Term 1 Chapter 3 | 5th Science - Energy | 5th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Energy
Chapter: 5th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Energy
Energy
UNIT 3
Energy

Learning Objectives
After completing this
lesson, students will be able to:
• know about different
forms of energy.
• explain the energy
charges in daily life.
• understand the law of
conservation of energy.
•
list out the uses of energy.
Introduction
Mala was standing in the row for her
morning school assembly. Suddenly she fainted and fell down. Her class teacher
rushed to her, took her to the class room and gave her water to drink. She came
to know that Mala had skipped her breakfast. She was given some food and then
she came back to normal. What do you understand from this?
We need energy to do our daily
activities. We get this energy from the food. In science, energy is defined as
capacity to do work. Let us study about different forms of energy and their
uses in this lesson.
I. Different forms of Energy
We do many works in our daily life. Many
of them are done physically. Some works are done with the help of instruments
and devices. But, they need energy to work. There are different forms of energy
like mechanical energy, heat energy, light energy, wind energy and so on. Let
us study about them one by one.
Activity 1
Find out what do we need
for the following

1. Mechanical Energy
Energy possessed by an object due to its
position is called mechanical energy. Mechanical energy can be classified into
two.
• Kinetic energy
• Potential energy
Kinetic energy
Energy possessed by a moving object is
known as kinetic energy. It is also known as energy of motion.
Examples: Moving car, Cricket ball bowled by a player, Bullet coming out of a gun.
Potential energy
Energy possessed by an object which is
at rest is known as potential energy. It is also known as stored energy of
position.

Examples: Object lifted above, Stone in the stretched rubber, Water in the dam.
Uses of mechanical energy
Mechanical energy can be used to do many
works. Some of them are given below.
• In hydro electric plants, kinetic
energy of water is converted into electrical energy.
• Wind mills convert kinetic energy of
winds into electrical energy.
• Mechanical energy of the hammer is
used to apply a force on a nail.
• Mechanical energy can bring a moving
body to rest and make a body at rest to move.

Activity 2
Find out the form of
energy in the following.

2. Wind Energy
Energy possessed by the wind is known as
wind energy.
Uses of wind energy
• Wind mills use wind energy to generate
electricity.
• Ships sail by the power of wind.
• Sports like wind surfing, sailing,
kite surfing use wind energy.
• Wind energy can be used for pumping
water.
Do you know?
Tamil Nadu stands first in
generating electricity from wind mills. Wind mills are located in places like
Aaralvaimozhi, Kayatharu and Gudimangalam.

3. Heat Energy
When the temperature of a substance is
raised, its atoms and molecules begin to vibrate and release a kind of energy.
This energy is known as heat energy or thermal energy. This energy flows from a
hat substance to cold substance.
If we put some ice cubes into water in a
glass. Water becomes cold. It is because, heat is transferred from water to
ice.
Do you Know?
Heat is the total energy
of the molecules in a body. Temperature is a measure of heat in a body.
Activity 3
Rub your hands together.
What do you feel in your hands? Do you feel the heat generated by friction? Yes
Activity 4
Take a small amount of lime powder in a glass. Add some water and stir well. Touch the glass outside. How do you feel? Heat
In both the cases, You can feel the heat. Thus, heat is produced by friction and chemical reactions also. Sun is the primary source of heat energy.
Use of heat energy
• Heat energy obtained from power stations
is used to generate electricity.
• Heat energy obtained from petrol and
diesel is used to run vehicles.
• We cook food with the help of heat.
Heat energy renders the food material soft and easy to digest.
• Hard substances like iron are heated
to mold them into different shapes.
• Heat is used to dry cloths and other wet substances.

4. Light Energy
Light is a form of energy which travels
in the form of wave. It contains a particle called photon which are the minute
packets of energy. It is the only form of energy visible to human eye. Light
does not require any medium to travel. It travels at a speed of 3,00,000 km/s.
Sunlight takes 8 minutes to reach earth.
Do you know?
Study of light is known as
optics.
Uses of light energy
• We are able to see objects with the
help of light energy.
• Plants use light energy to synthesis
their food.
• With the help of light energy, our
skin is able to synthesis Vitamin-D.
• Electricity can be produced with the
help of light energy.

