Term 3 Chapter 1 | 3rd Science - Our Environment | 3rd Science : Term 3 Unit 1 : Our Environment
Chapter: 3rd Science : Term 3 Unit 1 : Our Environment
Our Environment
Unit 1
Our Environment

Learning
Objectives
At
the end of the lesson the students will be able to
* differentiate biotic and abiotic
factors
* understand the interaction
between biotic and abiotic factors
* understand balanced ecosystem
*
understand the importance of planting trees
I. Environment
– Introduction
(Yazhini and her friends are going to school with her father)
Yazhini : Hey! Look at the
parrots! Where are they going, daddy?
Father : They are flying towards the pond. Now, they will settle on the
trees.
Fathima : Uncle! Uncle! Can you please take us there?
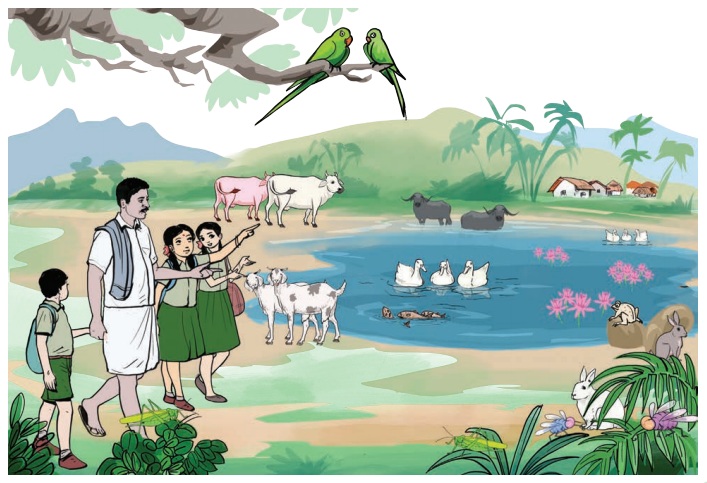

Stephen : Yes uncle. Shall we go and have a look at them?
Father : Oh! Yes!
(They are walking towards the pond)
Yazhini : We should be quiet while walking as, there are not only
parrots on the trees but also ant, spider, squirrel, myna and monkey.

Fathima : Oh! Oh! Look at the fish and frog in the pond. I can see a
turtle too.
Father : Yes! See how they live in the same place depending on one
another.
Stephen : See there, goat and cow are grazing near the pond.
Father : Children, we are getting late. We shall go to school.
Children : Yes uncle. Thank you very much for showing us this beautiful place.
Let Us Try
1. Write the names of
the animals that you
see in the previous page picture.
Cow Buffalo Goat
Rabit Monkey Turtle
2. Classify the following into natural things and man-made things.
(Dam, river, coconut tree, building, jasmine flower, hill,
cloud, silver vessel, cell phone, temple, cake, air, sun, ship, water, pencil,
book, doll, football, sunflower, crocodile, aeroplane)
Natural things: River, hill, cloud, air, sun, water, coconut tree, jasmine flower, sun flower, crocodile
Man-made things: Dam, building, silver vessel, cell phone, temple, cake, ship, pencil, book, doll, foot ball, aeroplane
Let Us Enjoy
Shall we mimic like the animals?
Crow, Cuckoo, Elephant, Parrot, Donkey, Cow, Goat, Dog
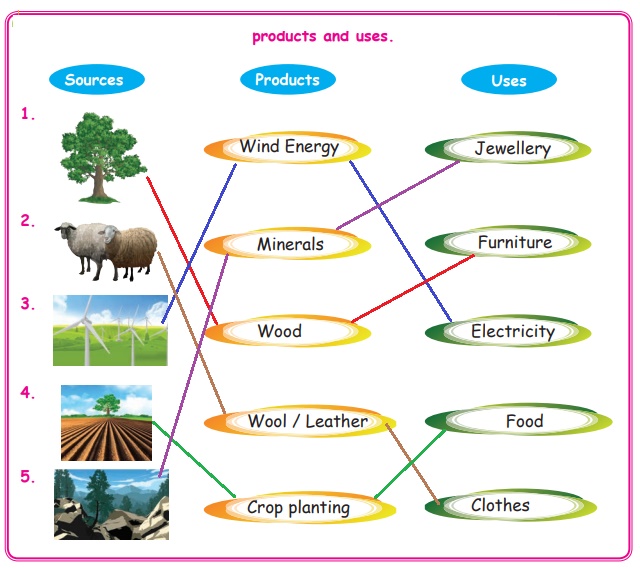
Let Us Connect
Match the following
sources with their
products and uses.
II. Environmental Factors
Our environment consists of everything around us. It has living
and non-living things. We are surrounded by living things such as
plants and animals and non-living things such as
water bodies, sunlight, air and land.
The living and non-living things in our environment interact
with one another. Our environment is a wonderful gift to us
given by the nature.
More to know
Environmentalist - A person who protects the environment.
As an environmentalist, you can volunteer to protect plants and
animals.

