Chapter: Biochemistry: Practicals
Estimation of Glucose (Orthotoluidine method)
ESTIMATION
OF GLUCOSE (ORTHOTOLUIDINE METHOD)
Aim
To estimate the amount of glucose present in the
given blood sample.
Principle
A solution of orthotoluidine in glacial acetic
acid when treated with glucose produces a blue coloured product with an
absorption maximum at about 640nm. The values obtained represent the true
glucose level.
Reagents Required
1. Stock solution
l00mg of glucose is weighed and made upto 100ml
with distilled water. Concentration of glucose = 1mg/ml
2. Working Standard solution
10ml of stock solution is diluted to 100ml with
distilled water.
Concentration of glucose = 100µg/ml
3. Orthotoluidine reagent
12.5 mg of thiourea and 12g of boric acid are
dissolved in 50ml of distilled water by heating over a mild flame. 75ml of
redistilled Orthotoluidine reagent and 375ml of analar acetic acid are mixed
separately. The two solutions are mixed and the total volume is made upto 500ml
with acetic acid. The reagent is kept overnight at 4°C.
4. Preparation of Blood Sample
0.2ml of blood sample is taken in a centrifuge
tube. To this 0.3ml of 10% sodium tungstate, 0.3ml of 2 / 3N sulphuric acid and
3.2ml of distilled water are added to precipitate the proteins. It is kept
aside for 10 minutes and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min. 1 ml of the
supernatant is taken for the estimation of glucose.
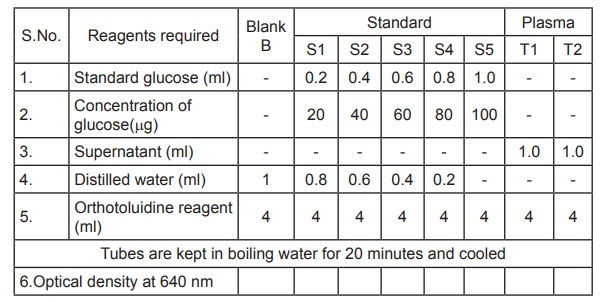
Procedure
Estimation of glucose
0.2-1.0 ml of standard glucose solutions are
pipetted out into five different test tubes labelled S1- S5 with the concentration
of 20 - 100µg. 1 ml of the deproteinised supernatant is pipetted out into two
different test tubes labelled as T1& T2. Final volume
is made upto 1ml using distilled water in all the standard tubes. 4 ml of
orthotoluidine reagent is added to all the test tubes. A blank is also prepared
simultaneously comprising 1ml of distilled water and 4 ml of orthotoluidine
reagent. All the test tubes are heated for 20 minutes in a boiling water bath.
The blue colour developed is measured at 640nm using a colorimeter.
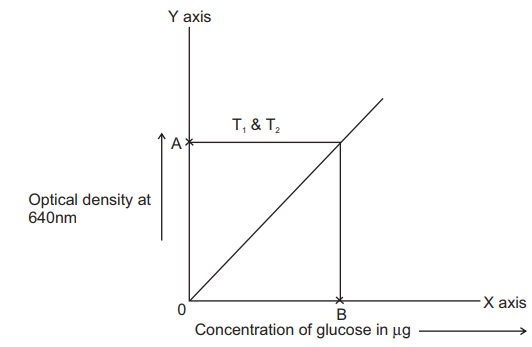
A standard graph is drawn with optical density
in Y axis vs concentration of glucose in X axis. The amount of glucose present
in the given blood sample is then calculated
Protocol for glucose estimation
Graph
Calculation
For T1&T2
The optical density A of T1& T2
corresponds to B µg of glucose 1.0 ml of supernatant contains B µg of glucose
Therefore,
4 ml of supernatant will contain= 4 x B/1.0 µg
of glucose = Z µg of glucose
0.2 ml of blood contains Zµg of glucose
Therefore,
100ml of blood will contain = 100 x Z / 0.2 µg of glucose
= Cmg
of glucose (1000µg=1mg)
Result
The amount of glucose present in 100ml of the
given blood sample is_____mg
Related Topics