Term 2 Unit 2 | Civics | 6th Social Science - The Constitution of India | 6th Social Science : Civics : Term 2 Unit 2 : The Constitution of India
Chapter: 6th Social Science : Civics : Term 2 Unit 2 : The Constitution of India
The Constitution of India
Unit 2
THE CONSTITUTION OF INDIA

Learning Objectives
• To know about the Cons
titution of India
• To recognise the
formation of our Cons titution
• To know the salient
features of our Cons titution
• To know the fundamental
rights and duties of the citizen of India
Pathway
The Lesson speaks about
the formation of the constitution of India. It gives guidelines to govern the
country, while ensuring the fundamental rights and duties of the citizens and
how it protects them.
Yazhinian and Sudaroli are brothers.
Yazh is student of standard six and Sudar is in standard four. Yazh was
preparing for his class test. Sudar after completing his home assignments was
watching an animated series on television. Sudar was watching it but the noise
level disturbed Yazh. Sudar was totally engrossed in the series and laughed and
clapped loudly. Yazh could not concentrate on his lessons.
So he asked Sudar to reduce the volume.
But Sudar was not ready to adhere to his elder brother’s advice. Inspite of
Yazh’s continuous request Sudar did not reduce the volume.
Yazh complained to his father that
Sudar did not decrease the volume of the television in spite of requesting him
several times. Yazh made it clear that he had a class test the following day.
“Isn’t your brother preparing for his
class test? Weren’t you wrong in troubling him?” continued his father.

“I was watching the TV. Yazh kept
disturbing and stopped me from watching it.” said Sudar.
“Studying for the test and watching
television are not the same” said his father.
But Sudar was not ready to accept the
fact. Sudar was consistent that he had all rights to watch a film as much as
Yazh had the right to study.
His father admitted that both had equal
rights. But one must not hinder another’s freedom. Sudar didn’t realise the
fact that he was very stubborn.
“Look Sudar. You have all rights to
watch the film” said his father.
“Yes dad”.
“Similarly, Yazh also has the right to
listen to his favourite song on TV Coundn’t he?”
“How can that happen? When I watch the
television he cannot do that.”
“When you can watch a film by
increasing its volume, Yazh can also hear music loudly.” said father.
“How will I watch the movie?”.
“How will Yazh study?” .
“Oh! I didn’t think of it. Okay dad, I
will not watch the movie while Yazh studies.” .
“No my child. You can watch the movie
without causing trouble to anyone,” .
“Don’t be angry Yazh. You study and I
promise I will not disturb you.”
Yazh smiled and patted Sudar’s back and
left the place.
Sudar’s mother was watching everything
silently. She said,” Even to run a small family don’t we need to follow so many
rules and regulations? How much more of that will we need to administer a
country?” she exclaimed.
“It is an ocean Deepa. In order to
administer people who follow different religions, speak different languages and
belong to different castes and culture and treat everyone equally, we need to
have a good code of laws and guidelines which we call as ‘The Constitution of
India.’
The next day Sudar and Yazh went to
school. It was the Republic Day also.
The celebration was a jubilant. The
students and teachers were standing in line around the flag post. Immediately
after the hoisting of the flag, a discussion was held with the chief guest for
the day, Mr. Arumugam, an expert in social sciences.
“Wish you a happy Republic Day!” wished
Mr. Arumugam.
“Wish you the same Sir.”
“Do you know why do we celebrate the
Republic Day?”
“Our Constitution was framed and came
into existence from 26th January 1950. That is why every year we observe this
day as the Republic Day.” said the history teacher Malarmathi.

“Yes, it is true. There are other
reasons why this constitution came into existence on 26th January 1950. When
the Congress met at Lahore in 1929, the members of the Congress unofficially
declared the same day as the Day of Poorna Swaraj or the Day of complete self
governance. The next year, 26th January 1930 was celebrated as the Independence
Day. That day has been observed as our Republic Day.”
“What do you mean by the “Constitution
of India” asked Nathar.
“Before that, let me ask a few
questions. You answer me. Then I will explain in detail about the constitution
of India.”.
“All right sir.”
(The students were prepared to answer
the questions)
“Are you following any rules and
regulation at home?”
“Yes sir”
“Are you following any rules at
school?” “Yes sir”
“Are both of them the same or
different?” “Mostly, they are different”
“Is it necessary to follow certain
rules in public places?”
“Yes, Sir”
“Why is it necessary?”
“We should not disturb anybody in
public” said Tamilselvi.
“It’s true. Also no one should disturb
us”said Selva
“Yes, I do accept it. But what if
someone compels you to follow some rules? How would you feel?”
“It would be difficult to do so.”
“How do you feel when you are asked to
make your own rules?”
“We would be proud and pleased to obey
our own rules.”
(Everyone agreed and nodded their
heads)