Our environment has two main factors:
(i) Biotic factors
(ii) Abiotic factors
Biotic Factors
Living organisms in our environment are called biotic factors. E.g., Lion, Plantain, Dove, Human beings etc.

Abiotic Factors
Non-living things in our environment are called abiotic factors.
E.g., Air, Soil, Water, Sunlight, Temperature etc.

Difference between biotic and abiotic factors
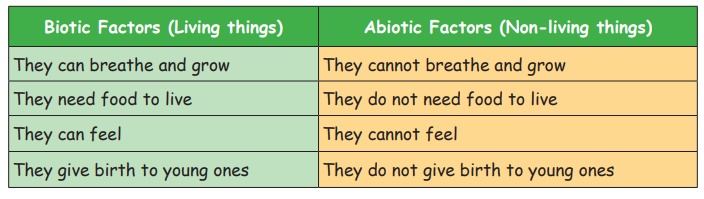
Biotic Factors (Living things)
They can breathe and grow
They need food to live
They can feel
They give birth to young ones
Abiotic Factors (Non-living things)
They cannot breathe and grow
They do not need food to live
They cannot feel
They do not give birth to young ones
Do you know
Plants cannot move around like animals. But they grow and their
shoots show movements towards the sun. So, the plants are also
biotic factor.
More to know
Amoeba is an unicellular organism. It has the ability to alter its
shape. It was discovered in 1755.
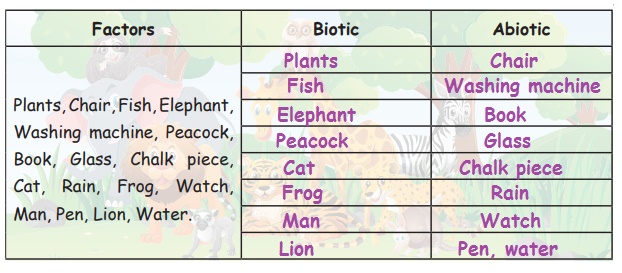
Let Us Try
1. Classify the following as Biotic / Abiotic factors.
2. Think and Answer
a. A swing goes to and fro. Is it living or non-living?
Answer: non-living
b. We get wood from trees which are the living things. A chair
is made from wood. Is the chair a living
thing or a non-living thing?
Answer: non-living thing

Try to Answer
Look at the picture and answer the question.
Which of the
non-living things can float?
a. Iron rod
b. Stone
c. Air filled
ball
d. Coin
Answer: c. Air filled ball

