Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Indian Economy Economic status Higher secondary school College
Elasticity of supply : concept, Types, Factors determining
Elasticity of Supply
The law of supply tells us that quantity supplied will respond to a change in price. The concept of elasticity of supply explains the rate of change in supply as a result of change in price. It is measured by the formula mentioned below
Elasticity of supply = Proportionate change in quantity / supplied Proportionate change in price
ep = ( ∆ qs / qs ) / (∆ p / p)
Where q represents the amount supplied, p represents price, ∆ - a change.
Elasticity of supply may be defined as 'the degree of responsiveness of change in supply to change in price on the part of sellers'.
Types of elasticity of supply
There are five types of elasticity of supply.
1. Perfectly elastic supply
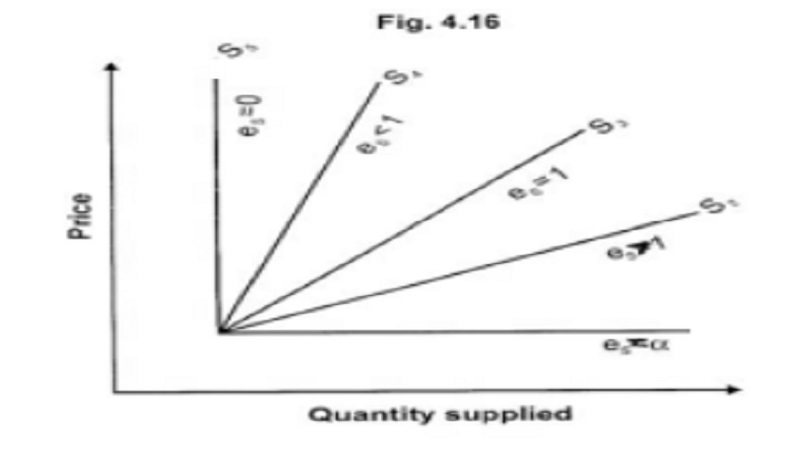
The coefficient of elasticity of supply is infinity. (eS is ∞ ). For a small change or no change in price, there will be infinite amount of supply. (SS1 in Figure)
2. Relatively elastic supply
The coefficient of elastic supply is greater than 1(es > 1). Quantity supplied changes by a larger percentage than price. (SS2 in figure 4.16)
3. Unitary elastic supply
The coefficient of elastic supply is equal to 1 (es = 1). A change in price will cause a proportionate change in quantity supplied. (SS3 in figure)
4. Relatively inelastic supply
The coefficient of elasticity is less than one (es < 1). Quantity supplied changes by a smaller percentage than price. (SS4 in figure)
5. Perfectly inelastic supply
The coefficient of elasticity is equal to zero (es = 0). A change in price will not bring about any change in quantity supplied. (SS5in figure)
Factors determining elasticity of supply
The following factors will influence the elasticity of supply
1. Changes in cost of production
2. Behaviour pattern of producers
3. Availability of facilities for expanding output.
4. Supply in the short and long period.
Related Topics