5. Electrical energy
We
know that all things are made up of atoms. Atoms posses particles like protons,
electrons and neutrons. Movement of electron in the objects causes an energy.
This energy is called electric energy. In our daily life we use batteries to
get electric energy. Electric energy is also generated from nuclear power
plants, hydroelectric plants and wind mills. It is also generated from solar
energy.
Do you know?
‘Electric eel’ generates electric
energy. It uses this energy to defend itself against its predators.

Uses of Electric energy
• Electric energy is needed for the
working of fan, light, television, washing machine, refrigerator etc.
• Electric iron box, electric stove and
electric water heater work by electrical energy.
• It is used to run cars and trains.
• It is used in factories to produce
materials.

Activity 5
Mention few
places where electric energy is generated in
plants.
6. Chemical energy
Chemical
energy is stored in subtances when atoms join together to form chemical
compounds. When two or more chemical substances react with each other, this
energy is released.
Uses of chemical energy
• The food we eat contains chemical
energy.
• Chemical energy in wood provides heat
energy which helps us to cook food.
• Chemical energy in coal is used to
generate electricity.
• Batteries we use in our daily life
contain chemical energy.
• Fuels like petrol and diesel posses
chemical energy which is used to run vehicles.

Activity 6
Observe the stove burning in your kitchen. Do you see the light and feel the heat? Where do you get these from?
Yes I see light and feel heat. These are from fire.
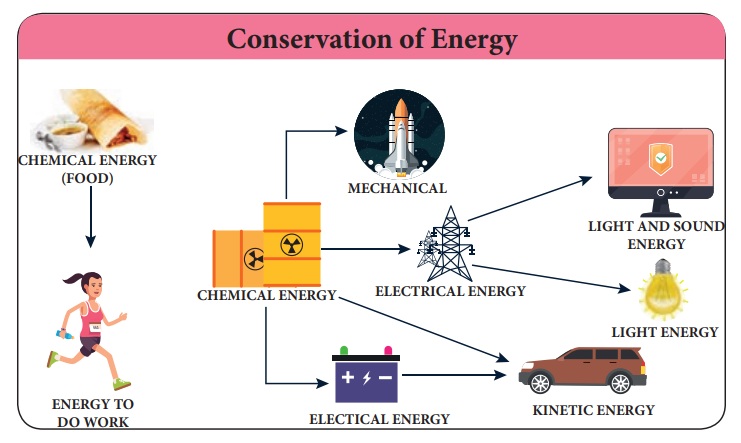
II. Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created and it cannot
be destroyed also. It is changed from one form to another form or transferred
from one object to another object. We can say many examples for conservation of
energy in our daily life.
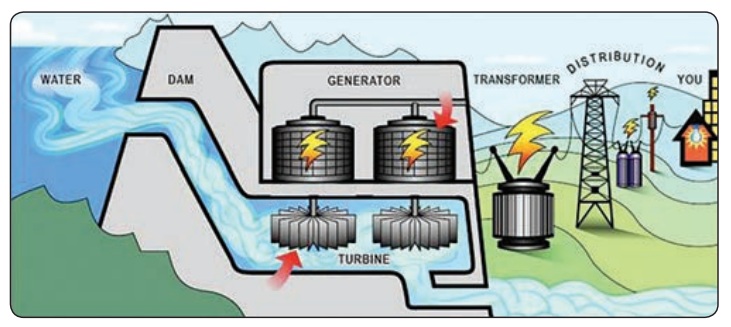
1. Water Dam
Water stored in water dams posseses
potential energy. When water falls down, potential energy of water is converted
into kinetic energy. Kinetic energy of water rotates the turbines and electric
energy is generated.
Do you know?
Law of conservation of
energy states that energy can neither be created nor be destroyed. One form of
energy is converted into another form of energy.
This law was given by
Julius Robert Mayar.
2. Electrical Appliances
Electric
energy is used in many domestic appliances such as electric stove, iron box and
fan. Electric energy flows into the coil in the devices. As current flows, it
heats up the coil. With the help of this heat energy, we do many useful works.
Thus, electrical energy is converted into heat energy. Electical energy is converted
to mechanical energy in fan, light enrgy in bulb and sound energy in computer.

3. Driving a Car
We use fuel in the form of petrol or diesel or gas to run vehicles. When this fuel burns in the engine, chemical energy is converted into heat energy. Burning fuel produces hot gases which pushes the piston in the engine to move the vehicle. Thus heat energy is converted into mechanical energy.
Do you know?
Photosynthesis changes solar energy into chemical energy.
Related Topics