Chapter:
Socialization Benefits and Stages in socialization Process
Socialization
In order
to reduce the anxiety that new employees may experience, attempts should be
made to integrate
the
person into the informal organization. The initial T&D effort designed for
employees is Socialization,
the
guided adjustment of new employees to the company, the job, and the work group.
I. Purposes of Socialization
Socialization
formats are unique to each firm. However, some basic purposes include
emphasizing these areas: the employment situation (job, department, and
company), company policies and rules, compensation
and
benefits, corporate culture, team membership, employee development, dealing
with change, and socialization.
a. The Employment Situation
A basic
purpose, from the firm‘s viewpoint, is to have the new employee become
productive as quickly as possible. Therefore, specific information about
performing the job may be provided at an early point in time.
b. Company Policies and Rules
Every job
within an organization must be performed considering the guidelines and
constraints provided by policies and rules. Employees must have an
understanding of these to permit a smooth transition to the workplace.
c. Compensation and Benefits
Employees
will have a special interest in obtaining information about the reward system.
Although this information is usually provided during the recruitment and
selection process, a review of the data is appropriate during Socialization.
d. Corporate Culture
The
firm‘s culture reflects, in effect, how we do things around here. This relates
to everything from the way employees dress to the way they talk.
e. Team Membership
A new
employee‘s ability and willingness to work in teams is most likely determined
before he or she is hired. In Socialization, the importance of becoming a
valued member of the company team may be emphasized.
f. Employee Development
Employees
should know exactly what is expected of them and what is required by the firm
for advancement in the job or via promotion.
g. Dealing With Change
Employees
at all levels must learn to effectively deal with change in order to survive in
their jobs. The best way individuals can be prepared for change is to
continually develop and expand their sKills.
h. Socialization
In order
to reduce the anxiety that new employees may experience, attempts should be
made to integrate the person into the informal organization.
1 Stages in socialization Process:
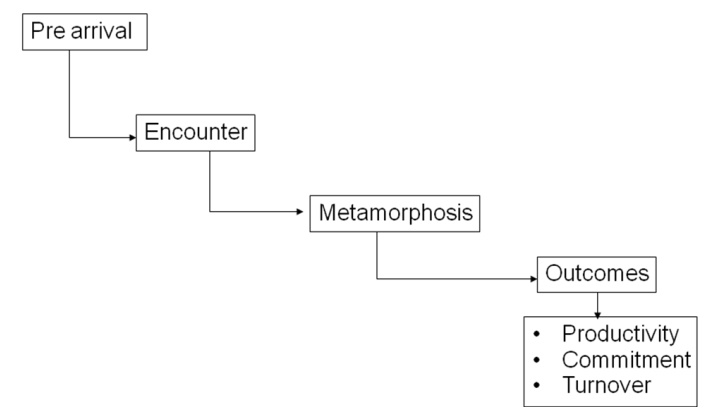
Socialization
can be conceptualized as a process made up of three stages.
a. Pre-arrival Stage:
This
stage explicitly recognizes that each individual arrives with a set of
organizational values, attitudes, and expectations. For instance, in many jobs,
particularly high skilled and managerial jobs, new members will have undergone
a considerable degree of prior socialization in training and in school.
Pre-arrival socialization, however, goes beyond the specific job. The selection
process is used in most organizations to inform perspective employees about the
organization as whole. In addition, of course, interviews in the selection
process also act to ensure the inclusion of the ―right type‖ determining those
who will fit in. Indeed, the ability of the individuals to present the
appropriate face during the selection process determines their ability to move
into the organization in the first place. Thus success depends upon the degree
to which aspiring members have correctly anticipated the expectations and
desires of those in the organization in charge of selection.
b. Encounter Stage:
Upon
entry into the organization, new members enter the encounter stage. Here the
individuals confront the possible dichotomy between their expectations about
their jobs, their coworkers, their supervisors, and the organization in general
and reality. If expectations prove to have been more or less accurate, the
encounter state merely provides a reaffirmation of the perceptions generated
earlier. However, this is often not the case. Where expectation and reality
differ; new employees must undergo socialization that will detach them from
their previous assumption and replace these with the organization‘s pivotal
standards. Socialization, however, cannot solve all the expectation
differences. At the extreme, some new members may become totally disillusioned
with the actualities of their jobs and resign. It is hoped that proper
selection would significantly reduce this latter occurrence.
c. Metamorphosis Stage:
Finally
the new member must workout any problems discovered during the encounter stage.
