Chapter: 12th Political Science : Chapter 10 : India and It’s Neighbours
India- Afghanistan Relations
India- Afghanistan Relations
India has sought to establish its presence in
Afghanistan from the early days of its independence in 1947.In 1950,
Afghanistan and India signed a “Friendship Treaty.”

India had robust ties with Afghanistan during King
Zahir Shah’s regime. Prior to the Soviet invasion in 1979, India had formalized
agreements and protocols withvarious Pro-Soviet regimes in Kabul. While India’s
role in Afghanistan King Zahir Shah was constrained during the Anti-Soviet
jihad, between 1979 and 1989, India expanded its development activities in
Afghanistan, focusing upon industrial, irrigation, and hydroelectric projects.

After the Taliban consolidated their hold on
Afghanistan in the mid-1990s, India struggled to maintain its presence and to support
anti-Taliban forces. However, Indian objectives in Afghanistan remained modest
given the constrained environment. India aimed to undermine the ability of the
Taliban to consolidate its power in Afghanistan, principally by supporting the Northern
Alliance in tandem with other regional actors. Working with Iran, Russia, and
Tajikistan, India provided important resources to the Northern Alliance, the
only meaningful challenge to the Taliban in Afghanistan. Since 2001, India has
relied upon development projects and other forms of humanitarian assistance.
Expanding India’s presence in Afghanistan through increased Indian training of Afghan
civilian and military personnel, development projects, and expanded economic
ties. India and Pakistan competition in Afghanistan is seen as a new “Great
Game”.

