Term 2 Chapter 3 | 3rd Science - Plants | 3rd Science : Term 2 Unit 3 : Plants
Chapter: 3rd Science : Term 2 Unit 3 : Plants
Plants
Unit 3
Plants

Learning Objectives
After learning this lesson, students will be able to
*
identify the parts of a plant
*
understand the functions of different parts of a plant
* classify plants based on their habitat
Warm-up
Unscramble the words and label the parts of the plant.
( ETSM, TORO, ELFA, FURTI, LOFEWR , SDEE )
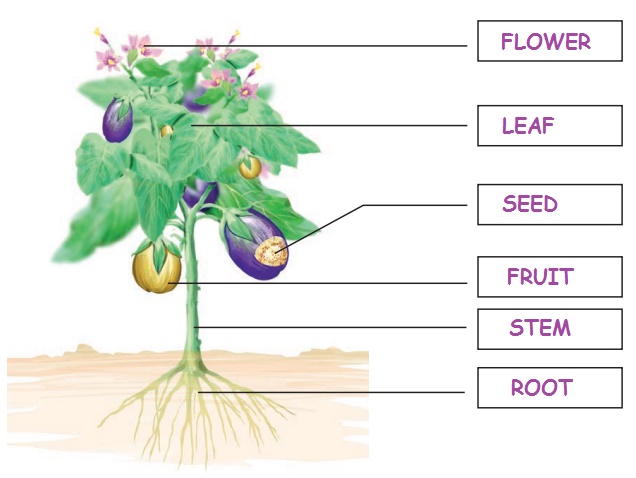
I. Plants
are nature‛s gift
A plant has many parts. Each part has a set of function to do.
The basic parts of a plant are root, stem, leaf, flower, fruit
and seed.
Let us learn about various parts of the plant, their structure
and function.
Root
The root is a part of the plant that usually grows under the
soil. Roots can be of different shapes and sizes. It grows away from sunlight
into the soil. They are of two main types: tap root and fibrous root.
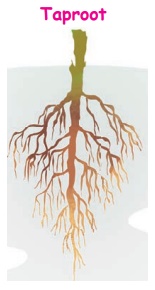
Taproot
Taproot has one main, thick root. It grows from the radicle and
goes deep into the soil. Many small thin roots grow out from the main root.
Plants such as carrot, beetroot, turnip, mango and neem have taproots.
Fibrous Root
A fibrous root consists of many thin roots of different sizes.
They grow from the base of the stem and all of them are bunched together. They
do not go deep into the soil. Plants such as grass, paddy, wheat and onion have
fibrous roots.

Functions of Root
Fixation: Root fixes the plant firmly to the soil. Without the roots, a plant
would fall on the ground.
Absorption: Roots absorb water and minerals required for the plant from the
soil.
Storage of food: In some plants, roots store food. E.g., Carrot, Radish, Beetroot.
Difference between
taproot and fibrous root
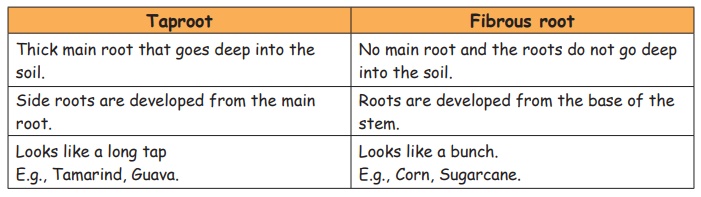
Taproot
Thick main root that goes deep into the soil.
Side roots are developed from the main root.
Looks like a long tap E.g., Tamarind, Guava.
Fibrous root
No main root and the roots do not go deep into the soil.
Roots are developed from the base of the stem.
Looks like a bunch. E.g., Corn, Sugarcane.
Do you know
Avecinnia plants have roots above the ground.

Let us Do
Take two small potted plants. Cut the root of one of the plants
and fix it in the pot. Now water the plants for two to three days. You will
observe that the plant without roots will wilt and die. In the absence of
roots, plants die.
This acivity proves that the function of the roots is to absorb Water and Minerals from the soil.
Let us Do
Take two coconut shells. Fill them with soil. Sow green gram in
one and paddy in another. Keep them under sunlight and water them. After a week observe the features of roots.
Let us Write
True or false

1. The roots grow into the soil. (True)
2.
Fibrous root has a main root. (False)
3.
Root absorbs water from soil. (True)
4.
Potato stores food in its root. (False)
5. Grass has fibrous roots. (True)
Stem
The stem is the main part of the shoot system. It grows towards
the sunlight. It looks green when it is young. Branches, leaves, buds, flowers
and fruits grow from the stem.

Herbs such as coriander and mint have a
thin and weak
stem. Trees such as peepal and banyan have very strong and thick stem called trunk. As trees grow older, their trunks grow wider.
Functions of the Stem
* It supports the whole plant.
* It transports food from leaf and
water from root to various parts of the plant.
* Some stems store excess food in them. E.g., Potato, Onion.

