Term 1 Chapter 2 | 3rd Science - States of Matter | 3rd Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : States of Matter
Chapter: 3rd Science : Term 1 Unit 2 : States of Matter
States of Matter
Unit 2
States of Matter

Learning Objectives
After learning this
lesson, students will be able to
* know the matter
surrounding us
* differentiate between solids, liquids and gases
* conduct simple experiments
* observe the properties of matter
* describe the nature of
the material
Matter
Teacher : Leela, look at the
picture and list out the things you see in it.
Leela
: Yes madam. Sun, river,
boat, house, tree, car, birds, …
Teacher : Very good. There are many
things in this picture. Some of them are natural and some are man-made.

You can see a number of things around
you. Everything you can see and touch is made up of matter. Anything that
occupies space and has mass is called matter
Let us Do
List out the some of the
matter around you.
Answer: 1. Book 2.Table 3.Cloud
4. Tree
More to know
What is mass?
Mass is a measure of how much matter is in an object.
* The air we breathe, the food we take, and the water we drink all
have matter in them.
Do you know that even you are made up of matter?
The space occupied by an
object is called its volume.
1. States and properties
of Matter
Matter can exist as solid, liquid or
gas.

i. Solid
*
rigid
* fixed shape
* fixed volume
ii. Liquid
* not rigid
* no fixed shape
* fixed
volume
iii. Gas
* not rigid
* no fixed shape
* no fixed volume
I. SOLIDS
Let us Try
Press a wooden pencil.
Is the pencil hard? Yes / No.
Solids are things that have a definite shape and volume. They occupy a
fixed space. The particles in solids
are packed very tightly. So they cannot move freely. Their shape can be changed only when
we break or cut them.
Some examples for solids
are given below.

II. LIQUIDS
Let us Do
1. Place 4 1L bottles of different shapes on the
table.
2. Take a bucket with water.
3.
Call one child to hold the empty bottles and the
other to fill water into them using a paper cup.
4. Ask the other children to fill the table as
given below.
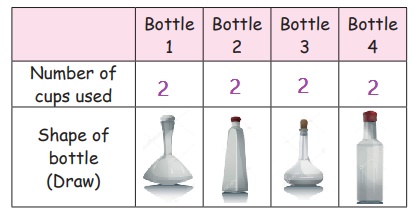
Did each bottle need the same number of cups to
get filled?
We can see that water takes up the same space in
each bottle and the shape of the water is same as the shape of the bottle.
Think Zone
1. What is the shape of water in your bottle?
The water takes up the shape of my bottle.
2. What happens if you pour water on the floor or table?
The water flours.
Look at these pictures
Here we can see that the shape of the liquid is
determined by the shape of the container.
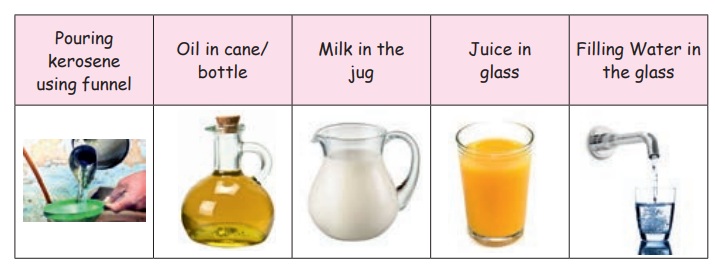
Liquids are the things that do not have a definite shape but occupies
space. They have a definite volume. They
take the shape of the container in which they are filled. The water moves from one place
to another. This is because the matter in liquid are loosely packed. So, liquids can flow freely.

Let us Touch and Feel
Different types of liquids are placed
in separate containers. Students are allowed to touch and feel every type of
liquid. They are asked to tell the type of the liquids on the basis of their
stickiness/concentration.

III. GASES
When a perfume is
sprayed or an agarbatti is lighted, the fragrance spreads all around the room.
How?
The matter in gases are very loosely packed. So they can move around freely in
all directions. Hence, gases do not have a definite shape and do not occupy a definite space or volume.
Most of the gases are colourless. But
when they are mixed with solid particles they show distinct colours.

Think Zone
Cooking gas in gas-cylinder has a smell. Why?
Because Ethyl mercaptan is added with LPG to find the leakage.
Here are some examples for gases

