg in children, should be administered subcutaneously if
the patient is merely hypotensive, and may be repeated as needed. Higher doses
and the intravenous route should be used if the reaction is severe, or if
cardiac arrest supervenes. High doses of epinephrine are more efficacious but
cases of myocardial ischemia or even infarction after epinephrine
administration have been reported. A review of 164 cases of fatal anaphylaxis
in the United Kingdom showed that epinephrine overdose caused at least three of
these fatalities. An intravenous infusion of epinephrine (1 mg in 250 mL at a
rate of 0.05–2 μg/min) should be considered if repeat doses are
necessary.
Epinephrine acts by two mechanisms: it reverses
vasodi-lation by its α-agonist effects, and it blocks further
degran-ulation of mast cells or basophils through its β-agonist effects. It may also improve cerebral perfusion
independent of its effect on blood pressure by β2-mediated vasodilation, and it is very effective in the treatment
of bronchospasm.
Other measures to be taken are:
·
Ventilation
with 100% oxygen.
·
Fluid
resuscitation with crystalloids or colloids. Increased vascular permeability
can transfer 50% of intravascular fluid into the extravascular space within 10
minutes. The amount of fluid administered should be based on hemo-dynamic
parameters.
·
Intravenous
steroids (e.g., methylprednisolone 1–2 mg/kg intravenously (IV); repeat q4–6
hourly as needed). Steroids may have no effect for 4–6 hours, but may pre-vent
persistent or biphasic anaphylaxis.
·
Anti-H1
medications (e.g., diphenhydramine 25– 100 mg IV).
· Anti-H2 medications (e.g., ranitidine
1 mg/kg IV).
·
Glucagon
(1–5 mg IV) in severe reactions. Glucagon directly activates adenyl cyclase and
bypasses the β-adrenergic receptor. It may reverse refractory hypoten-sion and
bronchospasm. Glucagon or atropine should be used in β-blocked patients to increase an inappropriately slow heart rate.
·
In case
of refractory hypotension, military antishock trousers (MAST) may significantly
improve hemody-namics.
If cardiac arrest supervenes, advanced cardiac
life sup-port (ACLS) protocols should be followed, including epi-nephrine,
atropine, and transcutaneous pacing in case of pulseless electrical activity.
In addition, rapid volume expansion is mandatory. Prolonged resuscitative
efforts are encouraged, since recovery is more likely to be successful in
anaphylaxis, in which the subject is often a young individ-ual with a healthy
cardiovascular system.
Therapeutic options for anaphylaxis are
presented in Table 87.1.
The chest should be auscultated since
bronchospasm is often triggered by anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reac-tions. If
bronchospasm does not respond to the treatment administered for anaphylaxis,
inhaled β2-agonists
and pos-sibly aminophylline should be added to the regimen. Volatile
anesthetics can also be used (if that is not already the case, and if the blood
pressure allows) for their bron-chodilating properties.
Related Topics