Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Indian Economy Economic status Higher secondary school College
Educational progress in Tamil Nadu
Educational
progress in Tamil Nadu.
Tamil
Nadu is an educationally progressive state in India. In literacy, it is one of
the three top states and it is next only to Kerala and Maharashtra. The
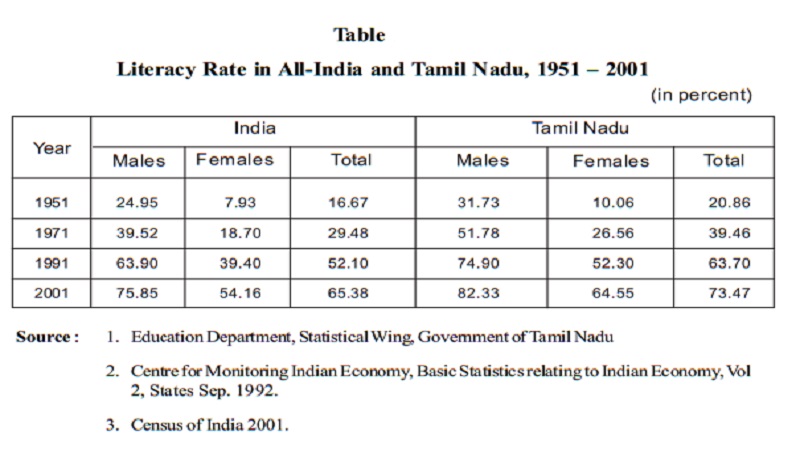
progress of education in Tamil Nadu in terms of literacy is given in Table. The literacy rates for both males and females are more than the national
average. According to 2001 census, the overall literacy rate for Tamil Nadu was
73.47 as against the national average of 65.38 percent.
Between
1991 and 2001, the percentage of enrolment at the secondary level has increased
from 13 percent to 59 percent.
There
was a steady increase in educational expenditure in Tamil Nadu from 1962-63 to
2000 - 2001. During the period, the expenditure on education increased from
Rs.26 crores to Rs.4949 crores. This is a remarkable increase.
The
National Policy on Education (NPE) 1986 of the Government of India gave first
priority to Universal Primary Education (UPE). The UPE goal aimed at
achievement of Education for All (EPA) covering only classes I and V.
The
main factors which influenced steady increase in enrolment of children in age
group 6-11 years in Tamil Nadu are : (1) easy accessibility of schools ; (2)
awareness among parents about the value of education ; 3) rising real per
capita income ; (4) implementation of Chief Minister's Nutritious Noon Meal
Scheme and 5) a number of inducements and concessions offered by the Government
in the form of free supply of books, free bus passes and so on.
Access
to schools, in terms of distance, is a major factor that has made Tamil Nadu
one of the three top states in literacy level. There is a primary school within
a distance of one kilometre from habitations (99 percent of habitations), upper
primary school within a distance of 3 kms (81 percent of habitations),
secondary school within a distance of 5 kms (78 percent of habitations) and
higher secondary school within a distance of 8 kms (76 percent of habitations).
This is a remarkable achievement when compared with the all - India situation.
In
recent years, there has been a decline in dropout rate. This has been made
possible by many factors such as Chief Minister's Nutritious Noon Meal scheme,
free health check ups, free education and other concessions like free bus
passes, slates, books and uniforms.
District Primary Education Programme
(DPEP) : The DPEP has been introduced with the object of achieving the goal of
universal primary education. It focuses on reducing gender disparities in
education.
Non-Formal Education and Adult
Literacy : The measures taken by the Government of Tamil Nadu under adult education
programme include :
Total Literacy campaign (TLC),
Post - Literacy campaign and
Continuing Education
All
these measures come under Arivoli Iyakkam
(Light of Knowledge movement). In this movement, an adult is defined as one in
the age group 15-35.
Related Topics