Chapter: Civil : Construction Materials: Stones, Bricks,Concrete Blocks
Classification Of Bricks
Classification Of Bricks
On Field Practice
Clay bricks are classified as
first class, second class, third class and fourth class based on their physical
and mechanical properties.
First Class Bricks
1. These are
thoroughly burnt and are of deep red, cherry or copper colour.
2. The
surface should be smooth and rectangular, with parallel, sharp and straight
edges and square corners.
3. These
should be free from flaws, cracks and stones.
4. These
should have uniform texture.
5. No
impression should be left on the brick when a scratch is made by a finger nail.
6. The
fractured surface of the brick should not show lumps of lime.
7. A
metallic or ringing sound should come when two bricks are struck against each other.
9. Water absorption should be 12-15% of
its dry weight when immersed in cold water for 24 hours. The crushing strength
of the brick should not be less than 10 N/mm2. This limit varies
with different Government organizations around the country.
Uses: First class bricks are recommended for
pointing, exposed face work in masonry structures, flooring and reinforced
brick work.
Second Class Bricks are
supposed to have the same requirements as the first class ones except that
1. Small
cracks and distortions are permitted.
2. A little
higher water absorption of about 16-20% of
its dry weight is allowed.
3. The
crushing strength should not be less than 7.0 N/mm2.
Uses: Second class bricks are
recommended for all important or unimportant hidden masonry works and centering
of reinforced brick and reinforced cement concrete (RCC) structures.
Third Class Bricks are
underburnt. They are soft and light-coloured producing a dull sound when struck
against each other. Water absorption is about 25 per cent of dry weight.
Uses : It is used for building temporary structures.
Fourth Class Bricks are
overburnt and badly distorted in shape and size and are brittle in nature. Uses:
The ballast of such bricks is used for foundation and floors in lime concrete
and road metal.
On Strength
The Bureau of Indian Standards
(BIS) has classified the bricks on the basis of compressive strength and is as
given in Table 2
Table 2 Classification of Bricks based on
Compressive Strength (IS: 1077)
Class : Average compressive
strength not less than (N/mm2)
35 35.0
30 30.0
25 25.0
20 20.0
17.5 17.5
15 15.0
12.5 12.5
10 10.0
7.5 7.5
5 5.0
3.5 3.5
Notes: 1. The burnt clay
bricks having compressive strength more than 40.0 N/mm 2 are known
as heavy duty bricks and are used for heavy duty structures such as bridges,
foundations for industrial buildings, multistory buildings, etc. The water
absorption of these bricks is limited to 5 per cent.
2. Each
class of bricks as specified above is further divided into subclasses A and B
based on tolerances and shape. Subclass-A bricks should have smooth rectangular
faces with sharp corners and uniform colour. Subclass-B bricks may have
slightly distorted and round edges.
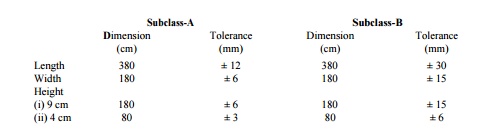
Subclass-A Subclass-B
Dimension(cm) Tolerance(mm) Dimension(cm) Tolerance(mm)
Length 380 ±
12 380 ± 30
Width 180 ±
6 180 ± 15
Height
(i)
9 cm 180 ± 6 180 ± 15
(ii)
4 cm 80 ± 3 80 ± 6
On the Basis of Use
Common Brick is a
general multi-purpose unit manufactured economically without special reference
to appearance. These may vary greatly in strength and durability and are
used for filling, backing and in walls where appearance is of no consequence.
Facing Bricks are made
primarily with a view to have good appearance, either of colour or texture or
both. These are durable under severe exposure and are used in fronts of
building walls for which a pleasing appearance is desired.
Engineering Bricks are
strong, impermeable, smooth, table moulded, hard and conform to defined limits
of absorption and strength. These are used for all load bearing structures.
On the Basis of Finish
Sand-faced Brick has
textured surface manufactured by sprinkling sand on the inner surfaces of the
mould.
Rustic Brick has mechanically textured
finish, varying in pattern.
On the Basis of Manufacture
Hand-made: These bricks are hand moulded.
Machine-made: Depending
upon mechanical arrangement, bricks are known as wire-cut bricks-bricks
cut from clay extruded in a column and cut off into brick sizes by wires;
pressed-bricks-when bricks are manufactured from stiff
plastic or semi-dry clay and pressed into moulds; moulded bricks-when
bricks are moulded by machines imitating hand mixing.
On the Basis of Burning
Pale Bricks are underburnt
bricks obtained from outer portion of the kiln. Body Bricks are well
burnt bricks occupying central portion of the kiln.
Arch
Bricks are overburnt also known as clinker bricks obtained from inner
portion of the kiln.
On the Basis of Types
Solid: Small
holes not exceeding 25 per cent of the volume of the brick are permitted;
alternatively, frogs not exceeding 20 per cent of the total volume are
permitted.
Perforated: Small holes may exceed 25 per
cent of the total volume of the brick.
Hollow: The total
of holes, which need not be small, may exceed 25 per cent of the volume of the
brick. Cellular: Holes closed at one end exceed 20 per cent of the
volume.
Note:
Small holes are less than 20 mm or less than 500 mm2 in cross
section.
Related Topics