Chapter: Web Technology : Host Objects
Servlet Life Cycle
SERVLET LIFE CYCLE
The life cycle of a servlet is controlled by the
container in which the servlet has been deployed. When a request is mapped to a
servlet,
1. If an
instance of the servlet does not exist, the Web container
a. Loads the
servlet class.
b. Creates
an instance of the servlet class.
c. Initializes
the servlet instance by calling the init method. Initialization is covered in
Initializing a Servlet.
2. Invokes
the service method, passing a request and response object. Service methods are
discussed in the section Writing Service Methods.
If the container needs to remove the servlet, it
finalizes the servlet by calling the servlet's destroy method. Finalization is
discussed in Finalizing a Servlet.
Handling Servlet Life-Cycle
Events
You can monitor and react to events in a servlet's
life cycle by defining listener objects whose methods get invoked when life
cycle events occur. To use these listener objects, you must define the listener
class and specify the listener class.
Defining The Listener Class
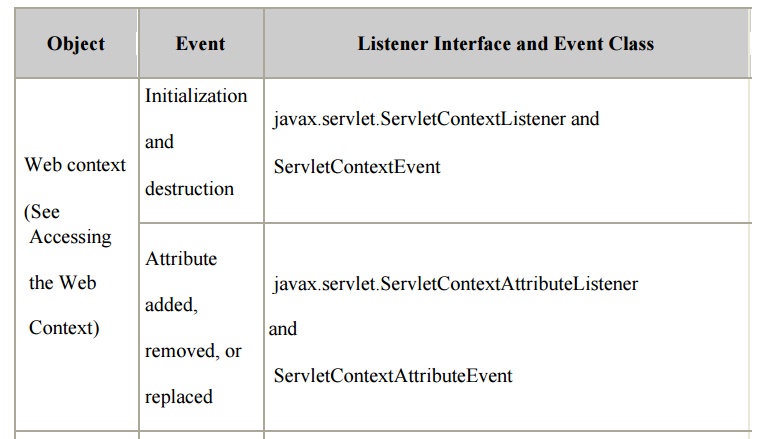
You
define a listener class as an implementation of a listener interface. Table
10-3 lists the events that can be monitored and the corresponding interface
that must be implemented. When a listener method is invoked, it is passed an
event that contains information appropriate to the event. For example, the
methods in the HttpSessionListener interface are passed an HttpSessionEvent,
which contains an HttpSession.

Related Topics