Chapter: Mechanical : Unconventional machining process : Electrical Based Processes
Electrical Based Processes
ELECTRICAL
BASED PROCESSES
ELECTRICAL
BASED PROCESSES
•
Electrical
Discharge `Machining (EDM)
•
Wire
Cut Electrical Discharge Machining (WCEDM)
1.
Electrical Discharge `Machining (EDM)
Electrical
discharge machining (EDM) is one of the most widely used non-traditional
machining processes. The main attraction of EDM over traditional machining
processes such as metal cutting using different tools and grinding is that this
technique utilizes thermoelectric process to erode undesired materials from the
work piece by a series of discrete electrical sparks between the workpiece and
the electrode. A picture of EDM machine in operation

The traditional machining processes
rely on harder tool or abrasive material to remove the softer material whereas
non -traditional machining processes such as EDM uses electrical spark or
thermal energy to erode unwanted material in order to create desired shape. So,
the hardness of the material is no longer a dominating factor for EDM process.
A schematic of an EDM process is shown in Figure 2, where the tool and the
workpiece are Immersed in a dielectric fluid.
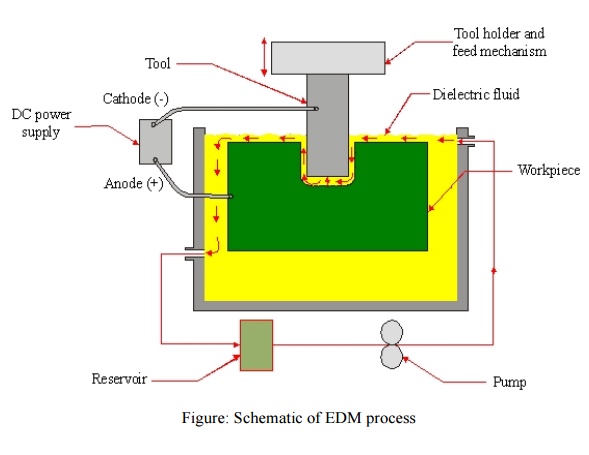
Figure: Schematic of EDM process
EDM
removes material by discharging an electrical current, normally stored in a
capacitor bank, across a small gap between the tool (cathode) and the workpiece
(anode) typically in order
1. Application of EDM
The EDM process has the ability to
machine hard, difficult-to-machine materials. Parts with complex, precise and
irregular shapes for forging, press tools, extrusion dies, difficult internal
shapes for aerospace and medical applications can be made by EDM process. Some
of the shapes made by EDM process are shown in Figure.

