Light | Physics | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Physics : Light
Chapter: 9th Science : Physics : Light
Answer the following questions
LIGHT
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
VI. Answer very briefly :
1.
According to cartesian sign convention, which mirror and which lens has
negative focal length?
Answer: Concave.
2.
Name the mirror(s) that can give (i) an erect and enlarged image, (ii) same
sized, inverted image.
Answer: Concave mirror.
3.
If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image
formed?
Answer: Infinity.
4.
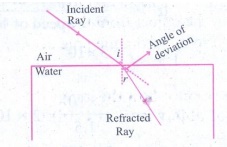
Why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium to another?
Answer: A ray of light bend when it travels from one
medium to another due to the change in velocity of light in two different
medium.
5.
What is the speed of light in vacuum?
Answer: The only medium in which speed of light is
equal to that in vacuum is air. Speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108
m/s. Armand Fizeau first measured the speed of light.
6.
Concave mirrors are used by dentists to examine teeth. Why?
Answer: As concave mirror produces virtual, erect and
magnified images when an object is placed in between focus and pole. So he can
clearly gets a magnified view of cavities.
VII. Answer briefly:
1. a) Complete the diagram to
show how a convave mirror forms the image of the object.
b. What is the nature of the
image?
Answer:
a) 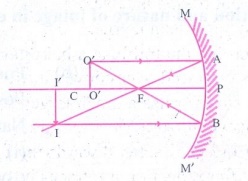
b)
Real, inverted and magnified.
2. Pick out the concave and
convex mirrors from the following and tabulate them. Rear-view mirror,
Dentist’s mirror, Torch-light mirror, Mirrors in shopping malls, Make-up
mirror.
Answer:

Concave Mirror
Dentist’s
mirror
Torch
light mirror
Make
up mirror
Convex Mirror
Rear
view mirror
Mirrors
in shopping malls
3. State the direction of
incident ray which after reflection from a spherical mirror retraces its path.
Give reason for your answer.
Answer: Incident
ray is directed towards the centre of curvature
Reason:
The ray is normal to the spherical mirror, so ∠i =0, ∠r=0
4. What is meant by
magnification? Write its expression. What is its sign for real image and
virtual image?
Answer: Magnification
is the increase in size of an image compared to true size.
Magnification
m = (height of the image h2 / height of the object h1)
=
( − image distance v / object
distance u)
So m = (h2/h1) = (− v/u )
(a)
Negative sign - real image
(b)
Positive sign - virtual image
5. Write the spherical mirror
formula and explain the meaning of each symbol used in it.
Mirror formula:
1 / f = (l / u)
+ ( 1 / v)
Here.
f- focal length of a spherical mirror
u - distance
of the object from the pole of the mirror
v - distance
of image from the pole of the mirror
VIII. Answer in detail:
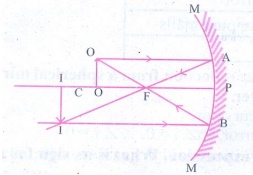
1. a) Draw ray diagrams to show
how the image is formed using a concave mirror, when the position of object is
(i) at C (ii) between C and F (iii) between F and P of the mirror.
b) Mention the position and
nature of image in each case.
Answer:
a)
(i) Object at C
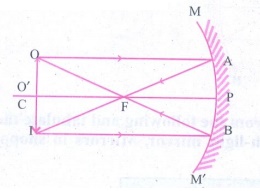
(b)
Position of object: At C
Position
of the image: At C
Nature
of the image:
(i)
Real
(ii)
Inverted
(iii)
Same size as object
(ii) Object between
C and F
Position
of object : Between C and F
Position
of the image : Beyond C
Nature
of the image :
(i)
Real
(ii)
Inverted
(iii)
Magnified
(iii) Object
between F and P of the mirror
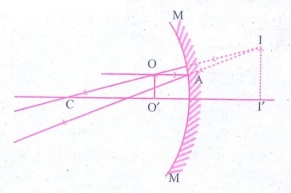
Position
of object : Between F and P
Position
of the image : Behind the Mirror
Nature
of the image :
(i)
Virtual
(ii)
Erect
(iii)
Magnified
2. Explain with diagrams how
refraction of incident light takes place from a) rarer to denser medium b)
denser to rarer medium c) normal to the surface separating the two media.
Answer:
a) rarer to denser
medium
When
a ray of light travels from optically rarer medium to optically denser medium,
it bends towards the normal.
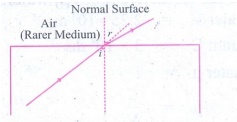
b) denser to rarer
medium
When
a ray of light from an optically denser medium to an optically rarer medium it
bends away from the normal
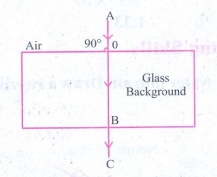
c) normal to the
surface separating the two media.
A
ray of light incident normally on a denser medium it goes without any
deviation.
IX. Numerical problems:
1. A concave mirror produces
three times magnified real image of an object placed at 7 cm in front of it.
Where is the image located?
Answer:
Here
given magnification m = 3
Object
distance u = −7 cm
Magnification
m = (− v/u) Real image
−3
= − v/u
3u = − v
v =
3u = 3 × 7 = −21 cm
The
image will be formed at a distance of 21 cm in front of concave mirror from its
pole.
2. Light enters from air into a
glass plate having refractive index 1.5. What is the speed of light in glass?
Answer:
Refractive
index of a glass plate μ = 1.5
Speed of light in vacuum is C = 3 × 108 ms−1
Speed of light in glass V = ?
μ = C/V = (Speed of light in vacuum / Speed of
light in medium)
1.5 = (3
× 108
/ v)
∴ v = (3 × 108 / 1.5) =
2 × 108 ms-1
Speed of light in glass = 2 × 108ms−1
3. The speed of light in water is
2.25 × 108 ms−1. If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108ms-1,
calculate the refractive index of water.
Answer:
Speed
of light in water V = 2.25 × 108 ms−1
Speed
of light in vacuum C = 3 × l08 ms−1
Refractive
index of water μ = ?
μ = (C / V)
μ = (3×108 / 2.25×108) =
1.33
∴ μ = 1.33
X. Higher Order
Thinking Skills.
1. Light ray emerges from water
into air. Draw a ray diagram indicating the change in its path in water.
Answer:

