Computer Science - Interface Vs Implementation | 12th Computer Science : Chapter 1 : Problem Solving Techniques : Function
Chapter: 12th Computer Science : Chapter 1 : Problem Solving Techniques : Function
Interface Vs Implementation
Interface Vs Implementation
An interface is a set of action that an object
can do. For example when you press a light switch, the light goes on, you may
not have cared how it splashed the light. In Object Oriented Programming
language, an Interface is a description of all functions that a class must have
in order to be a new interface. In our example, anything that "ACTS
LIKE" a light, should have function definitions like turn_on
() and a turn_off (). The purpose of interfaces is to allow the computer to
enforce the properties of the class of TYPE T (whatever the interface is) must have functions called X, Y, Z, etc.
A class declaration combines the external
interface (its local state) with an
implementation of that interface (the
code that carries out the behaviour).
An object is an instance created from
the class.
The interface defines an object’s visibility to
the outside world.
The difference between interface and
implementation is
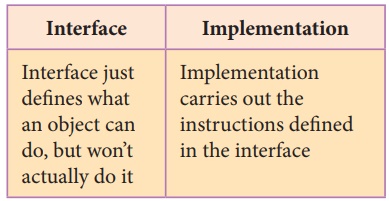
In object oriented programs classes are the
interface and how the object is processed and executed is the implementation.
Characteristics of interface
·
The class template specifies the interfaces to enable an object to
be created and operated properly.
·
An object's attributes and behaviour is controlled by sending
functions to the object.
For
example, let's take
the example of increasing a car’s speed.
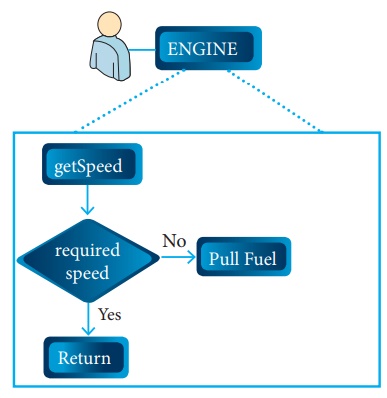
The person who drives the car doesn't care
about the internal working. To increase the speed of the car he just presses
the accelerator to get the desired behaviour. Here the accelerator is the
interface between the driver (the calling
/ invoking object) and the engine (the
called object).
In this case, the function call would be Speed
(70): This is the interface.
Internally, the engine of the car is doing all
the things. It's where fuel, air, pressure, and electricity come together to
create the power to move the vehicle. All of these actions are separated from
the driver, who just wants to go faster. Thus we separate interface from
implementation.
Let us see a simple example, consider the
following implementation of a function that finds the minimum of its three
arguments:
let min 3 x y z :=
if x < y then
if x < z then x else z
else
if y < z then y else z
Related Topics