Leaves
Leaves originate from the surface of
the stem. It is flat, thin and green. Leaves of different plants have different shapes, sizes and
colours. Some leaves have even a specific smell.
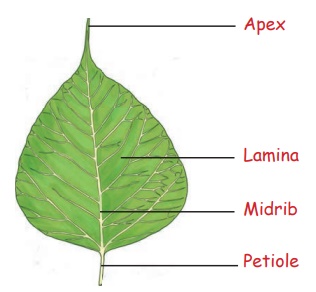
Functions
of Leaf
* Leaf prepares food for the
plant with the help of water, carbon dioxide and in the presence of sunlight
and chlorophyll. This process is called photo
synthesis. Hence, it is called the food factory of the plant.
* The
loss of water in the form of gas (water vapour) happens through the tiny pores
in the leaves. This process is called transpiration.
It gives cooling effect to the plant.
* Leaves of some plants are edible and rich in nutrients. E.g., Greens, Cabbage.
Let us Play
Collect the leaves of coriander, mint, eucalyptus, tamarind,
amla, neem and tulsi.
Select two students and cover their eyes with a handkerchief.
Give one leaf to each of them. and ask them to identify the leaf by touching or
and the other by smelling it. Find out who identifies more leaves.

Which method is easier to identify?
Touching or smelling?
Answer : smelling
Let us Do
Collect the leaves of different kinds of plants.
1. Arrange the leaves from small to big.
2. Group the leaves based on its colour.
Let us Write
Fill in the blanks.
1.
Stem grows towards the sunlight.
2. Leaves originate from the Stem.
3. Green part of the plant that makes food is called Leaf.
4.
Stem gives support to the whole plant.
5. Water from soil is absorbed by the root of the plant.
Flowers
Flowers are the most beautiful part of the plant. They are of different
shapes, size, colours and fragrance. A flower develops from the bud. The soft and brightly colored part of a flower is called petal. The green part that lies under the petal and supports it is
called sepal. The middle of the flower
has two parts called the stamen and pistil.
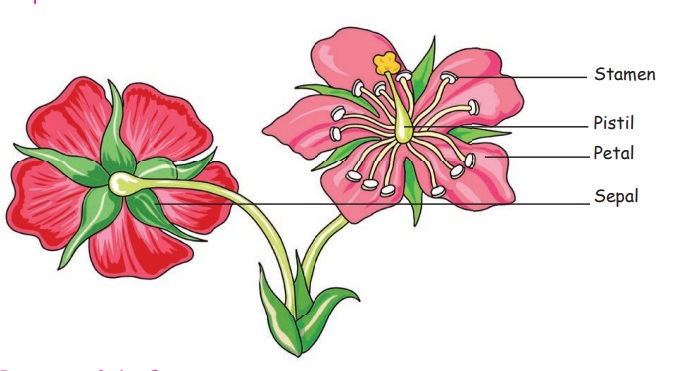
Functions of the flower
* It develops into fruit.
* It helps plant to reproduce.
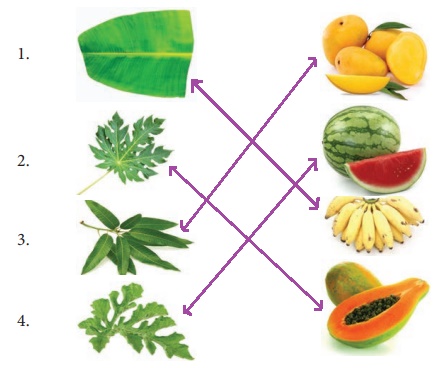
Fruits and Seeds
Fruit is the fleshy part of the plant. The fruits are developed
from the flowers. Most fruits
have seeds.
* Some fruits have only one
seed. E.g., Apricot, Mango, Coconut and Peach.
* Some fruits have many
seeds. E.g., Papaya, Watermelon and Orange.
* Some are seedless. E.g., Pineapple and Banana.

New plants are grown from seeds.
Think and Write
1.
List out the fruits that do not have seeds. Banana,
pineapple.
2.
Write down the names of the fruit trees that you have never seen, but have tasted
their fruits. apple, strawberry.
Let us Do
Connect the leaf with
its fruit.
IV. Plants and their habitat
Plants grow almost everywhere on Earth i.e. on land (terrestrial plants) and
in water (aquatic plants). The
plants adapt to their surroundings and hence have special characteristics based
on their habitat.
The natural home of a plant is called its habitat. Plants make suitable
adjustment with their surroundings to meet their requirements. This is known as
adaptation.
Terrestrial or Land Plants
The plants that grow on the land are of different habitats such as deserts, plains,mountains and forests. Let us learn about the adaptation of different land plants.
Plants in Desert
These plants grow in hot, dry
and sandy places. Deserts get very less rainfall and experience high
temperature. Hence, there is scarcity of water. Let us see how these plants
have adapted to this habitat.
* Leaves are changed to
spines to
reduce the loss of water.
* The stem is green and fleshy. They store water and produce
food.
* These plants have a long root that goes deep into the soil.
E .g., Opuntia, Date Palm and Aloe vera.

