Chapter: Total Quality Management : TQM Principles
Total Quality Management(TQM) Principles
TQM PRINCIPLES
LEADERSHIP
DEFINED
Leadership is interpersonal
influence exercised in a situation and directed through communication process,
towards the attainment of a specialized goal or goals. Thus leadership is a
process of influencing the activities of an individual or a group for goal
achievement in a given situation.
LEADERSHIP
CONCEPT
Leadership requires in order to
become successful as a leader , he needs an intimate and insightful
understanding of human nature – the basic needs, wants and abilities people, a
leader needs to know and understand the following;
1. People need both security and
independence at the same time.
2.People are sensitive and do respond to external rewards or
punishments. They are also strongly self-motivated.
3.Peoples sometime value a kind word of praise more than any
monetary reward.
4. They trust their gut reaction more
than statistical data.
5. A leader should simplify the task
ROLE
OF SENIOR MANGEMENT
Ø Senior management must practice
the philosophy of Management By Wandering Around (MBWA). They should get out of
the office and visit customers, departments, and plants within the organization
and suppliers
Ø Encourage subordinates to write
only important messages that need to be part of the permanent record.
Ø Senior management role is no
longer to make the final decision, but to make sure the teams decision is
aligned with the quality statement of the organization
Ø Problem solving and decision
making to the lowest appropriate level by delegating authority and
responsibility.
Ø Senior managers must stay informed
on the topic of quality improvement by reading books and articles attending
seminars and talking to other TQM leaders.
Ø The needed resources must be
provided to train employees in the TQM tools and techniques, the technical
requirements of the job and safety.
Ø Must be visibly and actively
engaged in the quality effort by serving on teams, coaching teams and teaching
seminars.
Ø They should lead by demonstrating,
communicating, and re-in forcing the quality statements.
Ø They should spend about one third
of their time on quality
Ø Senior managers are listening to
internal and external customers and supplies through visits, focus groups and
surveys.
Ø To create awareness of the
importance of TQM and provide TQM results in an ongoing manner.
Ø Senior managers should be able to
drive fear out of the organization, break down barriers, remove system
roadblocks, anticipating and minimize resistance to change and in general
change the culture.
QUALITY CIRCLE
Meaning
Quality council is composed of the
chief executive officer, the senior managers of the functional areas, such as
design, marketing, finance, production and quality and a coordinator or
consultant. Individual selected for the coordinated position should be bright
young person with execution potential.
Objectives
of quality council:
To raise the quality consciousness
in the organization through seminars, study tours and using forms of promotion.
To ensure effective functioning of
the organization on the quality statement and plan.
To encourage basic and applied
research and development in the field of quality and dissemination of its
results to the organization.
To raise the level of training of
personnel engaged in quality activities including the assessors and trainees.
To facilitate upgradation of
testing and calibration facilities and laboratories as well as to encourage the
overall quality of the organization.
DUTIES
OF QUALITY COUNCIL
q Develop with input from all
personnel; the core values Vision statement, Mission statement, and Quality
policy statement.
q Develop the strategic long term
with goals and the annual quality improvement program with objectives
q Determine and continually monitor
the cost of poor quality.
q Create the total education and
training plan.
q Determine the programme measures
for the organization.
q Continually determine those
projects that improve the process.
( internal and external customers)
q Establish or revise the
recognition and reward system to account for the new way of doing business.
QUALITY STATEMENT
In addition to the core values and
concepts, the quality statement includes the Vision statement, Mission
statement and Quality policy statement. Once developed they are occasionally
revised and updated. They are part of the strategic planning process, which
included goals and objectives.
VISION
STATEMENT
The vision statement is a clear
declaration of what an organization aspires to be in the future (in long term).
Its purpose is to provide a platform for the managers for thinking
strategically. A vision statement is usually an ideal condition, that might
never be reached but that will inspire the people to achieve.
Example: “THE HAPPIEST PLACE ON EARTH” - Disney Theme park.
MISSION
STATEMENT
The mission statement answers the
following questions. Who we are, who are the customers, what we do and how we
do it. This statement is usually one paragraph or less. It is easy to understand
and describe the functions of the organization. It provides a clear statement
of purpose for employees, customers and supplies.