This may mean going through changes. Hence the last stage is termed as
metamorphosis stage. Metamorphosis is complete as is the socialization process
– when new members have become comfortable with the organization and their work
teams. In this situation they will have internalized the norms of the
organization and their coworkers; and they understand and accept these norms.
New members will feel accepted by their peers as trusted and valued
individuals. They will have gained an understanding of the organizational
system- not only their own tasks but the rules, procedures and informally
accepted practices as well. Finally they will know how they are going to be
evaluated. They will know what is expected of them and what constitutes a good
job. Consequently, successful metamorphosis should have positive effect on a
new employees productivity and the employee‘s commitment to the organization,
and should reduce the likelihood that the employee will leave the organization
any time soon.
III. Many People Socialize new
Hires
New
employee socialization or orientation covers the activities involved in
introducing a new employee to the organization and to his or her work unit. How
is responsible for the orientation of new employee? This can be done by the
supervisor, the people in HRM, Peers, CEO, or combination of any of these.
a. HRM Department: HRM department can conduct the
orientation in order to socialize the newly
hired employees with the working environment of the organization. HRM plays a
major role in new employee orientation-the role of coordination, which ensures
that the appropriate components are in place. In addition HRM also serves as a
participant in program. As job offers are made and accepted, HRM should
instruct the new employee when to report to work. However, before the employee
formally arrives, HRM must be prepared to handle some of the more routine needs
of these individuals.
b. Supervisor: Immediate supervisor of
particular department can also be the source of informing the employees about the culture, rules, procedures and policies of
the organization. Mostly in smaller organizations, orientation may mean the new
member reports to supervisor, who then assigns the new member to other employee
who will introduce the new member to other coworkers. This may be followed by a
quick tour to show the different parts and departments of the organization.
c. Peers: Peers and coworkers of the new
hires can perform the orientation function in order to tell the expectation of employers and requirements of the organization
as can also answer the queries raised from the employee side.
Organizational culture: Organizational
culture itself can express the do‘s and don‘ts of any organization. Every organization has its own unique culture. This
culture includes longstanding, and often unwritten, rules and regulation; a
special language that facilitates communication among members; shared standards
of relevance as to the critical aspects of the work that is to be done;
standards
for social etiquette, customs for how members should relate to peers,
employees, bosses and outsiders; what is appropriate and smart behavior with in
organization and what is not.
e. CEO: Prior to mid 1980s, new employee
orientation operated, if at all, with out any output from the company‘s
executive management. But that began to change, due in part to management
consultants advocating that senior management become more accessible to employees.
The CEO‘s first responsibility is to welcome new employees aboard and talk to
them about what a good job choice they made. The CEO is in position to inspire
these new employees by talking about what it is like to work for the
organization. When CEO is present in the socialization process, the company is
sending a message that it truly cares for its employees.
IV. Employee Orientation program:
Orientation
or socialization process.
a. Introduction: Regarding the organization,
supervisor, trainers, and coworkers and to system
b. Job Duties: It provides job related
information like, Job location Job tasks Job safety requirements Overview of job, Job objectives Relationship to other
jobs
c. Organizational Issues: This
provides the information about the overall organization it may include; History of employer,
organization of employer, name & titles of key executive, employee‘s titles
and departments, layout of physical facilities, probationary period, overview
of production process, company policies and rules, disciplinary regulations,
employee handbook, safety procedures etc
d. Employee Benefits: This part
provides the information about the benefits that are offered by the organization like; Pay scales &
paydays, vacations rest break, training & education benefits, counseling,
housing facilities, insurance benefits, retirement program, employee-provided
services for employees, rehabilitation program
The Hiring Process
Hiring
process is completed here because orientation or the socialization process is
the last step of hiring.
B. Training
Training
is a process whereby people acquire capabilities to aid in the achievement of
organizational goals. It involves planned learning activities designed to
improve an employee‘s performance at her/his current job. Training refers to
the methods used to give new or present employees the skills they need to
perform their jobs.
C. Development
All
efforts to provide employees with the abilities the organizations will need in
the future
D. Training and Development Trends:
·
Skill requirements will continue to increase
·
Workforce will become significantly better educated
& more diverse
·
Corporate restructuring reshapes businesses
·
Technology will revolutionize certain training
delivery methods
·
The role of training departments will change
·
More flexible courses aimed specifically at
performance improvement
·
More firms will strive to become learning
organizations
·
Emphasis on human performance management will
accelerate.
Methods of socialisation
•
Stories
•
Rituals
•
Material symbols
•
Language
Socialisation benefits
•
Helps in understanding organisation culture
•
Contributes to employee‘s long term success
•
Helps in adjustment
•
Helps in employee engagement
•
Provides job satisfaction.