Plants | Term 2 Chapter 3 | 5th Science - Questions with Answers | 5th Science : Term 2 Unit 3 : Plants
Chapter: 5th Science : Term 2 Unit 3 : Plants
Questions with Answers
Plants ( Term 2 Chapter 3 | 5th Science )
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer.
1.
Male reproductive organ of the flower is
a) sepal
b) petal
c) androceium
d) gynoceium
Answer: c) androceium
2.
Pollination by wind is also known as
a) anemophily
b) hydrophily
c) entamophily
d) ornithophily
Answer: a) anemophily
3.
Dispersal of seed by water is known as
a) anemochory
b) hydrochory
c) zoochory
d) autochory
Answer: b) hydrochory
4.
Entamophily is known as
a) pollination by insects
b) pollination by wind
c) pollination by water
d) pollination by animal
Answer: a) pollination by insects
5.
Pollination takes place by wind in
a) grass
b) vallisneria
c) hydrilla
d) lotus
Answer: a) grass
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. Spreading of seeds from one place to
another is known as dispersal of seeds.
2. Autochory is known as Sell dispersal
method.
3. The seed is a fertilized ovule.
4. Paddy grow well in clay
soil.
5. The soil which contains bigger sized
particle is sand.
III. Match the following.
1. Earthworm - Destroys the egg and
larva of mosquitoes
2. Birds - Honey
3. Coconut - Ornithophily
4. Bee - Dispersal by water
5. Dragonfly - Vermi-compost
Answer:
1. Earthworm - Vermi-compost
2. Birds - Omithophily
3. Coconut - Dispersal by water
4. Bee - Honey
5. Dragonfly - Destroys the egg and larva of mosquitoes
IV. Answer briefly.
1.
Define pollination.
The transfer of pollengrains from
the anther to stigma of a flower is called pollination.
2.
What is germination of seed?
Under favourable conditions like
sunlight, water and soil, the embryo grows up into a new plant. This is called
germination.
3.
How soil is formed?
Soil is formed by the breaking of
rocks by the action of wind, water and climate.
4.
What is known as vermi-compost?
The process of decomposing
bio-degradable wastes by earthworms is known as vermi-compost.
5.
How the seeds are spread by water?
Fruits which are dispersed by water
have outer coats modified to enable them to float. The mesocarp (middle layer)
of coconut is fibrous and is easily carried away by water. They reach different
places and grow into a new plant. Eg : Lotus, Coconut.
V. Answer in detail.
1.
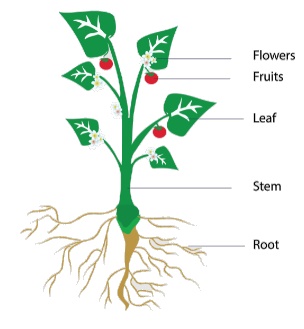
Write a note on parts of plants.
A plant has two important parts. The
part above the soil is called shoot system. The part below the soil is called
root system. The shoot system has stem, branches, leaves and flowers. The root
system has root and branches of root. Some plants have a main root and this is
called tap root. Some plants have bunches of roots called fibrous root.
2.
Explain the methods of pollination.
The transfer of pollengrains from
the anther of a flower to the stigma of the same flower is called self pollination.
The transfer of pollengrains of a flower to the stigma of another flower of a
different plant of the same species is called cross pollination.

In self pollination, seeds produce
weak plants and new varieties of plants cannot be produced. In cross
pollination, seeds produce good plants and new varieties of plants can be
produced. Pollination takes place through different agents. They are explained
below.
Pollination by Wind (Anemophily): The flowers pollinated by wind are mostly small in size and do
not have any attractive colour, smell and nectar.
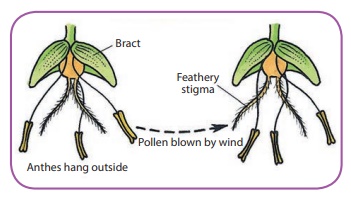
The pollen grains are non-sticky,
dry, light and powdery. Hence, they are easily carried by the wind. Eg: Maize,
Pine.
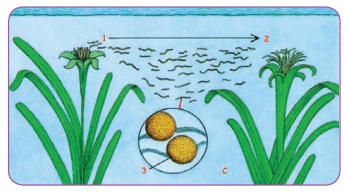
Pollination by Water (Hydrophily): The flowers of water plants are not colourful and they have no
nectar. Pollengrains of these plants have mucilaginous covering to protect them
from getting wet. They float in water and reach the other plant. Eg: Vallisneria,
Hydrilla, Zosteria.
Pollination by Insects (Entamophily): This is the most common type of pollination in plants like
sunflower, ladies finger, brinjal and pumpkin. Some flowers are large in size
and they have sweet smell. Some of these flowers produce nectar. They attract
insects like butterflies and honey bees.

3.
Draw the picture of a flower and label the parts.
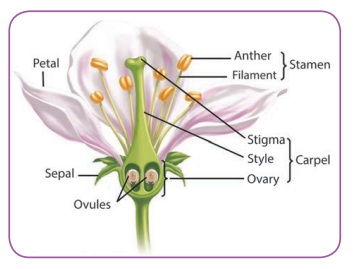
Activity 1
Take a hibiscus flower or a rose flower. Display the parts like sepal, petal, gynoecium and androecium in a chart paper and note down its colour and shape.
Activity 2
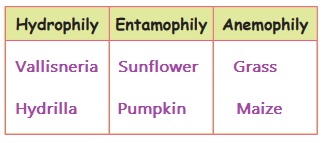
Classify the plants based on the pollination methods.
Vallisneria, Hydrilla, Sunflower, Grass, Brinjal, Maize, Pumpkin.
Activity 3
Collect seeds of different plants from your area. Find out whether they are monocotyledons or dicotyledons.
Activity 4
Collect variety of seeds with hair, wings, hooks and spines. Keep them in a card board box separately. Name them and collect information on how they are dispersed.
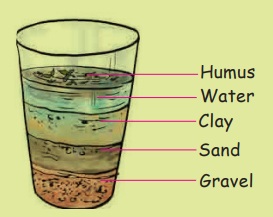
Activity 5
Take a little amount of soil and powder it. Put this soil in a glass tumbler. Mix it with water; stir it well with a small stick to dissolve the soil. Let it undisturbed for some time. Now you can see different layers of soil. The rotting matter floating on the water is called humus. The other layers are clay, sand and gravel. From this we can see that the soil is a mixture of various particles.
Activity 6
Visit a nursery garden near your area and observe how the varieties of saplings are growing there. Prepare a report about it.
Related Topics