Chapter: Power System Analysis : Fault Analysis : Balanced Faults
Importance Short Circuit (Or) For Fault Analysis
IMPORTANCE SHORT CIRCUIT (OR) FOR FAULT ANALYSIS
Fault
A fault in a circuit is any failure which interferes with the normal flow of current. The faults are associated with abnormal change in current, voltage and frequency of the power system.
Faults occur in a power system
The faults occur in a power system due to
(i). Insulation failure of equipment
(ii). Flashover of lines initiated by a lighting stroke
(iii). Due to permanent damage to conductors and towers or due to accidental faulty operations.
Various types of faults
(i) Series fault or open circuit fault
One open conductor fault
Two open conductor fault
(ii) Shunt fault or short circuit fault. Symmetrical fault or balanced fault
§ Three phase fault
Unsymmetrical fault or unbalanced fault
§ Line to ground (L-G) fault
§ Line to Line (L-L) fault
§ Double line to ground (L-L-G) fault
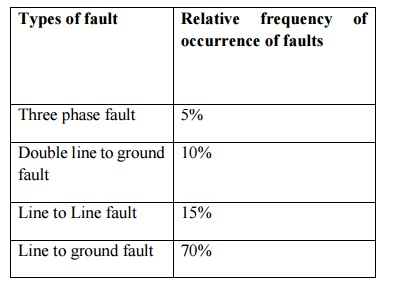
Relative frequency of occurrence of various types of fault
Symmetrical fault or balanced three phase fault
This type of fault is defined as the simultaneous short circuit across all the three phases. It occurs infrequently, but it is the most severe type of fault encountered. Because the network is balanced, it is solved by per phase basis using Thevenins theorem or bus impedance matrix or KVL, KCL laws.
Related Topics