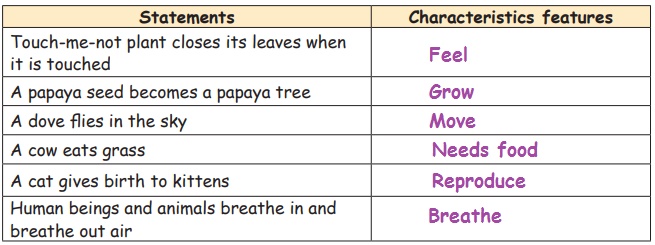
Let Us Try
The following statements describe some of the characteristics of
living things. Identify and write the
characteristic features using the given hints.
(Characteristics
Hints: Move, Breathe, Feel, Needs Food, Grow,
Reproduce)
Let Us Play
Divide the class into two groups and
ask the first group to write
any five biotic factors and the second
group to write any five abiotic factors seen around the school.
III.
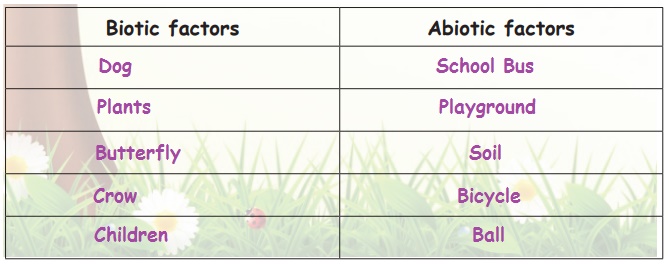
Interaction between biotic and abiotic factors
All biotic factors depend upon abiotic factors for their living.
Biotic and abiotic factors are linked to each other by the flow of energy through food. Plants are the most important among all the living organisms.
Because they only can make food from abiotic factors like air, soil, water and
sunlight.
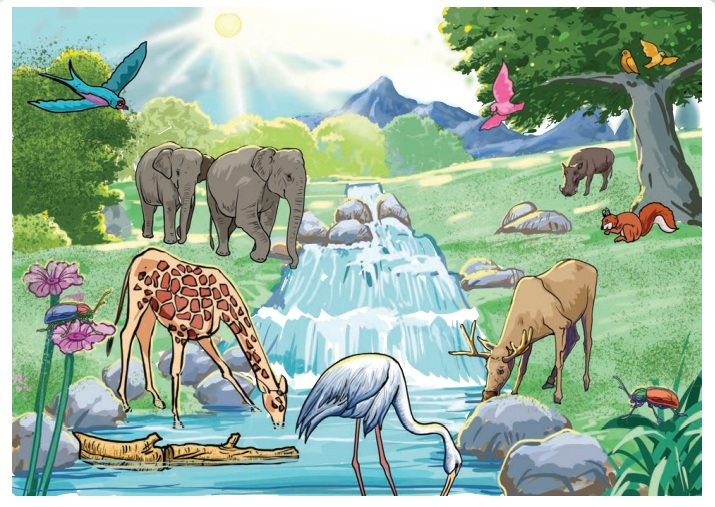
A few examples for interaction between biotic and abiotic
factors are given below.
From the above picture we understand that plants need water,
soil, air and sunlight to live.
Write the needs of the following.
1. Birds : Air, Water, Sunlight, Insects, Trees
2. Insects : Soil, Air, Plants, Small creatures
3. Human beings: Air, Water, Plants, Sunlight, Animals.
More to know
Ecology is the science that deals with the relationship between living
things and their environment.
Let Us Discuss
1. There is a large banyan tree in a park. Monkeys and birds
have made the tree their home. Humans too spend time under the tree. Discuss
with your friends, how the tree, monkeys, birds and humans are interdependent.
Birds and monkeys feed on the fruit. Birds build their nests in
the tree. The tree gives shade to human beings when the day is hot. The wood of
the tree is useful to human beings. The droppings of the birds are a manure to
the tree. Birds play a vital role in dispersal of seeds. Thus the tree,
monkeys, birds and human beings are interdependent.
2. Why is plant the
most important living thing?
Because they make food from abiotic factors.
3. Discuss in a group
and create an interlink of living and non-living factors.
Biotic and abiotic factors are linked to each other by the flow
of energy through food.
Let Us Try
1. Write the abiotic factors needed for the following biotic
factors to survive.
(Air, Water, Sunlight, Soil, Land, Wheat, Fruits, Grass, Hen)
a. Animals: Air, Water, Sunlight, Land, Grass
b. Plants: Air, Water, Sunlight, Soil
c. Human beings: Air, Water, Sunlight, Land, Wheat, Fruits, Hen
2. An animal that
a. flies in the air is: aerial
b. lives in water is: aquatic animals
c. moves on the ground is: Terrestrial animals
d. eats only plants is: Herbivores
IV. Balanced Ecosystem
Imagine an environment where there are only plants, deer and
lions.
* What will happen to the deer if we remove all the lions?
* What will happen to the plants if there are no lions to eat
the deer?
* If all the plants are eaten, what will happen to the deer?
It is important for the food chain to exist in any ecosystem to
make sure that the energy flows between the biotic and abiotic factors. A
balanced ecosystem supports animals, plants and microorganisms to grow in their
environment. An ecosystem is balanced, when the biotic and abiotic factors
are able to cycle the energy and food as per their need.
The biotic factors in an ecosystem includes producers, consumers
and decomposers.
1. Producers
The living things that can prepare their own food are called
producers. Green plants are the producers. They make their own food by the process of photosynthesis. Hence, they are called primary producers. Humans
and animals depend on plants for their food.