EXAMPLE:
BEN & JERRY‟S ICE CREAM – MISSION STATEMENT
PRODUCT
MISSION: TO make, distribute and sell the finest quality natural ice cream and
related products in a wide variety of innovative flavors made from Vermont
dairy products.
QUALITY
POLICY STATEMENT
QPS serve as a guide for everyone
in the organization. This statement clarifies the employees about how the
products and services must be provided to the customers. The CEO of the company
writes quality policy statement after a careful study and analysis of the
feedback from the workforce. Finally the quality council must approve the
statement.
EXAMPLE:
Meet
the requirements of the customers (both internal and external)
Go
ahead competition
Complete
utilization of the entire workforce.
STRATEGIC PLANNING
Organizations are finding that
strategic quality plans and business plans are inseparable. The strategic
planning is three to ten years and short term planning is one year or less. It
consists of goals and planning.
SEVEN
STEPS TO STRATEGIC PLANNING.
1. Identification of customer needs.
2. Determination of customer
positioning
3. Predict the future.
4. Gap analysis.
5. Closing the gap.
6. Aligning the plan to the mission
and vision.
7. Implementation of the plan.
1.
Identification of customer needs.
This steps provides a focus on customer satisfaction.
There needs and wants have to be
identified and satisfied.
The profile of the customers are
identified. Questions like who are our customers? Will they change in future?
What will they want in future?.
2.
Determination of customer positioning
The planners determine where the
organization wants to be in relation to the customers.
Expand the customer base products
or services.
Products with poor quality
performance should be removed or eliminated and replaced by better ones.
The organization needs to
concentrate its efforts on areas of excellence
3.
Predict the future
Predict the future conditions that
will affect their product or service Using effective tools for analyzing and
predicting future
Some products or services have
become absolute because it failed to foresee the changing technologies.
The mangers in the organization
anticipate a change in the first place, and then they can make necessary
arrangements by making investments on resources and be prepared to take on the
future.
The rate of change is continuously
increasing.
4.
Gap Analysis
The planners to identify the gaps
between the current state and future state.
The present position of the organization in the market in relation to
competition, profits, customer satisfaction employee satisfaction, etc. to the
intended position.
If any there is gap identified future strategies must be formulated
taking this gap in to consideration.
5.
Closing the Gap
After gap analysis plans must be formulated to reduce or close the
strategic gap.
To close the gap by establishing
goals and responsibilities.
All stakeholders should be
included in the development of the plan.
6. Alignment
It must be aligned with the mission,
vision, and core values and concepts of the organization.
7. Implementation
a. Resources
must be allocated to collecting data, designing changes and overcoming
resistance to change.
b. To
monitoring activities to ensure that progress is being made.
Monitoring by the steering
committee and periodical assessments are required for an effective and speedy
implementation
CUSTOMER
SATISFACTION
CUSTOMER
SATISFACTION MODEL:
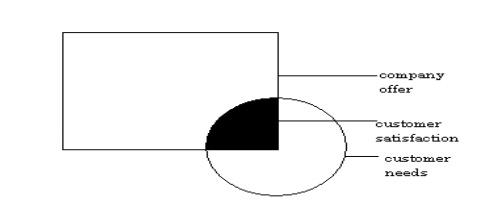
CUSTOMER:
A customer can be defined as one
who purchases a product or service. There are two distinct type of customer.
Customer satisfaction is achieved
when their expectations are matched by what is offered to them by the
organization. It is important for the organization to listen to the voice of
the customers to ensure that is marketing, production, R&D , distribution
and service truly meet the expectations of the customers.
There are two distinct types of
customers; they are external and internal customers.
A)External
Customers:
External customers can be defined
as the one who purchases the product of the organization for end usage or for
reselling or to use the product in his production process as raw material.
B)
Internal customers:
Internal customers are the
employees of the organization. As far as the top management in concerned they
have an obligation to keep internal customers satisfied.
CUSTOMER
PERCEPTION OF OUALITY:
An American society for quality
(ASO) survey on end user perception of
important factors that influenced purchases showed the following ranking.
1. Performance
2. Features
3. Service
4. Warranty
5. Price
6. Reputation
1.
PERFORMANCE
Performance of
the product is the ―fitness‖ the product or
service by the customer at the time of sale.
It indicates that
the product can be used as such without any further modification.
Availability,
which is the probability that a product will operate when needed.
