Computer Science - Example C++ Programs: Polymorphism | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 15 : Polymorphism
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 15 : Polymorphism
Example C++ Programs: Polymorphism
Illustration 15.1 C++ Program to demonstrate function overloading
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(int i)
{cout<< " It is integer " << i <<endl;}
void print(double f)
{ cout<< " It is float " << f <<endl;} void print(string c)
{ cout<< " It is string " << c <<endl;} int main() {
print(10);
print(10.10);
print("Ten");
return 0;
}
Output:
It is integer 10
It is float 10.1
It is string Ten
Illustration 15.2 C++ Program to demonstrate function overloading
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
long add(long, long);
long add(long,long,long);
float add(float, float);
int main()
{
long a, b, c,d;
float e, f, g;
cout << "Enter three integers\n";
cin >> a >> b>>c;
d=add(a,b,c); //number of arguments different but same data type
cout << "Sum of 3 integers: " << d << endl;
cout << "Enter two integers\n";
cin >> a >> b;
c = add(a, b); //two arguments data type same with above function call and different with below function call
cout << "Sum of 2 integers: " << c << endl;
cout << "Enter two floating point numbers\n";
cin >> e >> f;
g = add(e, f); //two arguments similar to the above function call but data type different
cout << "Sum of floats: " << g << endl;
}
long add(long c, long g)
{
long sum;
sum = c + g;
return sum;
}
float add(float c, float g)
{
float sum;
sum = c + g;
return sum;
}
long add(long c, long g,long h)
{
long sum;
sum = c + g+h;
return sum;
}
Output
Enter three integers
3 4 5
Sum of 3 integers: 12
Enter two integers
4 6
Sum of 2 integers: 10
Enter two floating point numbers
2.1 3.1
Sum of floats: 5.2
Illustration 15.3 Default argument and return type are not considered in overloading
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
long add(long, long);
long add(long long g=0);
int add(long,long); // [Error] ambiguating new declaration of 'int add(long int, long int)
int main()
{
long a, b, c;
int d;
cout<< "Enter two integers\n";
cin>> a >> b;
d=add(a,b); //arguments and datatype are same but return is different
cout<< "Sum of 2 integers: " << d <<endl; cout<< "Enter two long integers\n";
cin>> a >> b;
c = add(a, b);
cout<< "Sum of 2 long integers: " << c <<endl;
cout<< "Enter a long integers\n";
cin>> a ;
c = add(a); // [Error] ambiguating new declaration of 'int add(long int, long int)
cout<< "Sum of 2 long integers: " << c <<endl; }
long add(long c, long g) // 'long int add(long int, long int)' previously defined here
{
long sum;
sum = c + g;
return sum;
}
int add(long c, long g) // [Error] ambiguating new declaration of 'int add(long int,
long int)
{
int sum;
sum = c + g;
return sum;
}
long add(long c, long g=20) // [Error] redefinition of 'long int add(long int, long int)'
{
long sum;
sum = c + g;
return sum;
}
ERROR Message
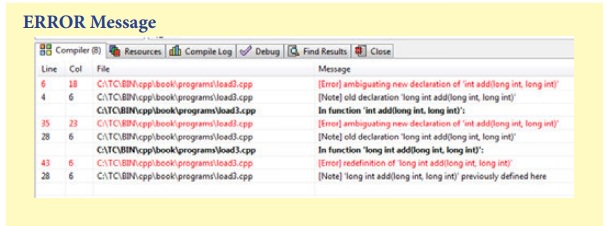
Illustration 15.4 constructor overloading
Compiler identifies a given member function is a constructor by its name and the return type.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class add
{
int num1, num2, sum;
public:
add()
{
cout<<"\n Constructor without parameters.. ";
num1= 0;
num2= 0;
sum = 0;
}
add ( int s1, int s2 )
{
cout<<"\n Parameterized constructor... ";
num1= s1;
num2=s2;
sum=0;
}
add (add &a)
{
cout<<"\n Copy Constructor ... ";
num1= a.num1;
num2=a.num2;
sum = 0;
}
void getdata()
{
cout<<"\nEnter data ... ";
cin>>num1>>num2;
}
void addition()
{
sum=num1+num2;
}
void putdata()
{
cout<<"\n The numbers are..";
cout<<num1<<'\t'<<num2;
cout<<"\n The sum of the numbers are.. "<< sum;
}
};
int main()
{
add a, b (10, 20) , c(b);
a.getdata();
a.addition();
b.addition();
c.addition();
cout<<"\n Object a : ";
a.putdata();
cout<<"\n Object b : ";
b.putdata();
cout<<"\n Object c.. ";
c.putdata();
return 0;
}
Output
Constructor without parameters..
Parameterized constructor...
Copy Constructor ...
Enter data ... 20 30
Object a :
The numbers are..20 30
The sum of the numbers are.. 50
Object b :
The numbers are..10 20
The sum of the numbers are.. 30
Object c..
