Term 1 Unit 2 | Civics | 7th Social Science - Political Parties | 7th Social Science : Civics : Term 1 Unit 2 : Political Parties
Chapter: 7th Social Science : Civics : Term 1 Unit 2 : Political Parties
Political Parties
Unit –II
Political Parties

Learning
Objectives
• To define what political party is and
to understand the importance of the political party
• To know the role and function of a
political party
• To understand the party system in
India and the role of opposition party
Student
Siva : Good morning Mam. May
I come in?
Teacher
Ms.Aadhi: Good morning Siva.
Always you will be on time. Why are you so late today?
Siva: Sorry mam. I was delayed due to a
procession.
Ms.
Aadhi: What is it about? Who
arranged this procession?
Siva
: My uncle said “That is the work of the
political party”.
Ms.
Aadhi: Oh. I see!
Siva
: What is political party mam? Why are
they doing so?
Ms.
Aadhi: Wait. Today I am going
to teach about political parties. Let us know all about that.
In
earlier times, emperors and kings ruled India. The king was the supreme head of
the Legislative, Executive and Judiciary branches. Governance was in the hands
of one person. The welfare of the people depended on the ruler. People had no
rights to do against the ruler. Later foreign powers made India as their
colonies. The colonies became states after Independence was declared.
In
1950 India became a democratic country. A vibrant democracy needs a strong
political party system. Party System is a modern phenomenon. In a democracy
people are able to voice their opinions on any subject.
What are Political Parties?
Political parties are the voluntary
associations of individuals with broad ideological identity who agree on some
policies, formulate an agenda and programme for the society. Political parties
seek to implement their policies by winning people’s support through election.
Parties vary in size and in the ways they organize themselves as well as in
their policies.
Any political party has three basic
components
• the leader
• the active members
• the followers
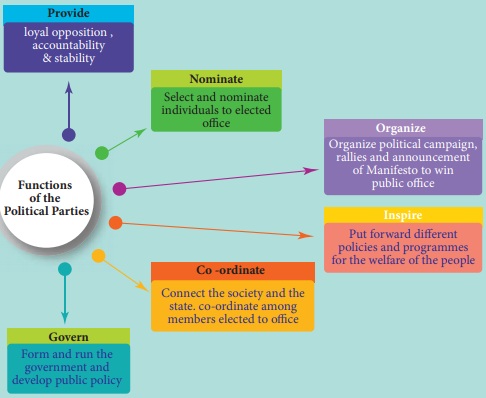
Importance of political parties
Political parties are the backbone of
democracy. Parties are not part of the formal arrangement of a government but
they are essential elements to form the government. They formulate public
opinion. They serve as intermediaries between the citizen and the policy
makers.
A party is recognized if
• it has been engaged in political activity
for five years.
• its candidates secure at least six percent
of total votes in the last general election.
Characteristics of Political Parties
Political parties
• consist a group of persons of common goals
and shared values.
• have its own ideology and programme.
• capture power only by constitutional means.
• endeavour to promote the national interest
and national welfare.
Party ‘manifesto’
During the campaign
before election, the candidates announce the programmes and policies that their
party will undertake if voted to power.
Types of Party System
There
are three major types of party system. Single Party System: a system in
which a single political party has the right to form the government.
Single party is existed in the communist countries such as China. North Korea
and Cuba.
Bi
– Party System: In Bi –Party system the power is
usually shared between two parties. Of the two parties one becomes the ruling
party and the other becomes opposition. eg Bi-Party system can be seen in U.K.
(the Labour Party and the Conservative Party) and in U.S.A (the Republican
Party and the Democratic Party)
Multi
– Party System
When
the competition for power is among three or more parties, the system is known
as multi party system. This type of party system is in existence in India,
France, Sweden and Norway etc.
Party system in India
Countries
that follow a federal system have two kinds of parties. India’s party system
originated in the late 19th century. In fact India has the largest number of
political parties in the world. In India we find the existence of political
parties at three levels. They are National parties, Regional parties, and Registered
but unrecognised parties (independent candidates). Every party in the country
has to register with Election Commission.

Election Commission – Statutory body The Election
Commission of India is an autonomous, constitutional authority responsible for
administering elections. Its head quarter is located in New Delhi.

