Organisation of Tissues | Biology | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Biology : Organisation of Tissues
Chapter: 9th Science : Biology : Organisation of Tissues
Answer the following questions
ORGANISATION
OF TISSUES
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
V. Answer briefly:
1. What are intercalary
meristems? How do they differ from other meristems?
Answer:
(i)
It lies between the region of permanent tissues and is part of primary
meristem. It is found either at the base of leaf e.g. pinus or at the base of
intermodes e.g. Grasses.
(ii)
It differs from apical meristem which is found in apices or growing points and
from lateral meristem which are arranged parallel and causes the thickness of
the plant part.
(iii)
Further apical meristem brings about increase in length and lateral meristem,
brings about increase in thickness of the plant. Intercalary meristem helps in
production of branches.
2. What is complex tissue? Name
the various kinds of complex tissues.
Answer:
(i)
Complex tissues are made of more than one type of cells that work together as a
unit.
(ii)
Complex tissues consist of parenchyma and
sclerenchyma cells. However, collenchymatous cells are not present in
such tissues.
(iii)
Common examples are xylem and phloem.
3. Mention the most abundant
muscular tissue found in our body. State its function.
Answer: Skeletal
muscle is the most abundant muscular tissue found in our body.
Functions:
(i)
These muscles are attached to the bones and are responsible for the body
movements and are called skeletal muscles.
(ii)
They work under our control and are also known as voluntary muscles.
(iii)
They possess many nuclei (multinucleate).
(iv)
For example they occur in the biceps and triceps of arms and undergo rapid
contraction.
4. What is skeletal connective
tissue? How is it helpful in the functioning of our body?
Answer: The
supporting or skeletal connective tissues forms the endoskeleton of the
vertebrate body. They protect various organs and help in locomotion. The
supportive tissues include cartilage and bone.
5. Why should gametes be produced
by meiosis during sexual reproduction?
Answer: In
meiosis, daughter cells formed after cell division have half the number of
chromosomes as compared to parent cell. When gametes are formed by meiosis they
will have half the number of chromosomes (haploid). When a haploid male gamete
and haploid female gamete fuse during sexual reproduction the zygote will be
diploid ie., It will have the same number of chromosomes like the parent cell.
This is very important because any abnormality in the number of chromosomes in
the zygote will lead to disorders.
6. In which stage of mitosis the
chromosomes align in an equatorial plate? How?
Answer: Metaphase (meta - after) The
duplicated chromosomes arrange on the equatorial plane and form the metaphase
plate. Each chromosome gets attached to a spindle fibre by its centromere. The
centromere of each chromosome divides into two each being associated with a
chromatid.
VI. Answer In detail:
1. What are permanent tissues?
Describe the different types of simple permanent tissues.
Answer:
Permanent tissues:
Permanent
tissues are those in which, growth has stopped either completely or for the
time being. At times, they become meristematic partially or wholly.
Different types of
simple permanent tissue:
Simple tissue: Simple
tissue are homogeneous-composed of structurally and functionally similar cells.
Eg : Parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Parenchyma:
(i)
Parenchyma are simple permanent tissue composed of living cells.
(ii)
Parenchyma cells are thin walled, oval, rounded or polygonal in shape with well
developed spaces among them.
(iii)
In aquatic plants, parenchyma possesses intercellular air spaces, and is named
as aerenchyma.
(iv)
When exposed to light, parenchyma cells may develop chloroplasts and are known
as chlorenchyma.
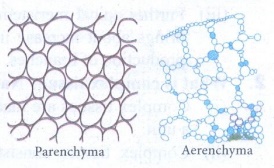
Functions:
Parenchyma may store water in many succulent and xerophytic plants. It also
serves the functions of storage of food reserves, absorption, buoyancy,
secretion etc.,
Collenchyma:
(i)
Collenchyma is a living tissue found beneath the epidermis.
(ii)
Cells are elongated with unevenly thickened walls. Cells have rectangular
oblique or tapering ends and persistent protoplast.
(iii)
They possess thick primary non-lignified walls.
