Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: The Obstetrician-Gynecologist’s Role in Screening and Preventive Care
Osteoporosi
OSTEOPOROSI
Osteoporosis
affects approximately 13% to 18% of Amer-ican women
aged 50 years and older, and another 37% to 50% have osteopenia, or low bone mineral density. Osteoporosis-associated
fracture, especially of the hip and spine, are leading causes of morbidity and
mortality, in-creasing in proportion to age. Osteoporosis is a largely
preventable complication of menopause. Screening strate-gies and pharmacologic
interventions are available to pre-vent and treat osteoporosis.
Bone
mineral density (BMD) is an indirect measureof bone
fragility. BMD is measured using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) of the
hip or the lumbar spine. The results are expressed in standard deviations
compared with a reference population stratified by age, sex, and race. The T-score is expressed as the standard
deviation from the mean peak bone mineral density of a normal, young-adult
population; and the Z-score is
expressed as the stan-dard deviation from the mean bone mineral density of a
reference population of the same sex, race, and age as the patient. Z- and
T-scores are used for hip and spine mea-surements. The World Health
Organization (WHO) de-fines a normal BMD T-score as >=−1. Osteopenia (low bone mass) is
defined as a T-score between −1 and −2.5. Osteo-porosis is defined as
a T-score ≤−2.5.
Because of variance in the measurements obtained by the different commer-cial
devices and at different sites, T- and Z-scores cannot be used as true
screening tests, but they are good predic-tors of the risk of fracture. This
information can be used to guide decisions about interventions including
lifestyle changes and medical therapy to prevent or slow bone loss.
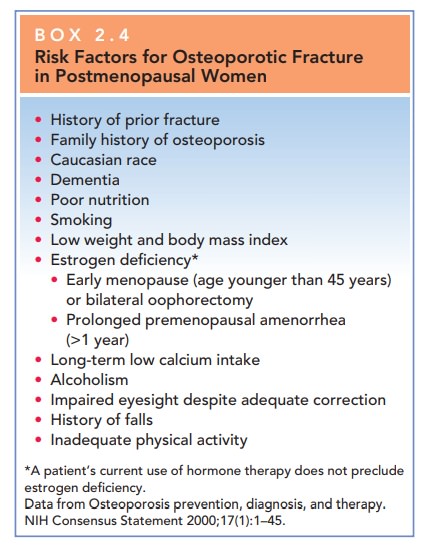
ACOG
recommends bone mineral density testing for all post-menopausal women starting
at age 65. Bone mineral density test-ing should also be performed in younger
postmenopausal women who have at least one risk factor for osteoporosis (Box
2.4). Inaddition, postmenopausal women who experience a frac-ture should have
bone mineral density testing to ascertain if they are osteoporotic; if so,
treatment for osteoporosis is added to the therapy for the fracture. Certain
diseases or medical conditions (e.g., Cushing disease, hyperpara-thyroidism,
hypophosphatasia, inflammatory bowel disease, lymphoma, and leukemia) and
certain drugs (e.g., phenobar-bital, phenytoin, corticosteroids, lithium, and
tamoxifen) are associated with bone loss. Women with these conditions or taking
these drugs may need to be tested more frequently.
Women should be counseled on the
risks of osteo-porosis and related fractures and the following preventive
measures:
·
Adequate calcium consumption (at
least 1000 to 1500 mg/d) using dietary supplements if dietary sources are not
adequate
·
Adequate vitamin D consumption
(400 to 800 inter-national units daily) and exposure to the natural sources of
this nutrient
·
Regular weight-bearing and
muscle-strengthening exer-cises to reduce falls and prevent fractures
·
Smoking cessation
·
Moderation of alcohol intake
· Fall prevention strategies
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes
mellitus is a group of disorders that share hyper-glycemia
as a common feature. Even when symptoms are not present, the disease can cause
long-term complica-tions. Ideally, it should be detected and treated in its
early stages. A screening fasting blood
glucose test is recommendedfor women beginning at age 45 and every 3 years
thereafter. Screening should begin at a younger age or more fre-quently in
individuals with risk factors, which include being overweight (body mass index >=25), a family history of diabetes
mellitus, habitual physical inactivity, having given birth to a newborn
weighing more than 9 pounds, history of gestational diabetes, and hypertension.
Thyroid Disease
Thyroid
disease is often asymptomatic and if untreatedcan lead to
serious medical conditions. Thyroid-stimulatinghormone
levels should be tested every 5 years starting at the age of 50.
Hypertension
It is estimated that
approximately 30% of adults aged 20 and older have hypertension, which is defined as a systolic blood pressure of ≥140 mm Hg or a diastolic blood
pres-sure of >=90 mm Hg.
Hypertension is one of the most im-portant risk factors for heart disease and
cerebrovascular accidents (CVAs), two of the three leading causes for
mor-tality among women. Hypertension is also a leading cause of mortality.
About a third of those with hypertension do not know they have it. Screening for hypertension is recom-mended
for women and girls 13 years of age and older. Screen-ing may be repeated every
2 years in persons with normal blood pressure or annually with higher levels.
Lipid Disorders
Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a
leading cause of death for both men and women in the United States and accounts
for approximately 500,000 deaths each year. Abnormal cholesterol levels have
been linked to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease.
Clinical tri-als have shown that a 1% reduction in serum cholesterol levels
results in a 2% reduction in CHD rates. Lipid lev-els are assessed with regard
to low-density lipoprotein(LDL),
high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and
triglyc-erides. About one in five adult Americans has a high
totalcholesterol level (>=240
mg/dL).
Current
guidelines recommend that women without risk factors have a lipid profile
assessment every 5 years, beginning at age 45 years. Earlier
screening may be appropriate inwomen with risk factors. Risk factors for high
cholesterol are a family history of familial hyperlipidemia, family his-tology
of premature (age younger than 50 years for men and younger than 60 years for
women) cardiovascular dis-ease, diabetes mellitus, and multiple coronary heart
dis-ease risk factors (e.g., tobacco use, hypertension).
Obesity
Obesity is
associated with increased risk for heart disease,type 2 diabetes, hypertension,
some types of cancer (endo-metrial, colon, breast), sleep apnea,
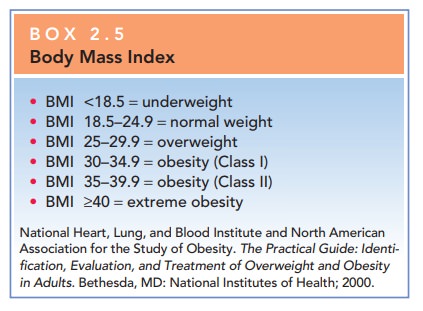
osteoarthritis, gall-bladder disease, and depression. Measurement of height andweight and the calculation of a BMI are
recommended as part of the periodic assessment (Box 2.5). Obese people with
a bodymass index (BMI) of 30 or more have up to twofold in-creased risk of
death.
Related Topics