Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Indian Economy Economic status Higher secondary school College
Determination of Equilibrium price and output under monopolistic competition
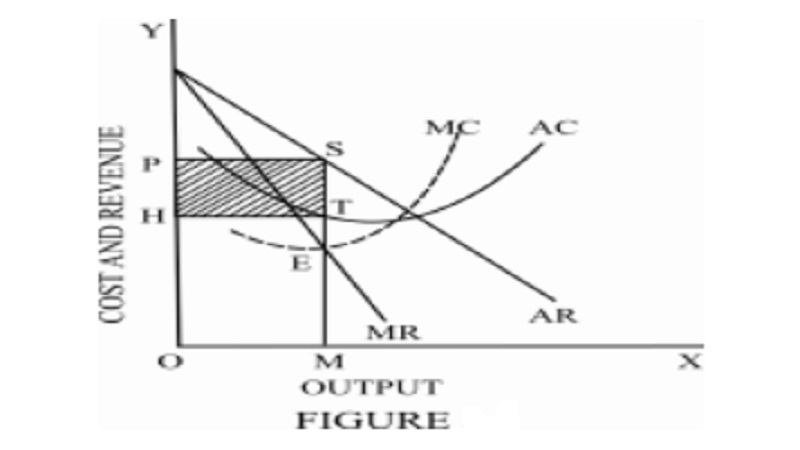
Determination of Equilibrium price
and output under monopolistic competition
The monopolistic competitive firm will come to equilibrium
on the principle of equalising MR with MC. Each firm will choose that price and
output where it will be maximising its profit. Figure shows the equilibrium of
the individual firm in the short period.
MC and AC are the short period marginal cost and average
cost curves. The sloping down average revenue and marginal revenue curves are
shown as AR and MR. The equilibrium point is E where MR = MC. The equilibrium
output is OM and the price of the product is fixed at OP. The difference
between average cost and average revenue is SQ. The output is OM. So, the
supernormal profit for the firm is shown by the rectangle PQSR. The firm by
producing OM units of its commodity and selling it at a price of OP per unit
realizes the maximum profit in the short run.
The different firms in monopolistic competition may be
making either abnormal profits or losses in the short period depending on their
costs and revenue curves.
In the long run, if the existing firms earn super normal
profit, the entry of new firms will reduce its share in the market. The average
revenue of the product will come down. The demand for factors of production
will increase the cost of production. Hence, the size of the profit will be
reduced. If the existing firms incur losses in the long-run, some of the firms
will leave the industry increasing the share of the existing firms in the
market. As the demand for factors becomes less, the price of factors will come
down. This will reduce the cost of production, which will increase the profit
earned by the existing firm. Thus under monopolistic competition, all the
existing firms will earn normal profit in the long run.
Related Topics