Reliability is
the consistent performance of the product every time is used Maintainability
which is the ease of keeping the product operational is also important.
2. FEATURE
Features are the secondary
characteristics or added facilities available with the core product.
FOR
EXAMPLE:
Primary function of an automobile
is transportation where as stereo system is a feature.
3. SERVICE:
Service
is emerging as a method for organizations to give the customer added value.
The product may work fine but if the service
which is attached to the product is not managed properly then it will lead to
customer dissatisfaction.
FOR
EXAMPLE:
Purchase of Air conditioner, the
seller has to come to your home to install and run the A/C machine. After that
he must come and service the A/C with regular internal and incase of any
problem immediately come and repair the problem.
4. WARRANTY:
The
warranty encourages customer to buy a product a service by reducing the risk of
the purchase division.
5. PRICE:
Customer is willing to pay a
higher price to obtain value. he evaluating product and services against those
of its competitors who provides the greatest value.
6. REPUTATION:
Find organizations by our overall
experience with them.
Customer satisfaction is based on
the entire experience with the organization not just the product.
FEEDBACK:
Customer feedback must be
continually solicited and monitored. Customer continually changes. They change
their minds, their expectations and their supplies. Customer feedback is not a
one-time effort it is a ongoing and active probing of the customer‘s mind.
IT ENABLES THE ORGANIZATION:
Discover customer
dissatisfaction.
Discover relative
priorities of quality.
Compare
performance with the competition.
Identify
customer‘s needs.
Determine
opportunities for improvement.
TOOLS USED:
1.
COMMENT CARD –attach with warranty
card.
Comment cards are simple cards
usually in the form of prepaid postage card which can be attached with the
product manual or the warranty card. or just included with the product the time
of purchase.
2.
Survey.
It is more effective and also
popular tool for obtaining opinions and perceptions about an organization and
its products and services.
Customers are asked to furnish the
answers related to the quality of the product and service.
3.
Focus group.
The focus group is like an in
depth interview, except that it involves a group rather than an individual. It
is a group interview that tries to stimulate people to talk freely about the
products.in a typical focus group, a few customers are invited to attend a
group discussion at a central interviewing location.
4.
Toll-free telephone numbers.
Toll free phone numbers (1600 –
inIndia, /800/888 in US) are an effective technique for receiving customer feedback.
Organizations can respond faster and more cheaply to a complaint on receiving a
complaint call.
5.
Customer visits.
Company personnel visiting
customers at their place will provide valuable information and feedback on the
product.
6.
The Internet
Web home pages and e-mails have
become very popular these days that they are fast replacing the conventional
methods of feedback mechanism.Customers also find it very easy and cheaper to
provide feedback to the supplier.
Using
customer complaints:
Every single complaint should be
accepted, analyzed and acted upon for its represents.
Information on customer
dissatisfaction is received into
the organization at the highest
level, there by providing a fast response.
Complaints can be seen as
opportunity to obtain information and provide a positive service to the
customers.
Activities
of the customer complaints:
Investigate
customer‘s experiences by actively soliciting feedback both positive and
negative and then acting it promptly.
Develop
procedures for complaint resolution.
Analyze
complaints but under stand that complaints do not always fit in to neat
categories.
Survey
response is received a senior manager should contact the customer and strive to
resolve them.
Establish
customer satisfaction measures and constantly monitor them. Provide a monthly
complaint report to the quality council for their evaluation and improvements.
SERVICE
QUALITY
CUSTOMER SERVICE is the set of
activities an organization used to win and retain customer‘s satisfaction. It
can be provided before during or after the sale of the product or exits on it‘s
own.
ELEMENTS
OF CUSTOMER SERVICE:
ORGANIZATION:
Identify
each market segment.
Write
down the requirements.
Communicate
the requirements.
CUSTOMER CARE:
Meet the
customer expectations. Get the customer point of view. Deliver what is
promised.
Make the
customer feel valued. Respond to all the complaints. Over respond to the
customer.
Provide a
clean and comfortable customer reception area.
COMMUNICATION:
Optimize
the trade-off between time and personal attention.
Minimize
the number of contact points.
Provide
pleasant knowledgeable and enthusiastic employees.
Write
documents in customer friendly language.
FRONT-LINE PEOPLE:
Serve
them as internal customer.
Hire people
who like people.
Give them
the authority to solve the problem.