Let us Do
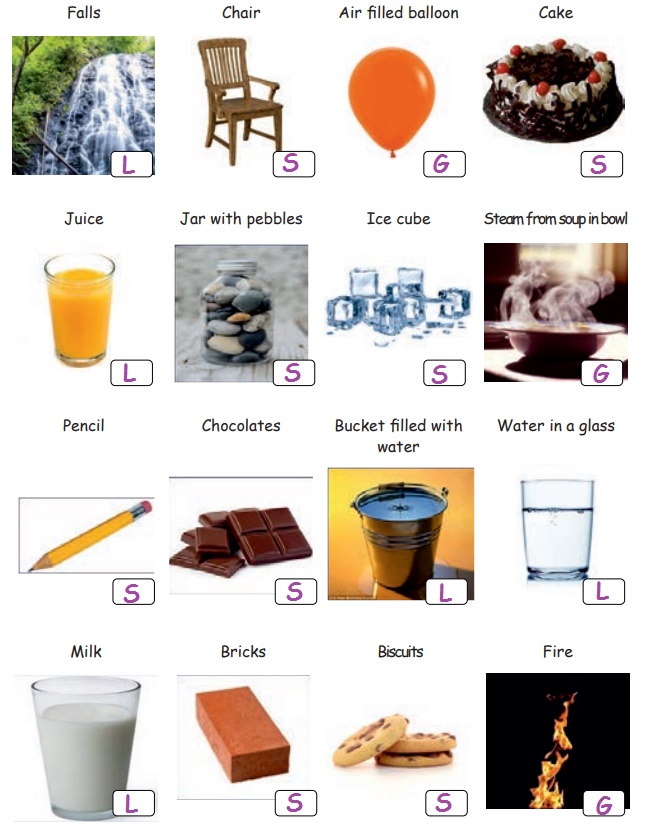
Say whether it is Solid
or Liquid or Gas (Put ‘S’ for Solid, ‘L’ for Liquid and ‘G’ for Gas).
Let us Read and Complete
the table
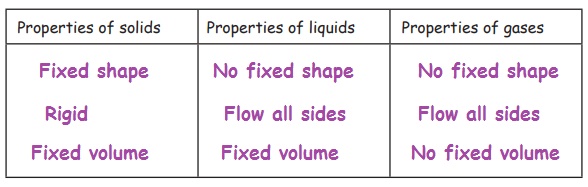
Here are some properties
of matter:
Fixed shape, No fixed shape, Fixed volume, No fixed volume, Flow all sides, Rigid

Copy the following table. Write each
property in the correct column of the table. Some properties may belong to more
than one column.
2. Change in States of
Matter
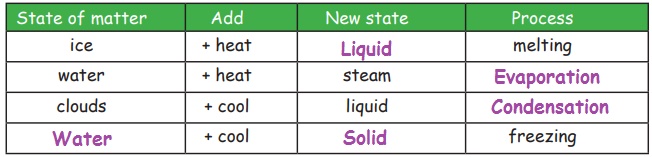
Matters change their state as the
temperature changes. Solid changes into liquid and liquid changes into gas on
heating. Gas becomes liquid and liquid becomes solid on cooling.
Melting
Change of solid into liquid on heating
is called melting. For example, if ice (solid) is heated, it will change
into water (liquid).

Let us Do
* Take some ice cubes in a container.
Heat the container and observe the changes.
Ice cubes melt.
* Take some cheese in a container.
Heat the container and observe the changes.
Cheese melts.
* Take some jaggery in a pan. Heat the
pan and observe the changes.
Jaggery melts.
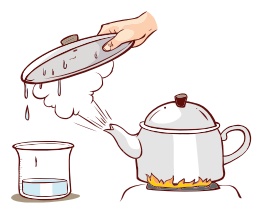
Evaporation
Change of liquid into vapour on
heating is called Evaporation. For example, if water is heated, it will
change into steam.

Freezing
Change of liquid into solid on cooling
is known as freezing. For example, water (liquid) poured in ice-tray and
placed in the freezer (fridge), gets cooled and becomes ice (solid).

Condensation
Changes of gas into liquid on cooling
is called condensation. For example; clouds (gas) on cooling condense
and fall as rain (liquid)
Let us think
What
makes the coconut oil freeze in winter season?

In winter season room temperature will drop down almost below 20°C which is less than the freezing point of coconut oil. So it freeze in winter season.
Complete the table
Think and answer
One of these cans was in the fridge and the other was not.

a) Which can was taken
from the fridge?
Can A.
b) How do you know?
Water droplets appear on the can A.
c) How did water droplets appear on the can A?
Because of condensation.
d) Why are there no water droplets on can B?
Can B is not kept in the fridge.
Let us Observe
Take a balance. Keep an air filled
football in one plate and an
empty football in another plate . What happens?
Air filled ball goes down. It is
because air has mass.

Do you know
Air is a mixture of gases. You can feel the presence of air when
the wind blows.
Let us Prepare - Anchor
chart
1.
Cut a chart into three pieces each of 15cm × 10
cm.
2. Write the properties of solid, liquid and gas
in separate sheets.
3. Draw pictures related to the points.
4. Design the sheets with colourful borders.
5. Paste all the sheets in a large chart paper.
Your anchor chart is ready. Hang it on the wall.

Let us Understand
* Keep a stone on the floor. Does it
move by itself?
No
* Pour
a mug of water on the floor. Does the water flow? Does it flow in one
direction?
Yes, the water flows. It flows in all direction.
* Take
an air filled balloon. Prick it with a needle. Does the air rush out?
Yes
* Fill
an open vessel with water. Press the surface of
the water with your hands. How do you feel?
Water overflows.
4. Materials Used / Not
Used For Heating
Look at the pictures.
Write down what you see.
(Wood, Leaves, Paper)

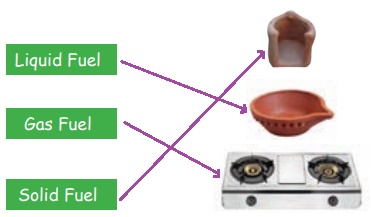
Fuels
*
Paper, firewood, dried leaves and
charcoal can be burnt.
* Liquids like kerosene, petrol and
diesel also burn on heating.
* Domestic gas burns and helps in
cooking.
Substances when burnt give out heat.
But in some substances, the heat released is very low. Thus, these are not used
for heating purpose.
Substances that give out more heat
while burning are used for heating purpose. These substances are called fuels.

Match the following.
Do you know
Electrical energy is also used as fuel for cooking and transporting.
Related Topics