The numbers are..10 20
The sum of the numbers are.. 30
Illustration 15.5 to find the perimeter of a rectangle using constructor overloading in a class.
//constructor declared as outline member function
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Perimeter
{
int l, b, p;
public:
Perimeter ();
Perimeter (int);
Perimeter (int,int);
Perimeter (Perimeter&);
void Calculate();
};
Perimeter :: Perimeter ()
{
cout<<"\n Enter the value of length and breath";
cin>>l>>b;
cout<<"\n\nNonParameterizd constructor ";
}
Perimeter ::Perimeter (int a)
{
l=b=a;
cout<<"\n\n Parameterizd constructor with one argument ";
}
Perimeter ::Perimeter (int l1, int b1)
{
cout<<"\n\n Parameterizd constructor with 2 argument ";
l=l1;
b=b1;
}
Perimeter ::Perimeter (Perimeter &p)
{
l= p.l;
b= p.b;
cout<<"\n\n copy constructor ";
}
void Perimeter ::Calculate(){
p = 2*(l+b);
cout<<p;
}
int main ()
{
Perimeter Obj;
cout<<"\n perimeter of rectangle is ";
Obj. Calculate ();
Perimeter Obj1(2);
cout<<"\n perimeter of rectangle ";
Obj1.Calculate ();
Perimeter Obj2 (2, 3);
cout<<"\n perimeter of rectangle ";
Obj2.Calculate ();
Perimeter obj3 (Obj2);
cout<<"\n perimeter of rectangle ";
obj3.Calculate ();
return 0;
}
Output
Enter the value of length and breath 10 20
Non Parameterizd constructor
perimeter of rectangle is 60
Parameterizd constructor with one argument
perimeter of rectangle 8
Parameterizd constructor with 2 argument
perimeter of rectangle 10
copy constructor
perimeter of rectangle 10
Illustration 15.6 binary operator overloading using ‘+’ and – symbol
//Complex number addition and subtraction
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class complex
{
int real,img;
public:
void read()
{
cout<<"\nEnter the REAL PART : ";
cin>>real;
cout<<"\nEnter the IMAGINARY PART : ";
cin>>img;
}
complex operator +(complex c2)
{
complex c3;
c3.real=real+c2.real;
c3.img=img+c2.img;
return c3;
}
complex operator -(complex c2)
{
complex c3;
c3.real=real-c2.real;
c3.img=img-c2.img;
return c3;
}
void display()
{
cout<<real<<"+"<<img<<"i";
}
};
int main()
{
complex c1,c2,c3;
int choice, cont;
do
{
cout<<"\t\tCOMPLEX NUMBERS\n\n1.ADDITION\n\n2.SUBTRACTION\n\n";
cout<<"\nEnter your choice : ";
cin>>choice;
if(choice==1||choice==2)
{
cout<<"\n\nEnter the First Complex Number";
c1.read();
cout<<"\n\nEnter the Second Complex Number";
c2.read();
}
switch(choice)
{
case 1 : c3=c1+c2; // binary + overloaded
cout<<"\n\nSUM = ";
c3.display();
break;
case 2 : c3=c1-c2; // binary –overloaded
cout<<"\n\nResult = ";
c3.display();
break;
default : cout<<"\n\nUndefined Choice";
}
cout<<"\n\nDo You Want to Continue?(1-Y,0-N)";
cin>>cont;
}while(cont==1);
return 0;
}
Output
COMPLEX NUMBERS
1.ADDITION
2.SUBTRACTION
Enter your choice : 1
Enter the First Complex Number
Enter the REAL PART : 3
Enter the IMAGINARY PART : 4
Enter the Second Complex Number
Enter the REAL PART : 5
Enter the IMAGINARY PART : 8
SUM = 8+12i
Do You Want to Continue?(1-Y,0-N)1
COMPLEX NUMBERS
1.ADDITION
2.SUBTRACTION
Enter your choice : 2
Enter the First Complex Number
Enter the REAL PART : 8
Enter the IMAGINARY PART : 10
Enter the Second Complex Number
Enter the REAL PART : 4
Enter the IMAGINARY PART : 5
Result = 4+5i
Do You Want to Continue?(1-Y,0-N)0
Illustration 15.7 concatenation of string using operator overloading
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class strings
{
public:
char s[20];
void getstring(char str[])
{
strcpy(s,str);
}
void operator+(strings);
};
void strings::operator+(strings ob)
{
strcat(s,ob.s);
cout<<"\nConcatnated String is:"<<s;
}
int main()
{
strings ob1, ob2;
char string1[10], string2[10];
cout<<"\nEnter First String:";
cin>>string1;
ob1.getstring(string1);
cout<<"\nEnter Second String:";
cin>>string2;
ob2.getstring(string2);
//Calling + operator to Join/Concatenate strings
ob1+ob2;
return 0;
}
Output
Enter First String:COMPUTER
Enter Second String:SCIENCE
Concatenated String is:COMPUTERSCIENCE
Related Topics