Challenge
them to develop better methods.
Be sure
they are adequately trained.
Recognize
and award performance.
LEADERSHIP:
Lead by
example.
Listen to
the front-line people.
Strive for
continuous process involvement.
CUSTOMER
RETENTION
Wheather retail or industrial
customer, are constantly watching out for better cheaper products and when a
competitor is able to offer the product better, that the customers usually
switch.
Any organization should develop a
very personal relationship with individual customers, so that they do not
switch over to the competitors.
CUSTOMER RETENTION represents the
activities the produce the necessary customer satisfaction that creates
customers loyalty, which actually improves the bottom line.
EMPLOYEE
INVOLVEMENT
TQM requires everybody‘s
involvement in the process and everyone should feel that the company belongs to
them. Employee involvement results in improved quality and productivity.
MOTIVATION:
MEANING/DEFINITION:
1. Motivation is a process that
starts with a physiological or psychological deficiency or need that activates
behavior or a derive that is aimed at a goal or an incentive.
2. Motivation is the result of
processes internal and external to the individual that arouse enthusiasm and
persistence to pursue a certain course of actor.
THEORIES
OF MOTIVATION:
MASLOW
THEORY
According to this theory every
individual is depicted as a wanting organism with a desire to rise from one
level to another level in the society. Maslow suggests five levels for every
individual with differing needs at every level.
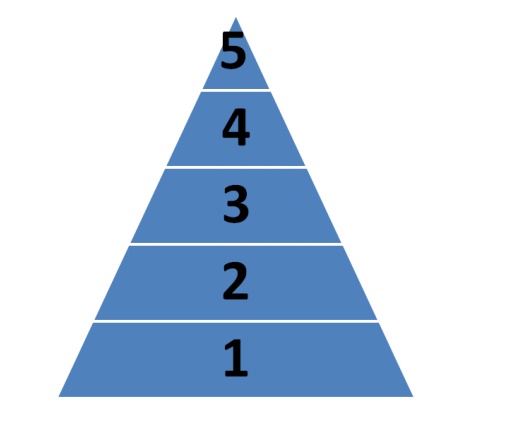
1. Basic or
physiological needs
The first need of a person is
physiological in nature. physiological needs are the necessities for survival.
Once this need is satisfied, they no longer act as motivators for the employee.
These factors when available are taken for granted and employees look for the
next level as motivators.
2.
Security or safety needs.
Employees now strive to achieve
the next level which is safety needs. These needs include safe place of work
and job security, which are very important for employees.
3. Social needs.
Since a man is social being, he
has a need to belong and to be accepted by the various groups. When social
needs are dominant, a person will strive for meaningful relationship with
others. He gets a fear of being rejected.
Conversely when an individual has
an opportunity to be a part of a group by feeling important and needed will
motivate that person.
4. Esteem needs.
Self esteem needs are concerned
with self respect, recognition, self worth and feeling of being unique.
5.
Self- actualization.
Individuals in an organization
must be given the opportunity to go as far as their abilities will take them.
Many organizations have a policy of promoting employees from within. This
motivates employees to contribute their maximum to the organization.
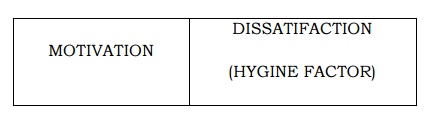
HERZBERG‟S
TWO-FACTOR THEORY:
He identified that people were
motivated by recognition, responsibility, achievement and job advancement. He
labels these factors as motivation.
He also identified that bad
feelings were associated with low salary, minimal fringe benefits. Power
working environment and ineffective supervision.
These factors were labeled as
dissatisfaction or hygiene factor
It should note that the presence
of extrinsic (hygiene factors) results in dissatisfaction, but the absence of
motivating factor does not make employee dissatisfied.
EMPLOYEE
EMPOWERMENT
MEANING:
Employee empowerment is making a
person completely responsible for a particular task; the individual who is
empowered becomes the process owner.
In the empowerment the individual
in given complete authority required to execute the process and ownership is
created.
Condition:
·
Every
one should understand the need for change in culture and attitude.
·
The
system must change to the new paradigm.
·
People
should be provided with necessary resources.