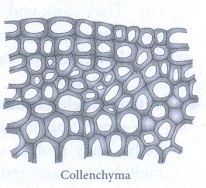
Functions: They
provide mechanical support for growing organs.
Sclerenchyma:
(i)
Sclerenchyma consists of thick walled cells which are often lignified.
(ii)
Sclerenchyma cells do not possess living protoplasts at maturity. Sclerenchyma
cells are grouped into (i) fibres and (ii) sclereids.
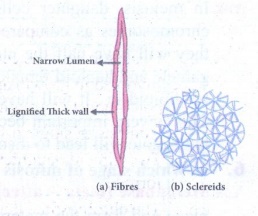
Fibres: Elongated
sclerenchymatous cells, usually with pointed ends. Their walls are lignified.
Fibres are abundantly found in many plants. Eg. Jute.
Sclereids:
(i)
Sclereids are widely distributed in plant body. They are usually broad, may
occur in single or in groups.
(ii)
Sclereids are isodiametric, with lignified walls. Pits are prominent and seen
along the walls.
(iii)
Lumen is filled with wall materials. Sclereids are also common in fruits and
seeds.
2. Write about the elements of
Xylem.
Answer:
Xylem:
(i)
Xylem is a conducting tissue which conducts water, mineral nutrients upward
from root to leaves.
(ii)
Xylem is composed of (1) xylem tracheids (2) xylem fibres (3) xylem vessels and
(4) xylem parenchyma.
(1) Xylem
tracheids:
1.
They are elongated or tube-like dead cells with hard, thick and lignified
walls.
2.
Their ends are tapering, blunt or chisel - like and are devoid of protoplast.
They
have large lumen without any content.
3.
Their function is conduction of water and providing mechanical support to the plant.
(2) Xylem fibres
1.
These cells are elongated, lignified and pointed at both the ends.
2.
Xylem fibres provide mechanical support to the plant.
(3) Xylem vessels
1.
They are long cylindrical, tube like structures with lignified walls and wide
central lumen.
2.
These cells are dead as these do not have protoplast.
3.
They are arranged in longitudinal series in which the partitioned walls
(transverse walls) are perforated, and so the entire structure looks-like a
water pipe.
4.
Their main function is transport of water and minerals from root to leaf, and
also to provide mechanical strength.
(4) Xylem
parenchyma
These
are living and thin walled. The main function of xylem parenchyma is to store
starch and fatty substances.
3. List out the differences between
mitosis and meiosis.
Answer:

Mitosis
1.
Occurs in somatic cells.
2.
Involved in growth and occurs continuously throughout life.
3.
Consists of single division.
4.
Two diploid daughter cells are formed.
5.
The chromosome number in the daughter cell is similar to the parent cell (2n).
6.
Identical daughter cells are formed.
Meiosis
1.
Occurs in reproductive cells
2.
Involved in gamete formation only during the reproductively active age.
3.
Consists of two divisions.
4.
Four haploid daughter cells are formed.
5.
The chromosome number in the daughter cell is just half (n) of the parent cell.
6.
Daughter cells are not similar to the parent cell and are randomly assorted.
VII. Higher Order
Thinking Skills:
1. What is the consequence that
occur if all blood platelets are removed from the blood?
Answer: Blood
platelets play a major role in clotting of blood whenever there is a wound/
injury. If blood platelets are removed from the blood, clotting of blood will not
occur. Incase of any injury/surgery etc., blood will be lost from the body in
excess and may even prove to be fatal.
2. Which are not true cells in
the blood? Why?
Answer: Red
blood cells or erythrocytes cannot be considered as true cells since they have a
nucleus only in the early stages. A mature RBC lacks a nucleus which is the
controlling centre of all living cells.
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY - 1
Rinse your mouth with water.
Using a tooth pick or ice-cream stick, scrap superficial cells from inner side
of the cheek and spread it on a clean glass slide. Dry the glass slide with the
scrap cells taken from the inner side of cheek. Add two drops of methylene blue
stain. Identify the cells under low and high power of the microscope.
Solution:
1.
Large irregularly shaped cells with cell walls.
2.
Dark blue nucleus at the central part of each cell.
3.
Lightly stained cytoplasm colour in each cell.
Related Topics