Figure: Difficult internal parts
made by EDM process
2. Working principle of EDM
As
shown in Figure 1, at the beginning of EDM operation, a high voltage is applied
across the narrow gap between the electrode and the workpiece. This high
voltage induces an electric field in the insulating dielectric that is present
in narrow gap between electrode and workpiece. This cause conducting particles
suspended in the dielectric to concentrate at the points of strongest
electrical field. When the potential difference between the electrode and the
workpiece is sufficiently high, the dielectric breaks down and a transient
spark discharges through the dielectric fluid, removing small amount of
material from the workpiece surface.
![]()
The volume of the material removed
per spark discharge is typically in the range of 10-6 to 10-6 mm3.
The material removal rate, MRR, in
EDM is calculated by the following formula: MRR = 40 I / Tm 1.23 (cm3/min)
Where, I is the current amp, TM is
the melting temperature of workpiece in 0C
3. Advantages of EDM
The main advantages of DM are:
•
By
this process, materials of any hardness can be machined;
•
No
burrs are left in machined surface;
•
One
of the main advantages of this process is that thin and fragile/brittle
components
can be machined without distortion;
• Complex
internal shapes can be machined
3. Limitations of EDM
The main limitations of this process
are:
•
This
process can only be employed in electrically conductive materials;
•
Material
removal rate is low and the process overall is slow compared to conventional
machining processes;
•
Unwanted
erosion and over cutting of material can occur;
•
Rough
surface finish when at high rates of material removal.
4. Dielectric fluids
Dielectric fluids used in EDM
process are hydrocarbon oils, kerosene and deionised water. The functions of
the dielectric fluid are to:
•
Act
as an insulator between the tool and the workpiece.
•
Act
as coolant.
•
Act
as a flushing medium for the removal of the chips.
The electrodes for EDM process
usually are made of graphite, brass, copper and copper-tungsten alloys.
5. Design considerations for EDM process are as follows:
•
Deep
slots and narrow openings should be avoided.
•
The
surface smoothness value should not be specified too fine.
•
Rough
cut should be done by other machining process. Only finishing operation should
be done in this process as MRR for this process is low.
2
WIRE CUT ELECTRICAL DISCHARGE MACHINING (WCEDM)
EDM,
primarily, exists commercially in the form of die-sinking machines and
wire-process, a slowly moving wire travels along a prescribed path and removes
material from the workpiece. Wire EDM uses electro-thermal mechanisms to cut
electrically conductive materials. The material is removed by a series of
discrete discharges between the wire electrode and the workpiece in the
presence of dielectric fluid, which creates a path for each discharge as the
fluid becomes ionized in the gap. The area where discharge takes place is
heated to extremely high temperature, so that the surface is melted and
removed. The removed particles are flushed away by the flowing dielectric
fluids.
The wire EDM process can cut
intricate components for the electric and aerospace industries. This
non-traditional machining process is widely used to pattern tool steel for die
manufacturing cutting machines (Wire EDM). The concept of wire EDM is shown in
Figure . In this
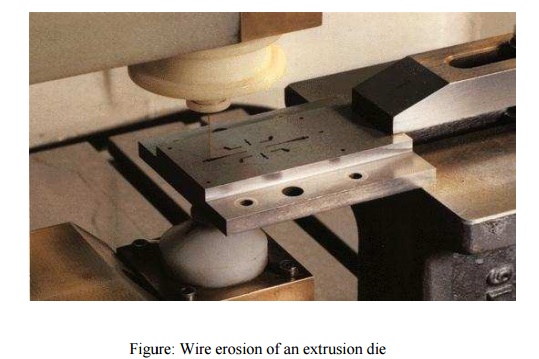
Figure: Wire erosion of an extrusion
die
The wires for wire ED M is made of
brass, copper, tungsten, molybdenum. Zinc or brass coated wires are also used
extensively in this process. The wire used in this process should posse’s high
tensile strength and good e lectrical conductivity. Wire EDM can also employ to
cut cylindrical objects with high precision. Th e sparked eroded extrusion dies
are presented in Figure.
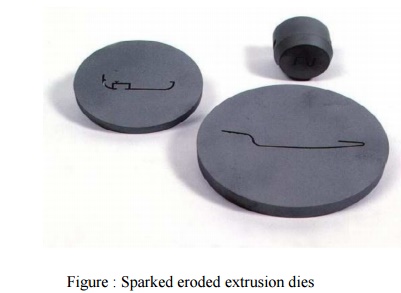
Figure : Sparked eroded extrusion
dies
This
process is usually used in conjunction with CNC and will only work when a part
is to be cut completely through. T he melting temperature of the parts to be
machined is an important parameter for this process rather than strength or
hardness. The surface quality and MRR of the machined surface by wire EDM will
depend on different machining parameters such as applied peak current, an d
wire materials.
The wires for wire EDM is made of
brass, copper, tungsten, molybdenu m. Zinc or brass coated wires are also used
extensively in this process. The wire used in this process should posses’ high
tensile strength and good electrical con ductivity. Wire EDM can also employ to
cut cylindrical objects with high precision. The sparked eroded extrusion dies
are presented in Figure 5.

Figure: Sparked eroded extrusion
dies
This process is usually used in
conjunction with CNC and will only work when a part is to be cut completely
through. T he melting temperature of the parts to be machined is an important
parameter for this process rather than strength or hardness. The surface
quality and MRR of the machined surface by wire EDM will depend on different
machining parameters such as applied peak current, an d wire materials.
Related Topics