More to know
A few plants do not produce their food and
they depend on other plants. They are called parasitic plants. E.g., Cuscuta
2. Consumers
The living things that eat the food prepared by the producers are called consumers. Most of the living
things depend directly or indirectly on producers for their food. Consumers can
be divided into three types based on their food
as herbivores
(plant eating animal), carnivores (flesh eating
animal), omnivores
(both plant and flesh eating animal).

3. Decomposers
Organisms that feed on the wastes, dead plants and animals are called decomposers. They return the nutrients to the soil.
E.g., Bacteria, Fungi.
Let Us Try
Classify the following biotic factors.
(Tulsi, Fungi, Mango tree, Rabbit, Eagle, Cat, Dog, Cucumber
plant, Human, Grass, Crocodile, Crow, Bacteria)
Producers : Tulsi, Mango tree, Cucumber plant,
Grass
Consumers : Rabbit, Eagle, Cat, Dog, Human,
Crocodile, Crow
Decomposers : Fungi. Bacteria
Let Us Discuss
1. Let us discuss and write.
Plants and human beings are living
things. Why do human beings depend on plants?
Human beings obtain food from plants and oxygen for respiration.
So they depend on plants.
2. Divide the students
into three groups and give them some pictures of living things. Ask them to
classify the pictures based on their food habits.
3. Take your students outside the classroom
or to a park. Ask them to note down the producers and consumers they could
identify there.
Let Us Try
The names of several natural resources are hidden in the box
below. Find as many as possible. Some words are repeated.
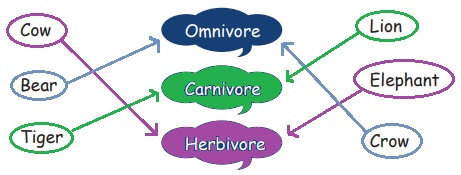
Let us Connect
Link the animals as herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
V. Plant Sapling
A young plant with a thin stem is known as a sapling. Survival of living things is impossible without plants. Planting and taking care of plants lead to a good environment.
Benefits of plants
* Provide oxygen for breathing
* Provide food and shelter to living
things
* Absorb harmful gases and smoke from
the surroundings
* Help in bringing rainfall
* Give wood for making furniture
* Offer a good environment to live

Do you know
“VAN MAHOTSAV”
Van Mahotsav means, “Festival
of forests”. It is an annual tree planting movement. This movement began in
India in July 1950.This festival is organised during the first week of July every year.
To create awareness among the
people, we can give saplings during celebrations, family functions and national
festivals. We can also plant saplings on our birthday.

More to know
Some important initiatives to protect our environment.
The Chipko Movement - 1970
The Environment Protection Act – 1986
National Green Tribunal – 2010
Appiko Movement – 1983
Let Us Do
A. Write any two uses
of trees.
1. Help in bringing rainfall
2. Provide oxygen
B. Conduct an awareness
campaign on ‘Save Our Environment’.
C. Plant saplings in your school campus.
D. Preparation of seed
ball
Take some clay, humus, add water and mix well. After mixing,
place
the available seeds inside them and make a seed
ball. Then dry and keep it safe. Distribute the seed balls to public on special
occasions of your school.
E. Write some slogans on ‘Save Plants’ and paste them on the tree
in your school campus/road sides. (E.g.,
Take care of the Earth and it will take care of you. It’s not yours, nor mine,
it’s ours)
1. Trees look fair, they clean the air.
2. Forests are our wealth. They preserve our health.
The nature of our future depends on
the future of our nature.
Related Topics