“The Constitution is an authentic
document containing the basic ideas, principles and laws of a country. It also
defines the rights and duties of citizens. The laws governing a country
originate from the consitutition. Every country is ruled on the basis of its
constitution”
“What are the things that make the
constitution of India?” asked Deepika.
“The constitution of India is the
ultimate law. We have to abide by it. It explains the fundamental concepts of
structure, methods, powers and the duties of Government bodies. It also lists
the fundamental rights and duties of the citizens. Directive Principles are
also mentioned in the constitution. So it is holistic in nature.”
“When did they begin to frame the
constitution?” asked Christopher.

“In 1946, nearly 389 members of the
constituent Assembly who belonged to different parties from different places
came together to frame the Constitution of India. The Chairman of the committee
was Mr. Rajendra Prasad.”
“Who were the other significant members
in the Constituent Assembly?”
“Jawaharlal Nehru, Sardar Vallabai
Patel, Moulana Azad, S. Radhakrishnan, Viajalakshmi Pandit and Sarojini Naidu
were the members in the Constituent Assembly”

“How many women members were there in
the Constituent Assembly?
“15 women members were in the
Constituent Assembly”
'The Father of the
Constitution of India’ is Dr.B.R. Ambedkar.
“The Drafting committee was formed with
eight members and its Chairman was B.R. Ambedkar; B.N.Rao was appointed as an
advisor. The committee met for the first time on 9th December 1946. On the same
day, the drafting of constitution of India started.”.
“How did they form the Indian
constitution?”
“The constitutions of nearly 60
countries including the UK, USA,former USSR, France , Switzerland etc., were
thoroughly examined and their best features have been adopted by our
constitution.”
“Did they draft it in a short span of
time?”
“No, nearly 2000 amendments were made
before the draft was finalised”
“When did they complete this work?”
“It took a period of 2 years, 11
months, and 17 days. It was completed on 26th November 1949".
“The constitution was accepted by the
Constituent Assembly. So, 26th November is celebrated as the Day of the
Constitution. isn’t it ?” said Karthikeyan
“Yes” said Mr. Arumugam

“How much was spent to frame the
constitution of India?” asked Nathar.
“They spent almost 64 lakhs”.
“What are the objectives of the
Constitution?”
“The Preamble of our constitution
stresses on the justice, liberty, equality and fraternity.”
“What is a Preamble?”