Empowerment is an environment in
which people have the ability the confidence and the commitment to take the
responsibility and ownership to improve the process and initiate the necessary
steps to satisfy customer requirements within well-defined boundaries in order
to achieve organizational values and goals
TEAMS
T-together E-everyone A-achieve
M-more
A team is defined as a group of
people working together to achieve common objectives or goals.
Teamwork is the cumulative actions
of the team during which each member of the team subordinates his individual
interests and opinions to fulfill the objectives or goals of the group.
TYPES OF TEAM
1. Process improvement team.
Here, five to six members from
various disciplines of the organization are brought together to solve a
problem. Usually the scope of the team is limited to the work unit.
The life cycle of the team is
usually temporary. The team is disbanded after the problem (process improved)
is solved.
2.
Cross-functional team.
Here the team is constituted by
the number of different functional areas such as production, engineering,
marketing, finance, e etc. it may also include customers and suppliers.
3. Natural team.
This type of team is not voluntary
in nature as it was with other teams. Here all members of the work unit are in
the team and the manger is also part of the team.
4. Self-management work groups.
They are an extension of natural
work team without the supervisor. These teams are the essence of the empowered
organization. These teams not only do the work but also manage it.
STAGES
OF TEAM DEVELOPMENT:
1. Forming.
Forming is the fist and beginning
stage of the life cycle of a team.
A facilitator is appointed by the
quality council and he meets with the senior management to charter the path the
solution of the problem should take.
Once team is assembled, a meeting
is called and the facilitator briefs the problem to the team, and then
determine the type of training the team members may need and identify an
appropriate team leader.
2. Storming.
In this stage all members of the
team are fully aware of the quality problem they are faced with.
They will be interested in proving
themselves by exhibiting their individual skills.
3. Norming.
In this stage members have
understood each other well. Everyone knows each others strengths and weakness
and capabilities and limitations.
The roles of the members are
clearly defined, mission and objectives are clear and the course to be taken to
solve the problem is also clear.
4. Performing.
In this stage, the team members
have understood the project better and begin performing by diagnosing and
solving problems and choosing and implementing changes.
BARRIES
OF TEAM PERFORMING:
1.
Poor training for the group members.
2. Improper reward schemes.
3. Lack of planning.
4. Lack of management commitment in
monitoring the team program.
5. Poor communication.
6. Too many members in team.
Role
of team leader:
1. Ensure the smooth and effective
operation of the team.
2. Handling and assigning the
responsibilities.
3. Good record keeping.
4. Preparing and presenting the
report.
5.
Prevents
other members from dominating.
6. Use positive interpersonal
dominating.
7. Serve as a contact point between
the team and qty council.
8. Monitors the status and
accomplishments of member assuming firmly completion of assignments.
9. Prepares the meeting agenda i.e.
time, date, location.
Role
of team member:
1. Contributes best.
2. Sharing knowledge.
3.
Listen
carefully and ask question.
4. Negotiate important points.
5. Supports the decisions of the
team.
6. Trust support concern for other
team members.
7. Understands and is committed to
team objectives.
8. Respects and is tolerant of
individual differences.
9. Acknowledges and worker through
conflict openly.
10.Carries out assignments between
meetings such as connecting data observing charting data and returning report.
11.Gives honest sincere
appreciation.
Recognition
and reward:
Recognition and reward are basic
motivational tools used to motivate employees to encourage them to maintain and
improve their present level.
Publicly
acknowledging the contributions of an individual is called recognition.
This acknowledgement may be in the
form of a certificate or a verbal praise.
On the other hand the rewards are
tangible such as cash reward, gold coins etc
Reward can be delayed but the
recognition of the contributions must be done immediately.
Purposes:
1. Reward system reminds the
continual improvement required for the TQM journey.
2. Serves as a platform for
encouraging the super performances.
3. Serve as a goal for the employee.
4. Serve as a morale booster.
Performance
appraisal
Performance appraisal is the
judgement of employee‘s performance in the organization.
Performance appraisal is defined to
show the employees how they are doing. This serves as a basis for promotion,
salary increases etc those who are rated poorly should be allowed to undergo
special counseling and skill up-grading programmer.
It should help people to assess
themselves and improve.
Appraisal
format:
1. Ranking- compares employees by ranking
from highest to lowest.
2. Narrative-
gives a written description of
employee‘s strength and weakness.
3. Graphic-indicate the major duties
performed by the employees and rate each
duty with a sale, which is usually from 1(poor) to 5(excellent).
