Chapter: Software Architectures : Quality Attribute Workshop
Quality Attribute Workshop
Definition
Quality attribute workshops (QAWs) provide a method for analyzing a
system’s architecture against a number of critical quality attributes, such as
availability, performance, security, interoperability, and modifiability, that
are derived from mission or business goals. The QAW does not assume the
existence of a software architecture. It was developed to complement the
Architecture Tradeoff Analysis MethodSM (ATAMSM) in
response to customer requests for a method to identify important quality
attributes and clarify system requirements before
there is a software architecture to which the ATAM could be applied
Introduction
In
software-intensive systems, the achievement of qualities—such as performance,
availability, security, and modifiability—is dependent on the software
architecture. In addition, quality attributes of large systems can be highly
limited by a system’s requirements and constraints.
Thus, it
is in our best interest to try to determine as early as possible whether the
system will have the desired qualities. Quality requirements should be
described concretely before an architecture is developed. We distinguish system
architecture from software architecture according to the following two
definitions:
·
system architecture: the fundamental and unifying system structure
defined in terms of system elements, interfaces, processes, constraints, and
behaviors [INCOSE 96]
·
software architecture: the structure or structures of the system, which
comprise software elements, the externally visible properties of those elements
and the relationships among them [Bass 03]
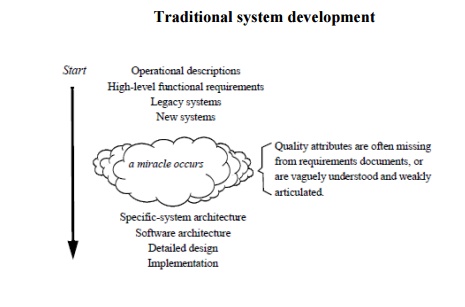
Development of software-intensive systems begins with a description of the system’s operation and high-level functional requirements, and any constraints on the system, such as legacy or new systems. From these items, the architect derives a system architecture and a software architecture that can then be used to drive detailed design and implementation. (See Figure 1.) The process of creating those architectures is often unstructured.1 Quality attributes could be missing from the requirements document, and even if addressed adequately, they are often vaguely understood and weakly articulated.
The Quality Attribute Workshop (QAW) is a facilitated method that engages system stakeholders early in the system development life cycle to discover the driving quality attributes of a software-intensive system. The QAW is system-centric and stakeholder focused; it is used before the software architecture has been created. The QAW provides an opportunity to gather stakeholders together to provide input about their needs and expectations with respect to key quality attributes that are of particular concern to them.
Both the system and software architectures are key to realizing quality
attribute requirements in the implementation. Although an architecture cannot
guarantee that an implementation will meet its quality attribute goals, the
wrong architecture will surely spell disaster. As an example, consider
security. It is difficult, maybe even impossible, to add effective security to
a system as an afterthought. Components as well as communication mechanisms and
paths must be designed or selected early in the life cycle to satisfy security
requirements. The critical quality attributes must be well understood and
articulated early in the development of a system, so the architect can design
an architecture that will satisfy them. The QAW is one way to discover,
document, and prioritize a system’s quality attributes early in its life cycle.
Related Topics