Animal Kingdom | Biology | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Biology : Animal Kingdom
Chapter: 9th Science : Biology : Animal Kingdom
Answer the following questions
ANIMAL
KINGDOM
TEXT BOOK EXCERCISES
V. Answer very briefly:
1. Define taxonomy.
Answer: Taxonomy
is the science of classification which makes the study of wide variety of
organisms easier and helps us to understand the relationship among different
group of animals.
2. What is nematocyst?
Answer: The
tentacles of organism belonging to phylum coelenterata bear stinging cells
called cnidoblast or nematocyst.
3. Why coelenterates are called
diploblastic animals?
Answer: The body
wall of coelenterates is diploblastic with two layers, namely outer ectoderm
and inner endoderm separated by non-cellular jelly -like substance called mesoglea.
Due to presence of two layers in body wall, they are said to be diploblastic
animals.
4. List the respiratory organs of
amphibians.
Answer:
Respiration is through by gills, skin, buccopharynx and lungs.
5. How does locomotion take place
in starfish?
Answer:
Locomotion in starfish is affected by tube feet.
6. Are jellyfish and starfish
similar to fishes? If no justify the answer
Answer:
(i)
Jelly fish is a coelenterate. Their bodies are
made of calcium carbonate.
(ii)
Starfish fish is an echinoderm.
(iii)
Cat fish is a fish species.
(iv)
Jelly fish and star fish are invertebrates.
(v)
Fishes are vertebrates.
7. Why are frogs said to be
amphibians?
Answer: They are
the first vertebrates to live on land with dual adaptation to live in aquatic and land
environments. This double life is expressed as amphibious.
VI. Answer briefly:
1. Give an account on phylum
Annelida.
Answer: (i) These
are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, first true coelomate animals with
organ-system grade of organization.
(ii)
Body is externally divided into segments called metameres joined by ring like
structures called annuli.
(iii)
It is covered by moist thin cuticle.
(iv)
Setae and parapodia are locomotor organs.
(v)
Sexes may be separate or united (hermaphrodites), e.g- Nereis, Earthworm,
Leech.
2. Differentiate between flat
worms and round worms?
Answer:
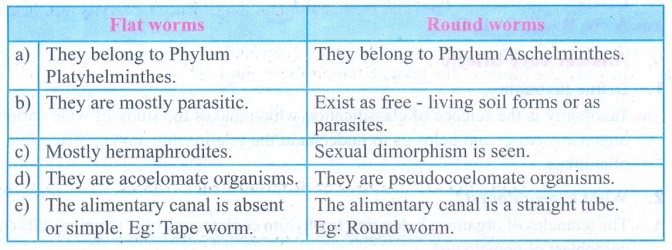
Flat worms
•
They belong to Phylum Platyhelminthes.
•
They are mostly parasitic.
•
Mostly hermaphrodites.
•
They are acoelomate organisms.
•
The alimentary canal is absent or simple.
•
Eg: Tape worm.
Round worms
•
They belong to Phylum Aschelminthes.
•
Exist as free - living soil forms or as parasites.
•
Sexual dimorphism is seen.
•
They are pseudocoelomate organisms.
•
The alimentary canal is a straight tube.
•
Eg: Round worm.
3. Outline the flow charts of
Phylum Chordata.
Answer:
Flow chart of
phylum Chordata:
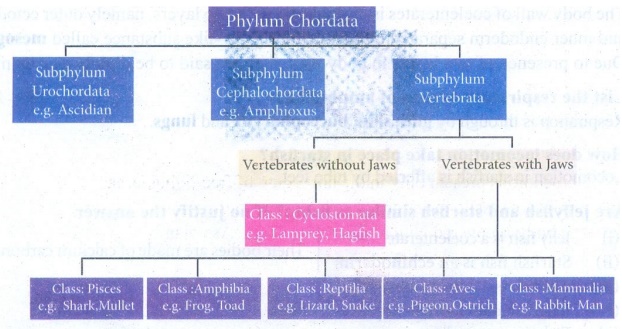
4. List five characteristic
features of fishes.
Answer:
(i)
Fishes are poikilothermic (cold-blooded), aquatic vertebrates with jaws.
(ii)
The streamlined
body is divisible into head, trunk and tail.
(iii)
Locomotion is by paired and median fins.
(iv)The
body has a covering of scales.
(v)
Respiration is through gills.
(vi)
The heart is two chambered with an auricle and a ventricle.
There
are two main types of fishes.
(i)
Cartilaginous fishes, with skeleton made of cartilages e.g. Sharks, Skates.
(ii)
Bony fishes with skeleton made of bones e.g. Carps, Mullets.
5. Comment on the aquatic and
terrestrial habits of amphibians.
Answer:
Aquatic habits of
amphibians:
(i)
The larva of amphibians (tadpole) lives in water and breathes with gills.
(ii)
External fertilization occurs in frog with water as a medium of fertilization.
(iii)
The adult frog has webbed feet to swim in water.
(iv)
The skin is moist and glandular which helps in Respiration.
Terrestrial habits
of amphibians:
(i)
The adults live on land and breathe through lungs. Bucco-pharynx also helps in
Respiration.
(ii)
The fore limbs are short and help to hop on land.
6. How are the limbs of the birds
adapted for avian life?
Answer: (i)
Forelimbs of birds are modified into wings with feathers for flight.
(ii)
The hind limbs are adapted for walking perching or swimming.
VII. Answer in detail:
1. Describe the characteristic
features of different Prochordates.
Answer:
Prochordata
(i)
The prochordates are considered as the forerunners of vertebrates.
(ii)
Based on the nature of the notochord, prochordata is classified into subphylum
Urochordata and subphylum Cephalochordata.
Subphylum
Urochordata:

(i)
Notochord is present only in the tail region of free-living larva.
(ii)
Adults are sessile forms and mostly degenerate.
(iii)
The body is covered with a tunic or test.
E.g. Ascidian
Subphylum
Cephalochordata
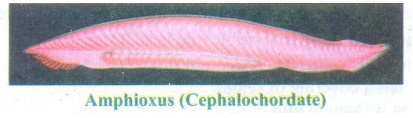
(i)
Cephalochordates are small fish like marine chordates with unpaired dorsal
fins.
(ii)
The notochord extends throughout the entire length of the body. E.g. Amphioxus
2. Give an account on phylum
Arthropoda.
Answer:
(i)
Arthropoda is the largest phylum of the animal kingdom.
(ii)
They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate animals.
(iii)
The body is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen.
(iv)
Each thorasic segment bears paired jointed legs.
(v)
Exoskeleton is made of chitin and is shed periodically as the animal grows.
(vi)
The casting off and regrowing of exoskeleton is called moulting.
(vii)
Body cavity is filled with haemolymph (blood).
(viii)
The blood does not flow in blood vessels and circulates throughout the body
(open circulatory system)..
(ix)
Respiration is through body surface, gills or tracheae
(air tubes).
(x)
Excretion occurs by malphigian tubules or green glands. Sexes are
separate. E.g., Prawn, Crab, Cockroach, Millipedes, Centipede, Spider,
Scorpion.
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY - 1
Identify the following pictures
of Arthropods

Observation:
1.
Scorpion
2.
Arachnid
3.
Cockroach
4.
Crab
5. Crustacean
Related Topics