In 2005, India proposed Afghanistan’s
membership in SAARC and in April 3, 2007 it joined.
India-Afghanistan: Strategic interests
Afghan is India’s natural ally. India is interested
in retaining Afghanistan as a friendly state from which it has the capacity to monitor
Pakistan and cultivate assets to influence activities in Pakistan. While India
is keenly interested in cultivating a significant partnership with Afghanistan,
Pakistan is trying to deny India such opportunities.
India’s interest in Afghan is more than just
Pakistan-centric and reflects its aspiration to be seen as a regional power.
Islamic fundamentalism in Pakistan and Afghanistan has dangerous effects in the
domestic social fabric of India.
India-Afghanistan: Economic interests
Afghanistan has a mineral wealth of about US $1-3
trillion which includes Iron ore, Lithium, Chromium, Natural Gas, Petroleum
etc. Safeguarding Indian investments and personnel in Afghanistan is of utmost
importance to India as Indian investment in Afghan amounts to about US $3bn.
The top commodities exported by India were man-made
staple fibers, cereals, tobacco, electrical machinery, dairy product, eggs,
honey, rubber products, pharmaceuticals, clothing accessories, boilers and
machineries whereas the imports mainly comprised of fresh fruits, dried
fruits/nuts, raisins, vegetables, oil seeds, precious/semi-precious stones etc.
TO achieve the possibilities of trade, India and Afghanistan signed a
Preferential Trade Agreement in March 2003 under which India allowed
substantial duty concessions ranging from 50% to 100% to certain category (38
items) of Afghan dry fruits. In November 2011, India removed basic customs
duties for all products of Afghanistan (except alcohol and tobacco) giving them
duty free access to the Indian market. India is one of the major export
destinations of Afghanistan’s goods.
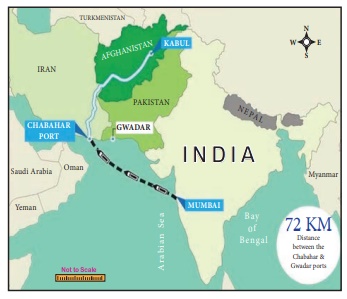
The operation of the Chabahar port in Iran could substantially
increase Afghanistan’s exports by providing a new transit route for Afghan to trade
with India and the rest of the world. Recently the Indian government has
approved USD 85 Million for upgrading the capacity of Chabahar Port in Iran for
an alternate trade transit route for Afghanistan.
India-Afghanistan: Security Interests
India faced many security challenges from the
Taliban in Afghan during the 1990s.Pakistan has raised and supported several
militant groups such as Lashkar-e-Taiba, Harkat-ul-Mujahideen/Harkat-ul-Ansar,
and Harkat-ul-Jihad-al-Islami among others, which operate in India. All of
these groups have trained in Afghanistan, with varying proximity to the Taliban
and by extension Al-Qaeda. Thus India is absolutely clear that Afghanistan
should not again become a terrorist safe haven. Radical ideologies and
terrorism spreading in this region are a security threat for India.
With Pakistan increasing its strategic depth in
Afghanistan, it can reverse the gain of India. Pakistan can incubate and move
around various anti-India groups in Afghan especially in Loya Paktia. The
golden crescent comprising of Iran, Afghan, and Pakistan is a worry for India,
especially with respect to the issue of drug abuse in Punjab. Islamic State is
using Afghan as an outpost in Asia as it has come under stress in Iraq and
Syria.
Indian policy on Afghanistan
In 2011, India became the first country that
Afghanistan signed a strategic partnership agreement. Until then, India was
following the US demand of India’s limited cooperation with Afghanistan. India
has repeatedly stressed that its relationship with Afghanistan is independent
of Pakistan. India argues that the tripartite relationship between India,
Pakistan, and Afghanistan is mutually independent. In both the 1965 and 1971
wars, Afghanistan was non-committal and did not support India. On the Kashmir
issue, Afghanistan has not publicly supported India. India has not entered the
debate on the Durand Line.
India also realises that stability can result in
Afghanistan only if all the major actors and countries have a stake in its
stability, growth and prosperity. India has been championing efforts to attract
regional and trans-regional investment into Afghanistan that provides a viable
alternative to the dominant narrative of extremism and offers job opportunities
to its population by pioneering events like the Delhi Investment Summit on
Afghanistan in June 2012. Recognising that the region holds the key to peace in
Afghanistan, India is spearheading commercial confidence building measures in
the region within the purview of the Heart of Asia Process. Multilaterally, it
helped initiate a dialogue on Afghanistan through various platforms like the
Afghanistan-India-US trilateral and the Afghanistan-India-Iran trilateral that
seek to bring together international partners with disparate worldviews in
pursuit of the common goal of securing peace and prosperity in Afghanistan.
India also expressed its support to international cooperation on Afghanistan at
the UN and at various international conferences focused on the future of
Afghanistan, including the seminal Tokyo Developmental Conference in July 2012
and London Conference in December 2014.
In 1999, Pakistan terrorists hijacked
Indian Airlines flight IC:814 and landed it in Kandahar,Afghanistan during
Taliban rule.
In 2015, in a first major offensive military
platform to Kabul, India gifted three Mi 25 attack helicopters. The delivery
marks the first time India has gifted offensive combat capability to Afghanistan,
a sensitive topic in the past due to strong objections by Pakistan. Under the
agreement, India will also train Afghan defence personnel in operations.
Way Ahead
India’s developmental approach has earned it
immense goodwill among the Afghan people. However, the “soft power” strategy
has limitations. Thus, India is in the dilemma between continued soft-power or to
aggressively push its hard power.
While India’s principled position that it will not
directly or publicly talk to the Taliban until it engages the Afghan
government, it is necessary that India stays abreast of all negotiations and
isn’t cut out of the resolution process. It is hoped that a robust channel is
open between Indian intelligence agencies and all important groups in
Afghanistan, including the Taliban, in order to ensure that Indian interests,
development projects, and citizens are kept secure.
India should leverage the goodwill it enjoys among
the Afghan people. India must intensify its dialogue with regional and global
stakeholders, and impress upon them that any dialogue with the Taliban must not
come at the cost of the hard-fought victories of the Afghan people in the past two
decades; on establishing constitutional democracy and the rule of law, and
securing the rights of women and minorities. It is time for India to engage the
Taliban to secure its interests. India also needs to reassess its policy
choices in close coordination with Russia and Iran, constantly reminding them
that complete surrender to the Taliban’s demands will be detrimental to their
own security.
Indian Developmental projects in Afghanistan
·
The restoration of the Stor palace in
the same city.
·
Rebuilding of the Habibia High
School, also in the capital, and providing it with grants-in-aid.
·
Financing the establishment of the
Afghan National Agriculture Sciences and Technology University (ANASTU) in
Kandahar and assisting it in various ways.
·
Constructing the Chimtala power
substation in Kabul.
·
Building the cricket stadium in
Kandahar; Lets Afghanistan’s national cricket team use an Indian stadium as its
home ground.
·
Building a cold storage warehouse in
Kandahar.
·
Upgrading telephone exchanges in some
provinces.
·
Expanding the national television
network.
·
Digging tube wells in some of the
provinces.
· India has donated buses, helicopters, Ambulance etc., to Afghanistan.
Related Topics