“The preface of the constitution is the
Preamble. According to it, India is a Sovereign, socialist, Secular democratic
republic.”
“What does it mean by ‘Sovereign’?”
“The constitution has granted the people
the right to rule. The members of the parliament and the legislative assembly
are elected by the people. The right to decide is only in the hands of the
representatives. Sovereignty refers to the ultimate power of the country.”
“What is the meaning of “Secular?”
“Law allows all the citizens of a
country, the right to follow different faith and religious beliefs. All
citizens enjoy the freedom of worship. The country does not have a religion of
its own. All the religions in our country hold the same status.”
“The Government of India rules through
the Parliament, doesn’t it?”
“Yes, the Constitution of India
provides a Parliamentary form of Government, both at the centre and the state.
In a Parliamentary System, the Executive is collectively responsible to the
Legislature. The party which has the majority forms the government.”
“What are fundamental rights?”
“Fundamental rights are the basic human
rights of all citizens.”
“What are they?”
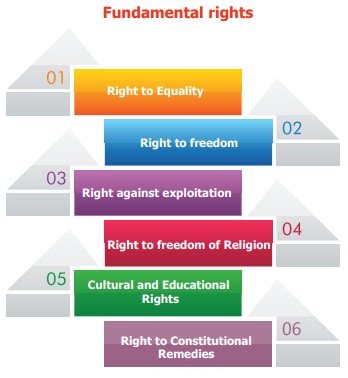
“They are Right to Equality. Right to
freedom, Right against exploitation, Right to freedom of Religion, Cultural and
Educational Rights and Right to Constitutional Remedies.”
“You mentioned about Directive Principles.
What do you mean by that?” “There are certain guidelines to be followed while
the governments frame law. Though these are not mandatory, they should be taken
into account.”
“What is Universal Adult Franchise?”
“Every Indian citizen has the right to vote
when they attain 18 years of age, irrespective of any caste, religion, gender
or economic status.”
“Like fundamental rights, every citizen
will have duties too, won't they?”
“Yes, There are duties respecting the
National flag and National Anthem, respect and protect the Constitution, follow
our great leaders who fought for our freedom, to protect our country, readiness
to serve our country if necessary, treating everyone as brothers irrespective
of their castes, religions, languages, races etc., to conserve our ancient
heritage, and conserve natural elements like forests, rivers and lakes and
fauna, to develop science, humanity and feelings of reformation to avoid
non-violence and protect government property, parents or guardians providing
educational opportunities to children between 6-14 years etc., have been added
as our duties” Mr.Arumugam concluded his discussion.
The original copies of
the Cons titution of India (Hindi,English) are preserved in special Helium
filled cases in the Library of the Parliament of India.
FACTS
• Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, N. Gopalasamy,
K.M.Munshi, Syed Ahmed sadullah, P.L. Mitter, N.Madhava Rao, T.T.K, T.P.
Khaitan were the legal experts of the Drafting Committee.
• The Chairman of the
Drafting Committee Dr. B.R. Ambedkar was considered the Chief architect.
• When the Cons titution
was drafted, there were 395 articles in 22 parts and 8 schedules. At present
our Indian Cons titution contains 448 articles in 25 parts and 12 schedules.
• 101 amendments were
made till 16.09.2016.
HOTS
Prepare
a lis t of your immediate duties?
GLOSSARY
1. Democracy
- a type of government in which representatives are elected by the people
of that country.
2. Drafting
- a Committee set up to Committee prepare the draft of th Constitution
3. Preamble
- an introduction to a book or a written document.
4.
Republic - a country with an elected head of state
5. Secular
- a state which does not discriminate anyone on religious grounds
6. Socialist
- equal distribution of a country’s wealth and equal opportunities in all
fields.
7. Sovereign
- an independent country not subject to any external power or influence.
RECAP
• 26th January is observed as our
Republic Day.
• The Constitution is an authentic
document containing the basic ideas, principles and laws of our country
• The father of the Constitution of
India is Dr. B. R Ambedkar.
• The Preamble of our Constitution
stresses on justice, liberty, equality and fraternity.
• According to the Preamble, India is a
sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic
• All citizens enjoy the freedom of
worship
• The Executive is collectively
responsible for the legislature
• Fundamental rights are the basic
human rights of all citizens.
• Directive principles are certain
guidelines which are not mandatory
• Universal Adult Franchise is every
Indian citizen’s right to vote when they attain 18 years of age.
• Every citizen has certain duties too.
ICT CORNER
The Constitution of India
Let us learn
about The Constitution of India
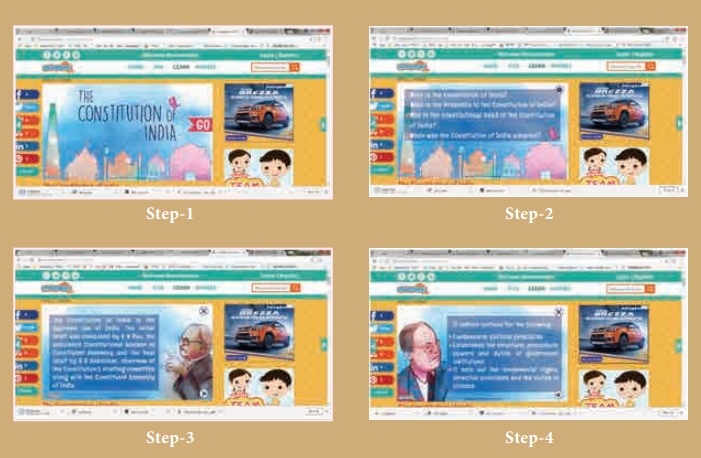
Step 1:
Type the URL or scan the QR code to open The Constitution of India page .
Through this page we are going to learn about the constitution of India.
Step 2: Click the GO button in that page. Here
we get some questions. Click any question to learn the related concepts.
Step 3: To know more , click the next button
in the lower right corner. Now we get more information.
Step 4: To go to the next concept , click
button in the upper right corner .
URL:
http://mocomi.com/constitution-of-india/
Related Topics