4. Forced
choice-places
each employee‘s in a category with a predetermined percentage for example excellent 10%, very poor 25%, grave 30%,
fair 25%, poor10%.
BENEFITS
1. PROMOTION
2. SALARY INCREASE
3. BONUS
4. INCENTIVES
5. INDENTIFYING TRAINING NEEDS
6. IMPRORING SKILLS OF THE EMPLOYEE‘S
7. TO IMPROVE EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE
8. TO RATING THE CUSTOMERS.
CONTINUOUS PROCESS IMPROVEMENT
CPI is the care of TQM. CI in the
business process as war as production process is desired for the growth of the
organization.
CPI is possible by
1. Making all process effective and
adaptative.
2. Accepting the change in the
customer requirements and tuning ourselves to meet demand.
3. Improving the productivity by
eliminating waste.
4. Permanently eliminating the ‘non-value
adding activities‘.
5. Our self with the best player in
the field.
6. Using advanced tool like
DOE(design of experiments), SPC, quality function development etc .
JURAN‟S
TRILOGY
Juran‘s trilogy consists of three
managing process quality planning, quality control and quality improvement.
Quality
planning:
The quality planning starts with identifying external customers of a business.
Identify who are the customers.
·
Determine
the needs of those customers
·
Translate
those needs into the business possibility
·
Develop
a product that can respond to those needs
·
Optimize the
product features so as to meet
the organizations needs and
customer‘s needs.
Quality
Improvement
Develop a process which is able to produce the Product.
Optimize the process.
Quality
control:
Prove that the process can be
producing the producet under operating conditions with minimal inspection.
Transfer the process to
operations.
The
quality control involves checking the products produced with specification.
QUALITY
IMPROVEMENT STRAREGIES
1.
REPAIR:
There are two levels of repair.
a)
In
the first level the team or an individual working in the process identifies the
problem and eliminates the root cause of the problem. This brings in permanent
solution for the problem.
b) In the next level the faulty
product reaches the customer. The customer then indicates that he has received
a bad product and the product is either replaced or repaired. This is temporary
solution to the problem.
c)
It
is important to note that the repair strategy will not make the process better
than the original design.
2.
CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT/
REFINEMENT:
Refinement
is doing things a little bit, faster, better, easier, or with less waste.
It is
the process products and services are required to keep the quality improvement
process alive. But management may fail to notice the small improvement and
influence fail to reward the improvement efforts. This will result in
dissatisfaction and loss of involvement.
3.
INNOVATION:
The processes and products by
innovative methods.
For example: automation of
process.
4.
PARADIGM SHIFT (RE-INVENTION):
When a
company understand that the existing processes cannot ensure the customer
satisfaction it is better to reinvent the process.
PDSA CYCLE
STEWART developed the
plan-do-check-act (PDCA) cycle and late Deming modified it to plan-do-study-act
(PDSA) cycle.
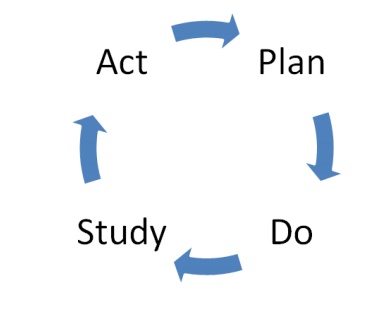
Plan:
By management. Do: By the operator. Study:
quality manager Act: management
Plan
It is important to establish the stage of the
change to be introduced.
Plan on how you are going to collect the
information about the differences that occur after the implementation of the
plan.
What is to be done and how to achieve.
Do:
Put the plan into practice.
There may be changes that should
only be measured over long periods.
Record any unexpected event,
problems and other observations. Star analyzing the data.
Study
Review and reflect on the data
collected in the previous step
Find out whether there has been
any improvement in the process. Did your expectations match the reality of what
happened?
Find out what could have been done
differently.
Act
Carry out an amended version of
what happened during the ―Do" stage and measure any differences
PROBLEM
SOVING METHOD FOR PROCESS IMPROVEMENT.
5s-concept
1. Seiko (Proper arrangements)
This is the proper identification
of materials, equipments and tools, data and information which are necessary or
not necessary,.
Provide the necessary space for
the required or necessary items which you require to perform the necessary
task.
