Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : History and General Features of Indian Railways
Organization of Indian Railways
Organization of Indian
Railways
Indian Railways (IR) is at present the biggest
public undertaking of the Government of India, having a capital-at-charge of
about Rs 560,000 million. The enactments regulating the construction and
operation of railways in India are the Indian Tramway Act of 1816 and the
Indian Railway Act of 1890 as amended from time to time. The executive
authority in connection with the administration of the railways vests with the
Central Government and the same has been delegated to the Railway Board as per
the Indian Railway Act referred to above.
1 Railway Board
The responsibility of the administration and
management of Indian Railways rests with the Railway Board under the overall
supervision of the Minister for Railways. The Railway Board exercises all the
powers of the Central Government in respect of the regulation, construction,
maintenance, and operation of the Railways.
The Railway Board consists of a
chairman, a financial commissioner for railways, and five other functional
members. The chairman is the ex-officio principal secretary to the Government
of India in the Ministry of Railways. He reports to the Minister for Railways
and is responsible for making decisions on technical and administrative matters
and advising the Government of India on matters of railway policy. All policy
and other important matters are put up to the Minister through the chairman or
other board members.
The financial
commissioner for railways is vested with the full powers of the Government of
India to sanction railway expenditure and is the ex-officio secretary to the
Government of India in financial Ministry of Railways matters. The members of
the Railway Board are separately in charge of matters relating to staff, civil engineering,
traffic, mechanical engineering, and electrical engineering. They function as
ex-officio secretaries to the Government of India in their respective spheres.
To be able to
effectively tackle the additional duties and responsibilities arising from
increased tempo of work, the Railway Board is assisted by a number of technical
officers designated additional members and executive directors, who are
in-charge of different directorates such as civil engineering, mechanical,
electrical, stores, traffic and transportation, commercial, and planning and
are responsible for carrying out technical functions. These officers, however,
do not make major policy decisions.
2 Research Design and Standards
Organisation
The Research Designs
and Standards Organisation (RDSO) is headquartered at Lucknow. It is headed by
a director general who has a team of specialists from different fields of
railways. RDSO functions as a technical adviser and consultant to the Railway
Board, the zonal railways, and production units as well as to public and
private sector undertakings with respect to the designs and standardization of
railway equipment.
RDSO
has also been approved for its quality management system ISO 9001:2000.
3 Zonal Railways
The entire railway
system was earlier divided into nine zonal railways. To increase efficiency,
the Railway Ministry decided to set up seven new railway zones, namely, North
Western Railway at Jaipur, East Central Railway at Hajipur, East Coast Railway
at Bhubaneswar, North Central Railway at Allahabad, South Western Railway at
Bangalore, West Central Railway at Jabalpur, and South East Central Railway at
Bilaspur. All the new railway zones have been fully functional from 1 April
2003.
Presently, Indian Railways
is divided into 16 zones, each having different territorial jurisdictions which
vary from 2300 to 7000 route km. The route kilometres of various zonal railways
are given in Table 1.3.
Table
1.3 Zonewise track
length as on 31 March 2004
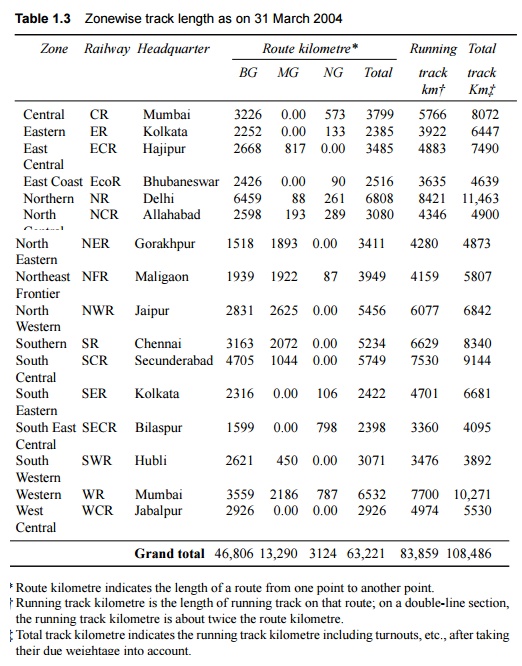
Route kilometre indicates the length of a route from
one point to another point.
†
Running track kilometre is the length of
running track on that route; on a double-line section, the running track
kilometre is about twice the route kilometre.
‡
Total track kilometre indicates the
running track kilometre including turnouts, etc., after taking their due
weightage into account.
