India’s International Relations - India and International Organisations | 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 5 : India’s International Relations
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 5 : India’s International Relations
India and International Organisations
India and International Organisations
India is
a potential superpower and has a growing international influence all around the
world. Being a newly industrialised country, India has a great history of
collaboration with several countries. It has acted as prominent member of
several international organisations and has been a founding member of some.
India is a member of formal groupings like UNO, NAM, SAARC, G20 and the
Commonwealth. India has been extending a helping hand to the UNO, in all her
efforts in ending military conflicts, and in promoting peace and progress among
the nations.
BRICS
Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa are leading emerging economies and political powers at the regional and international level. The BRICS organisation’s headquarters is in Shanghai, China. BRICS opened up a possibility for countries of the Global South to challenge the Global North. India is an active member and this collaboration paves way for India to build its global profile.
Reason for the formation of BRICS
To be an
alternative to World Bank and IMF to challenge U.S. supremacy
To
provide self-owned and self-managed organisations to carry out developmental and
economical plans in its member nations
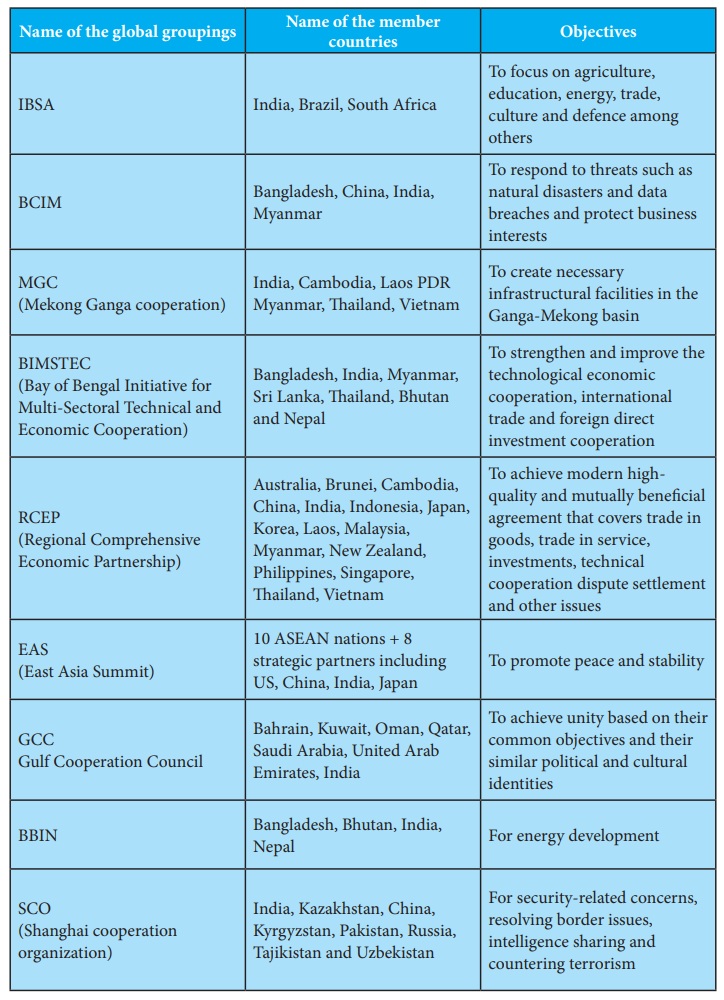
India is
actively engaged in general economic diplomacy, which is evident in the country
being part of several economic coalitions, as listed in the table below.
Objectives of BRICS
• To achieve
regional development
• It acts
as a bridge between developed and developing countries
• Tocontributeextensivelytodevelopment
of humanity
• To
establish a more equitable and fair world
• Boost
intra BRICS trade in their local currencies to increase trade cooperation and
cope with the current international financial crisis
• To
promote the technological information exchange among the member states
The acronym BRICS was coined by Jim
O’Neill, a famous British economist. He predicted that by year 2050 Brazil,
Russia, India and China would become bigger than the six most industrialised
nations in dollar terms and would completely change the power dynamics of the
last 300 years.
• To
enhance inclusive economic growth that will lead to an increase in the creation
of jobs, fight against poverty and accelerate the economic transformation of
members.
The financial architecture of BRICS
The New
Development Bank (NDB) is a multilateral development bank. Its primary focus is
lending for infrastructure projects. It aims to contribute to development plans
established nationally through projects that are socially, environmentally and
economically sustainable. It gives priority to projects aimed at developing
renewable energy sources.
The
Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) is a framework for providing protection
against global liquidity pressures, which includes currency issues.
BRICS payment system
At the
2015 BRICS Summit, ministers from the BRICS nations initiated consultations for
a payment system that would be an alternative to the Society for Worldwide
Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) system.
The factors that bolster co-operation among members
First,
the common need among developing countries to construct an economic order that
reflects the current situation will drive the BRICS efforts. In this matter,
the idea of NDB and CRA are defining changes and will have huge geo-economic
and geopolitical impact.
Second,
the BRICS alternative idea in the landscape of global governance will attract
support from other countries.
Third,
the expansion of BRICS interaction to other sector will make it more strong
partnership.
OPEC
OPEC, the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting
Countries (a group of oil-producing nations), is an intergovernmental
organisation founded in Baghdad, Iraq, and headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela are the OPEC’s Founder Members.
There are
three categories of memberships: Founder Members, Full Members and Associate
Members. At present there are 15 member nations (two are located in South
America, six in the Middle East and seven in Africa). OPEC membership is open
to any country that exports crude oil and which shares the ideals of the
organisation.
OPEC’s mission
• To
coordinate oil policies in its member countries
• Help
stabilise oil markets
• To secure
fair and stable income to petroleum producers
• An
efficient, economic and regular supply of oil to consuming nations
• A fair
return on capital to those investing in the petroleum industry
How does OPEC help other countries?
The OPEC
Fund for International Development (OPID) is an institution that helps finance
projects with low interest loans. It also provides grants to social and
humanitarian projects.
The OPEC LOGO

It is the result of an international
design competition held in 1969. An Austrian designer Svoboda won the
competition with her design, which combined the different letters of the
organisation’s name in a rounded design
OPEC has an Information Centre with over 20,000
volumes including books, reports, maps and conference proceedings related to
petroleum, energy and the oil market. The Information Centre is open to the
public and is often used by researchers and students.
India’s relationship with OPEC
India is
one of the biggest consumers of crude oil. OPEC obviously has vested interest
in India’s economic growth. We import 86% of crude oil, 70% natural gas, 95% of
cooking gas from OPEC countries. India has been identified as a great partner
for OPEC mainly because of its high oil demand.
India
doesn’t have enough oil reserves. India can’t produce oil. Devoid of necessary
oil reserves India strongly focuses on agriculture, and industrial production.
Conclusion
Apart
from economic and trade cooperation, India also aspires to have a warm
relationship with its neighbours and extended neighbours in the field of
education, health, fighting terrorism, disaster management, employment for its
citizens, curbing organised crimes, technology development and so on.
Related Topics