Chapter: 9th Science : Universe
Building Block of the Universe
Building Block of the Universe
The basic constituent of
the universe is luminous matter i.e., galaxies which are really the collection
of billions of stars. The universe contains everything that exists including
the Earth, planets, stars, space, and galaxies. This includes all matter,
energy and even time. No one knows how big the universe is. It could be
infinitely large. Scientists, however, measure the size of the universe
by what they can see. This is called the ŌĆśobservable universeŌĆÖ. The observable
universe is around 93 billion light years (1 light year = the distance that
light travels in one year, which is 9.4607 ├Ś 1012 km) across.
One of the interesting
things about the universe is that it is currently expanding. It is growing
larger and larger all the time. Not only is it growing larger, but the edge of
the universe is expanding at a faster and faster rate. However, most of the
universe what we think of is empty space. All the atoms together only make up
around four percent of the universe. The majority of the universe consists of
something scientists call dark matter and dark energy.
1. Age of the universe
Scientists think that
the universe began with the start of a massive explosion called the Big Bang.
According to Big Bang theory, all the matter in the universe was concentrated
in a single point of hot dense matter. About 13.7 billion years ago, an
explosion occurred and ejected all the matter in all directions in the form of
galaxies. Nearly all of the matter in the universe that we understand is made
of hydrogen and helium, the simplest elements, created in the Big Bang. The
rest, including the oxygen that we breathe, the carbon, calcium, and iron in
our bodies, and the silicon in our computer chips are formed in the cores of
stars.

The gravity that holds these stars together generally keeps these elements deep inside their interiors. When these stars explode, these fundamental building blocks of planetary systems are liberated throughout the universe.
2. Galaxies
According to astronomers
galaxies were formed shortly after the Big Bang that happened 10 billion to
13.7 billion years ago. Immediately after the Big Bang, clouds of gases began
to compress under gravity to form the building blocks of galaxies. A galaxy is
a massive collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar
systems. Scientists believe that there are one hundred billion (1011)
galaxies in the observable universe. The size of the galaxies ranges having a
few hundred million (108) stars to one hundred trillion (1014)
stars. Galaxies are also in different shapes. Depending on their appearance
galaxies are classified as spiral, elliptical, or irregular. Galaxies occur
alone or in pairs, but they are more often parts of groups, clusters, and super
clusters. Galaxies in such groups often interact and even merge together.

Our Sun and all the
planets in the solar system are in the Milky Way galaxy. There are many
galaxies besides our Milky Way. Andromeda galaxy is our closest neighboring
galaxy. The Milky Way galaxy is spiral in shape. It is called Milky Way because
it appears as a milky band of light in the sky. It is made up of approximately
100 billion stars and its diameter is 1,00,000 light years. Our solar system is
25,000 light years away from the centre of our galaxy. Just as the Earth goes
around the Sun, the Sun goes around the centre of the galaxy and it takes 250
million years to do that.

3. Stars
Stars are the
fundamental building blocks of galaxies. Stars were formed when the galaxies
were formed during the Big Bang. Stars produce heat, light, ultraviolet rays,
x-rays, and other forms of radiation. They are largely composed of gas and
plasma (a superheated state of matter). Stars are built by hydrogen gases.
Hydrogen atoms fuse together to form helium atoms and in the process they
produce large amount of heat. In a dark night we can see nearly 3,000 stars
with the naked eye. We donŌĆÖt know how many stars exist. Our universe contains
more than 100 billion galaxies, and each of those galaxies may have more than
100 billion stars.

Though the stars appear
to be alone, most of the stars exist as pairs. The brightness of a star depends
on their intensity and the distance from the Earth. Stars also appear to be in
different colours depending on their temperature. Hot stars are white or blue,
whereas cooler stars are orange or red in colour.
They also occur in many
sizes. Some stars have radii a thousand times larger than that of our own Sun.
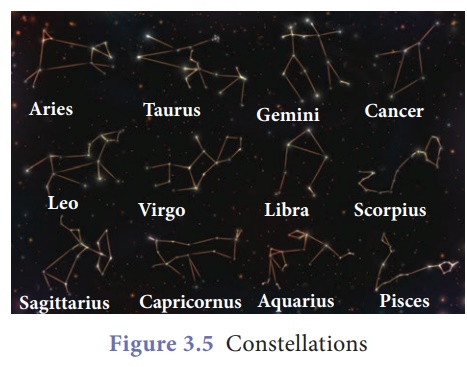
A group of stars forms
an imaginary outline or meaningful pattern on the space. They represent an
animal, mythological person or creature, a god, or an object. This group of
stars is called constellations. People in different cultures and countries
adopted their own sets of constellations outlines. There are 88 formally
accepted constellations. Aries, Gemini, Leo, Orion, Scorpius and Cassiopeia are
some of the constellations.
Related Topics