2. Seiton (orderliness)
Every equipment or data or anything
should be placed in its appropriate and unique place.
So that a simple eraser or pencil
can be found at the same place every time by everybody in the organization.
This reduces confusion and avoids
wastages of time.
The place in which it is stored
should be easily accessible and appropriate.
3. Seiso (Cleanliness)
The shop floor should be free of
wastage, oil spills, cotton wastes etc., The tools also should be clean, the
machines should be clean and the entire organization should be free from dirt
and any unexpected objects lying around.
Keep the work place clean and make
data and information easily available and constantly updated in order to
support decision making.
4. Seiketsu (personal cleanliness).
A person should be clean and his
cloths should be clean. Only a clean person can be conscious about keeping his
workplace clean and neat. Moreover unclean person present a work situation were
co-workers become uncomfortable to work in.
Personal cleanliness automatically
creates a favourable condition at work place for physical and mental health,
free from dirt, pollutants etc.
5. Shitsuke (Discipline).
This may not only be the jobs
related to the organization but also personal work.
Job discipline is the habit and
skill development to perform the job according to standards, to observe company
rules and policies at all times.
This habit of discipline is
developed as a result of excursing mental, moral and physical strength.
KAIZEN
The philosophy that defines
management role in continuously encouraging and implementing small improvements
involving everyone.
It is the process of continuous
improvement in small increments that make the process more efficient,
effective, under control and adaptable.
Improvements are usually that make
the accomplished at little or no expenses without sophisticated techniques or
expensive equipment. It focuses on simplification.
Kaizen is possible only when the
management is able to hear the workers. It requires an effective communication
in both the directions.
KAIZEN
REQUIRES THE USE OF THE FOLLOWING:
1. The data about value adding and
non-value adding activities.
2. The knowledge about various types
of waster (Muda). Over production, delay, transportation, processing,
inventory, wasted motion and defective parts.
3. Documentation of the operating
procedure.
4. Principles of time study.
5. Following the 5s concept.
6. Fewer inventories – use JIT.
7. Mistake proofing- to prevent or
detect errors.
8. Effective use of teams to solve
problems and to improve the performance.
SUPPLIER PARTNERSHIP
The
relationship between customer (company) and the supplier. Customer and supplier
have the same goal to satisfy the end user. Both the customer and the supplier
have limited resources they must have work together as partners to maximize
their return on investment.
Principles of customer-supplier
relations:
1. Both the customer and supplier are
responsible for the quality control.
2. Supplier and customer should be
independent of each other.
3. The customer must communicate to
the supplier about his requirements.
4. There should be agreement with
respect to quality, price, mode of delivery and payment mode.
5. The supplier should supply quality
materials that will result in customer satisfaction.
6. Provisions for the easy settlement
of the disputes.
7. Mutual exchange of information.
PARTNERING
Meaning:
Partnering is a long-term
commitment between two or more organization for the purpose of achieving
specific business goals and objectives by maximizing the effective of each
participants resources.
Benefits:
1. Improve quality.
2. Increased efficiency.
3. Lower cost.
4. Opportunity for innovation.
5. Continuous improvements of product
and services.
KEY
ELEMENTS OF PARTNERING:
1.
LONG-TERM COMMITMENT:
Long-term commitment provides the
needed environment for both partners to work toward continuous improvement.
Problems require time to solve or
process need constant improvement.
Each partner contributes its
unique strengthen to the processes.
Investment in new equipment or
systems may be required.
These
must be a to far organization involvement from the CEO to the workers.
2. TRUST:
Mutual trust forms the basis for a
strong working relationship.
Open and frequent communication
avoids misdirection and disputes while strengthening the relationship.
The parties should have access to
each other business plans and technical information.
They may share or integrate
resources such as training activities, administration systems and equipment.
Both parties become mutually
motivated when win-win solution not rather than win-lose solution.
3.
SHARED VISION:
Shared goal and objectives ensure a common
direction and must be aligned with each parties.
Employees of both parties should think and act
for their common good.
Understand each other‘s business
so that equitable decision are made
Sharing of business plan.
SOURCING
SOURCING is the process of
identifying the suppliers for the items required by an organization for produce
or manufacturing the product. There are three types of sourcing
1.
Sole sourcing:
The organization is forced to use
only one supplier. Only one organization producing the item.
2.