2. When a ray of light passes
from air into glass, is the angle of refraction greater than or less than the
angle of incidence?
Answer:
Light
bends towards the normal because glass is denser than air.
It
bends towards normal, since light has to travel with lesser speed in glass but
within short time.
r
< i. Angle of refraction is less
than the angle of incidence.
3. What do you conclude about the
speed of light in diamond, if the refractive index of diamond is 2.41?
Answer:
Refractive
index of diamone μ = 2.41
μ = (c
/ v)
2.41 = (3 ×108 / v )
v = (3
×108 / 2.41)
v = 1.24 × 108 ms−1
∴ Speed Of light in diamond (1.24
× 108 ms−1) is less than the speed of light in air (3 × 108
ms −1).
The
refractive index of diamond is 2.42, it means that speed of light in air
(vacuum) is 2.42 times the speed of light in diamond.
lntext Activities
ACTIVITY - 1
Stand before the mirror in your
dressing table or the mirror fixed in a steel almirah. Do you see your whole
body? To see your entire body in a mirror, the mirror should be atleast half of
your height. Height of the mirror = Your height/2.
Solution:
(i)
If the height of a person is 5 feet, then he should use a plane mirror of 2 (1/2)
feet height and fix in a steal almirah.
(ii)
Now if he stand before it his full body will be seen on the mirror because
height of the mirror = Our hieight / 2
ACTIVITY - 2
Hold a concave mirror in your
hand (or place it in a stand). Direct its reflecting surface towards the sun.
Direct the light reflected by the mirror onto a sheet of paper held not very
far from the mirror. Move the sheet of paper back and forth gradually until you
find a bright, sharp spot of light on the paper. Position the mirror and the
paper at the same location for few moments. What do you observe? Why does the
paper catches fire?
Solution:
A
concave mirror converges all the light rays coming from the Sun. All these
light rays converge and meet at the focus of the mirror.
So,
all the heat and light is focused at the principal focus (F). When a paper is
kept at the focus (F), it starts burning, as this point is very hot.
ACTIVITY - 3
Take a convex mirror. Hold it in
one hand. Hold a pencil close to the mirror in the upright position in the
other hand. Observe the image of the pencil in the mirror. Is the image erect
or inverted? Is it diminished or enlarged? Move the pencil slowly away from the
mirror. Does the image become smaller or larger? What do you observe?
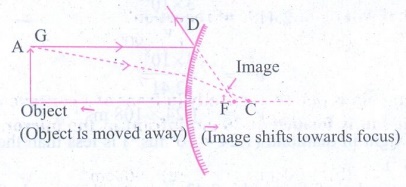
Solution:
(i) When a pencil is hold in the upright
position in front of a convex mirror, its diminished, erect image is formed
which is virtual and therefore seen in the convex mirror.
(ii)
When the pencil is moved away from the convex mirror size of image becomes
smaller and smaller but image remains erect.
(iii)
As we move away, the object from the convex mirror, image shifts towards the
focus.
ACTIVITY - 4
Refraction of light
at air - water interface
Put a straight pencil into a tank
of water or beaker of water at an angle of 45° and look at it from one side and
above. How does the pencil look now? The pencil appears to be bent at the
surface of water.

Solution:
Both the above activities are the result of refraction of light. The bending of light rays when they pass obliquely from one medium to another medium is called refraction of light.
Related Topics