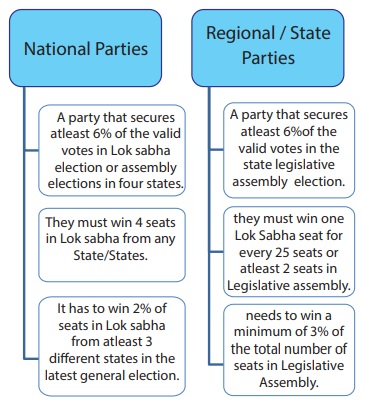
Criteria for Recognition
The
Election Commission of India has some criteria for the recognition of political
parties in India.
Recognized
parties
Parties
that fulfill these criteria are called recognized parties. They are given a
unique symbol by the Election Commission.
A
registered but unrecognized political party cannot contest election on its own
symbol. This party has to choose one symbol form free symbol 'poll panel'
announced by the Election Commission.
Free symbols ‘Poll panel’
As per the Election
Symbols order 1968, symbols are either reserved or free.
• A reserved symbol is
meant for a recognized political party.
• A free symbol is
reserved for unrecognized party.
Majority Party
The
Political Party whose number of candidates elected is more than the others is
called the majority party. The Majority Party forms and runs the government.
They select and appoint their ministers to run the government. They play a
decisive role in making laws for the country.
Minority Party
Those
with lesser number of elected candidates are called the minority party.
Opposition Party
The
party which gets second largest number of seats next to the majority party in
the election is called the Opposition party. An effective opposition is very
essential for the successful operation of the democracy. They are as important
as that of ruling party. They check the autocratic tendencies of the ruling
party. They critically examine the policies and bills introduced by the
government. They raise their voice on the failures and wrong policies. They
highlight important issues which are not acted upon the Government. The leader
of the opposition party enjoys the rank of Cabinet Minister.
Coalition Government
In
a Multiparty system a single party sometimes may not secure the majority
required to form the government. In such a case, some parties join together to form
the government. Such government is called Coalition Government.
Electoral Symbols and its
importance
An
electoral symbol is a standardised symbol allocated to a political party. They
play an important role in elections. They can be easily identified, understood,
remembered and recognized by the voters. The Election commission has stopped
allotting animals as symbols. The only exceptions are the lion and the
elephant. The symbol of nationally recognized parties is standard throughout
India. That symbol will not be allotted to any other party or individual.
State
parties are allotted to certain symbols that no other party can use the symbol
in that particular state but which different parties in different states can
use the same symbol. (e.g Shiv Sena in Maharashtra and Jharkhand Mukti Morsha
in Jharkhand use bow and arrow as their symbol).
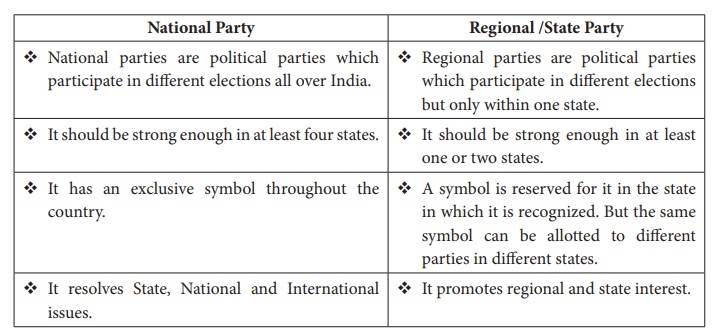
National
Party
•
National parties are political parties which
participate in different elections all over India.
•
It should be strong enough in at least four states.
•
It has an exclusive symbol throughout the country.
•
It resolves State, National and International issues.
Regional
/State Party
•
Regional parties are political parties which participate in different elections
but only within one state.
•
It should be strong enough in at least one or two states.
•
A symbol is reserved for it in the state in which it is recognized. But the
same symbol can be allotted to different parties in different states.
•
It promotes regional and state interest.
Both
National and Regional parties trigger the growth of the nation and work for the
welfare of the people.
Summary
• Modern age is an age of mass society and of
large population and party system is a modern phenomenon.
• A group of people with broad common interest
who organize to win elections, control government and thereby influence
government policies.
• There are three major types of party system
(i.e.) single party system, Bi - party system, and Multi - party system.
• In India we have Multi – party system.
• Individual citizen who are not members of a
party may also be elected. They are known as Independents.
• Election Commission is responsible for free
and fair elections in India.
Glossary
1.
Democracy: Government by the people
ஜனநாயகம்
2.
Election manifesto: a public
declaration of policies and aims by political parties தேர்தல் அறிக்கை
3.
Opposition party: a party
opposing to the other parties எதிர்க்கட்சி
4.
Federal system: system of
government in which several states form a unity but remain independent in
internal affairs கூட்டாட்சி
அமைப்பு
5.
Election commission: a body for
implementation of election procedures தேர்தல் ஆணையம்
6.
Electoral symbols: symbols
allocated to a political party தேர்தல்
சின்னங்கள்
7. Cabinet Minister: member of a parliament or legislative assembly cabinet அமைச்சர்
ICT CORNER
ELECTION COMMISSION OF INDIA
This activity enables the
students to know about the Election Commission of India

PROCEDURE :
Step
1: Open the Browser and Install the URL
link given below
Step
2: Select “Election India” (Eg: Parties)
to get a brief information about “National Parties”
Step
3: Click the Menu button and select any
title (E.g Leaders) to view about the leaders profile
Step
4: Touch the menu button and select “Dash
board” to know about the status Of upcoming elections and National parties
URL:
https://play.google.com/store/search?q=election
(or) scan the QR Code
*Pictures
are indicative only
*If browser
requires, allow Flash Player or Java Script to load the page.
Related Topics