Chapter: Obstetrics and Gynecology: The Obstetrician-Gynecologist’s Role in Screening and Preventive Care
Immunizations
IMMUNIZATIONS
In the United States, vaccination
programs that focus on infants and children have decreased the occurrence of
many childhood diseases. However, many adolescents and adults are affected by
vaccine-preventable diseases, such as influenza, varicella, hepatitis A,
hepatitis B, measles, rubella, and pneumococcal pneumonia. Each year it is
estimated that pneumococcal infection, influenza, and hepatitis B cause as many
as 45,000 deaths in adults. Obstetrician–gynecologists and other clinicians who
pro-vide general well-woman examinations and preconception care have
opportunities in which to counsel women on the need for immunizations and can
provide immunizations or referrals to vaccination clinics or services.
It may be helpful to ask new
patients to provide pre-vious vaccination records. The clinician should attempt
to gather a complete immunization history from each pa-tient, including risk
factors indicating the need for immu-nization. If there are doubts about past
immunizations, it is safest to assume that a patient has not been immunized and
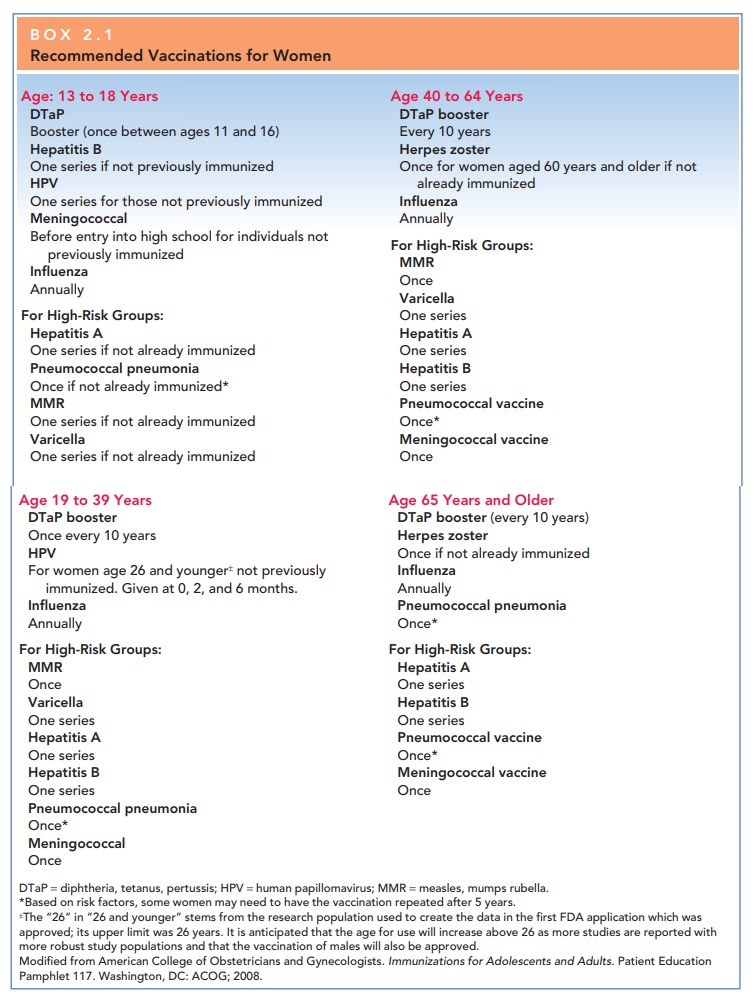
initiate the appropriate vaccination series. The rec-ommended vaccinations for
women are listed in Box 2.1. Immunization recommendations change quickly; the
most current recommendations can be accessed at the CDC’s National Immunization
Program Web page (www.cdc. gov/vaccines).
The HPV vaccine is discussed in
detail later, Cervical Neoplasia and Carcinoma. The American College
of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends the initial vaccination for girls
aged 11–12 years. Although obstetrician–gynecologists are not likely to care
for many girls in this age group, they are critical to the widespread use of
the vaccine for females aged 13–26. During a health care visit with a girl or
woman in the age range for vacci-nation, an assessment of the patient’s HPV
vaccine status should be conducted and documented in the patient record. The
quadrivalent HPV vaccine is most effective when given before any exposure to
HPV infection, but sexually active women can receive and benefit from the
quadriva-lent vaccine.
Related Topics