Plants on Mountain
These plants grow in cold and
freezing places. There is a cool weather in
mountain. Let us see how these plants have adapted to this habitat.
* These trees are conical
in shape. This shape allows snow to slide from
the trees easily.
* Needle like leaves help them to survive in cold conditions
like snow.
* These trees do not shed leaves.
* They have cones instead of flowers. These cones protect the
seeds during harsh winter. E.g., Pine tree.

Plants in Plains
* Plants in plains need
to adapt to both dry conditions and extreme temperatures.
* They grow in warmer climate and usually shed their leaves in winter to protect themselves
from cold.
* They have flat and broad leaves.
* They have thick and woody stem. E.g., Mango, Banyan, Teak.
Do you know
Banyan, Peepal and Tamarind trees live more than hundred years.
Plants in Coastal Areas
* They are tall and mostly straight.
* The leaves are called frond.
* The frond look like feathers meant for protection from wind.
* These plants tolerant to saline (salt) water. E.g., Coconut tree.

Let us Connect
Match the plants with their living places.
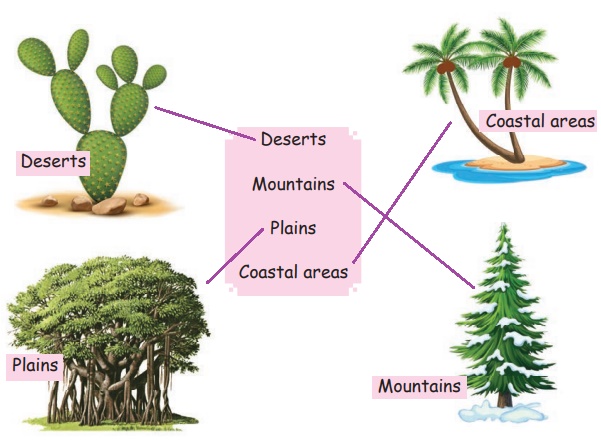
Let us Try
A. Select the ‘INCORRECT‛ statement from the following.
1.
Desert plants grow in hot, dry and sandy places.
2.
Plants in coastal areas tolerant to saline water.
3.
Mountain plants have needle like leaves.
4. Teak is an example of desert plant. (Incorrect)
B. Tick (√) the odd
one.
1. Teak Tamarind Mango Opuntia✔
2. Opuntia Aloe vera Pine✔ Date palm
C. Circle the places
which are land habitats.
Forest
Pond Mountain River
Tree Ocean Desert Cave
V. Plants in Water
The
plants that grow in water bodies like ponds and lakes are called water
plants or aquatic plants. They
are classified into following types.
1.
Free floating plants
2.
Fixed rooted plants
3.
Submerged plants
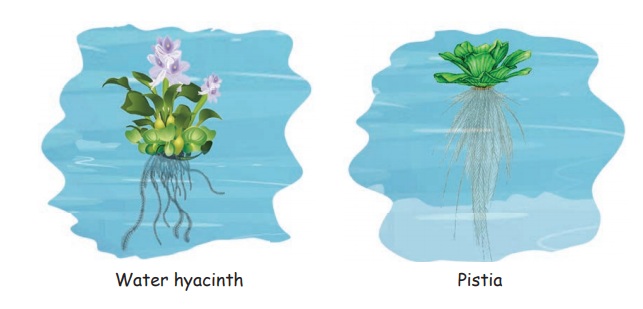
1. Free Floating Plants
* These are found on the surface of the water.
* They freely float with the help of spongy body filled with air.
* They have poorly developed roots.
E.g., Water hyacinth (Agaya thamarai), Pistia.
2. Fixed
Rooted Plants
* These plants have root that are fixed in the bottom of
the water bodies.
* These plants have air tubes
in their stem to help them float.
* Their leaves are broad and coated with wax to make them water proof.
E.g., Water lily, Lotus.

3. Submerged
Plants
*
These plants are completely submerged in the
water.
* Their stem is thin and leaves are very small.
* There is no opening on the leaf surface.
* They breathe through stem. E.g., Vallisneria,
Hydrilla.

Let us Try
A.
Mark ‘L” for land plants and ‘W‛ for water plants.
B. Colour the Water hyacinth plant.

C. Write true or false.
1.
Fixed rooted plants are present in water bodies. (False)
2.
Leaves of lotus are submerged in the water.( False)
3.
Lotus plants are found in many ponds. (True)
4. Water hyacinth freely float with the help of spongy body filled
with air. (True)
Related Topics