Multiple sourcing:
Two or more suppliers are
available for the required item.
It eliminates dependency.
Usually these suppliers are chose
in term of price, quality and delivery.
It will result in better quality
low cost and better service.
If there is a strike going on in
one of the supplier‘s company the manufacturer need not wait for him.
3.
Single sourcing:
Though there are number of suppliers available
for a particular commodity selecting a single vendor for the organization to
supply the item is called single sourcing.
It results in long-term product.
Supplier
Selection
The company before going for selecting a
supplier should finalize on ―Make or Buy‖ decision. The following questions
must be answered before
proceeding with the suppliers.
1. How critical is the item to the
final product/ service
2. Is it possible to produce the item
internally? Do we have technology to produce it? If not, can we develop it?
3. Are there any specialized
suppliers for the item? Or can we develop such a supplier?
Finally the decision is made to
outsource, the following points must be considered for evaluating the
suppliers.
a.
The supplier‘s
ability to understand the management philosophy of the organization.
b. The technical expertise available
now and the ability to cope up with the future technical requirements.
c.
The supplier‘s
ability to consistently supply the raw materials that meet the specifications of the purchaser.
d. The supplier‘s ability to meet the demand and
ability to increase the volume of
production when demanded.
e.
The
credibility of the supplier in maintaining the corporate secrets.
f.
System
of delivery and communication systems available with the supplier.
g. The track record of the supplier
with the company.
Supplier
Rating.
To assess the performance of the
suppliers with respect to quality, speed if delivery, and service, the supplier
rating is done. Supplier rating is the process of categorizing the suppliers on
the basis of quality, prompt delivery, and services.
1.
Supplier
rating enables the company to obtain an overall rating of the supplier
performance.
2.
It
ensures complete communication with customers on all the key areas.
3.
It
enhances the customer- supplier relationship by providing an objective feedback
of the supplier‘s performance.
4.
It
provides the supplier‘s with a factual record of mistakes, so that the
suppliers can eliminate them in future.
For example
Supplier Rating System. - Scorecard.
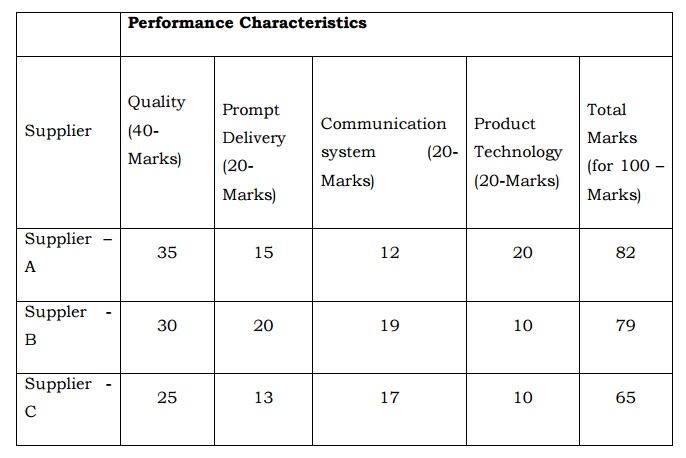
The above the clearly show - the
supplier –A having more score comparing with the B and C. so it is conclude
that the supplier –A is good performance.
RELATIONSHIP DEVELOPMENT
Sustaining
the relationship with the suppliers is important after initiating the customer
supplier partnering process. To keep the relationship alive and growing the
following activities are carried out.
1. Inspection
The purpose of this inspection
process is to gain confidence in each other‘s performance and finally
automating the inspection activity. There are four phase in the inspection
process.
a.
100%
inspection
b. Sampling inspection
c.
Audit
d. Identity Checks.
2. Training
It is always better to educate the
suppliers on what we expect from them and what quality means to us in the
business process. This is possible by allowing the suppliers to undergo
training programmes conducted by the senior officials at customer‘s sites.
3.
Team Effort
In all the possible areas the
teams must involve officials from the suppliers side also. This will enhance
the understanding of the suppliers and their role in the business process will
be clear to them.
The team meeting must be arranged
at both the customer and the supplier premises.
4.
Recognition
The
customer should
recognize the supplier‘s performance by awarding them with a place in the preferred suppliers list. A certificate
of contribution to the business must be given to them. This recognition will
surely develop the relationship between the customer and the supplier
Related Topics