The zonal railways take
care of the railway business in their respective areas and are responsible for
management and planning of all work. Each zonal railway is administered by a
general manager assisted by additional general managers and heads of
departments of different disciplines, namely, civil engineering, mechanical,
operating, commercial, accounts, security, signals and telecommunications,
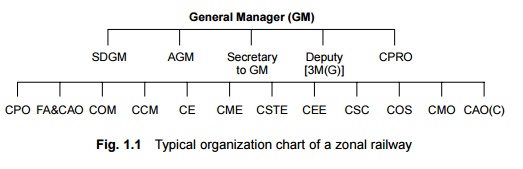
electrical, personnel, medical, etc. The typical organization of a zonal
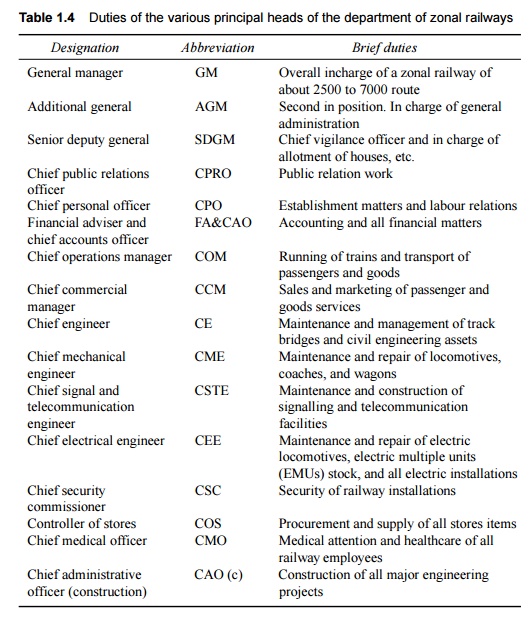
railway is given in Fig. 1.1. The duties of the various heads of departments
are given in Table 1.4.
4 Production Units
Apart from zonal
railways, there are six production units. The details given in Table 1.5.
Table
1.5 Production or
manufacturing units
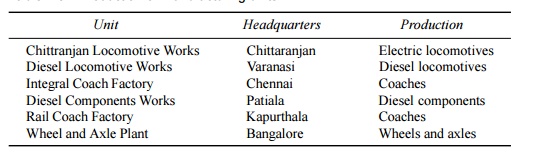
Unit Headquarters Production
Chittranjan
Locomotive Works Chittaranjan Electric locomotives
Diesel
Locomotive Works Varanasi Diesel locomotives
Integral
Coach Factory Chennai Coaches
Diesel
Components Works Patiala Diesel components
Rail
Coach Factory Kapurthala Coaches
Wheel
and Axle Plant Bangalore Wheels and axles
5 COFMOW
The Central
Organisation for Modernization of Workshops (COFMOW) was set up in 1979 as a
specialized agency to implement the various workshop modernization programs of
Indian Railways. Most of the workshops of IR are over 100 years old and COFMOW
is modernizing these workshops in a planned way with the assistance of the
World Bank.
COFMOW also provides
consultancy and engineering inputs for technology upgradation, productivity
improvement, machinery selection, and procurement besides training of personnel
in operation and maintenance of manufacturing infrastructure.
COFMOW has been
actively involved in the conversion of metre gauge rolling stock repair
workshops to broad gauge repair shops by identifying and selecting compatible
machinery and plants. At present, COFMOW is actively involved in the
upgradation of manufacturing facilities at DLW and CLW to equip them to
manufacture state-of-the-art locomotives of General Motors and Alstom design,
respectively.
COFMOW has recently
assisted Indian Railways in placing an order for 12 locomotive simulators at a
total cost of Rs 980 million. These simulators will help the Railways in
providing safe and efficient operation of trains to meet the demands of
increasing traffic by training the staff under simulated operating conditions.
6 Divisions
Zonal railways work on
the divisional system. Each railway is divided into three to six divisions,
each division having approximately 700 to 1000 route km in its territory. There
are about 67 divisions of Indian Railways. Each division works under the overall
control of a divisional railway manager, who is assisted by one or two
additional divisional railway managers. There are divisional officers in charge
of each discipline either in the junior administrative grade or the senior
scale, namely, divisional superintending engineer (DSE) or divisional engineer
for civil engineering, senior divisional mechanical engineer or divisional
mechanical engineer for mechanical engineering, senior divisional commercial
manager or divisional commercial manager for commercial work, etc.
In
the case of the engineering branch, the DSE or senior divisional engineer is
normally the head of the unit in the division. Under each DSE, there are two to
three divisional engineers (DENs), each in charge of approximately a 800 to 1000
integrated track km and assisted by two to three assistant engineers (AENs) in
the maintenance of track and works. An AEN has about 400 integrated track km
under his charge. The total number of DENs and AENs for maintenance work in
Indian Railways is approximately 300 and 600, respectively. The AENs are
assisted by permanent way inspectors (PWI) for maintenance of track structure.
Each PWI has a jurisdiction of 50-70 route km of the track. The total number of
PWIs for normal maintenance work on Indian Railways is roughly 3000.
Related Topics