Chapter: Java The Complete Reference : The Java Language : Exception Handling
Exception Types - Java
Exception
Types
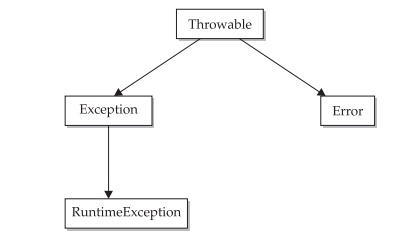
All exception types are
subclasses of the built-in class Throwable.
Thus, Throwable is at the top of the
exception class hierarchy. Immediately below Throwable are two subclasses that partition exceptions into two
distinct branches. One branch is headed by Exception.
This class is used for exceptional conditions that user programs should catch.
This is also the class that you will subclass to create your own custom
exception types. There is an important subclass of Exception, called RuntimeException.
Exceptions of this type are automatically defined for the programs that you
write and include things such as division by zero and invalid array indexing.
The other branch is topped by
Error, which defines exceptions that
are not expected to be caught under normal circumstances by your program.
Exceptions of type Error are used by
the Java run-time system to indicate errors having to do with the run-time
environment, itself. Stack overflow is an example of such an error. This
chapter will not be dealing with exceptions of type Error, because these are typically created in response to
catastrophic failures that cannot usually be handled by your program.
Related Topics