Fluids | Physics | Science - Answer the following questions | 9th Science : Physics : Fluids
Chapter: 9th Science : Physics : Fluids
Answer the following questions
FLUIDS
TEXT BOOK EXERCISES
V. Answer in brief:
1. On what factors the pressure
exerted by the liquid depends on?
Answer:
The
pressure exerted by the liquid depends on the
(i) Depth
(ii)
Density of the liquid
(iii)
Acceleration due to gravity.
2. Why does a helium balloon
float in air?
Answer:
Helium
balloon floats in air because helium gas is less dense than air.
3. Why it is easy to swim in
river water than in sea water?
Answer:
The
question itself is wrong. It is easier to swim in sea water than in the river
water. It is because sea water has (i) greater density and (ii) larger buoyant
force than river water.
4. What is meant by atmospheric
pressure?
Answer:
The
pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere is called atmospheric
pressure.
5. State Pascal’s law.
Answer:
Pascal’s law: The
external pressure applied on an incompressible liquid is transmitted uniformly
throughout the liquid.
VI. Answer in detail:
1. With an appropriate
illustration prove that the force acting on a smaller area exerts a greater
pressure.
Answer:
1.
Take a nail. It has two ends. One end is sharp and other end is a bulged head.
2.
We usually keep the pointed end on the wall or wood and hammer on the bulged
head.
3.
So very small area creates a large pressure.
4.
Thus the nail penetrates into the wall or wood.
2. Describe the construction and
working of mercury barometer.
Answer:
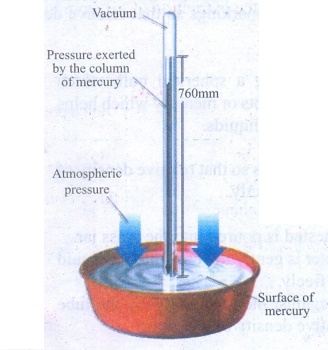
Mercury Barometer
1.
It is designed by Torricelli.
Construction:
1.
Mercury Barometer consists of long glass tube closed at one end and opened at
other.
2.
Mercury filled through open end and close that end by thumb and open it after
immersing it into a trough of mercury.
Working:
1.
The Barometer works by balancing the mercury in the glass tube against the
outside air pressure.
2.
If air pressure increases, it pushes more of the mercury up into the tub.
3.
If air pressure decreases, more mercury drains from the tub.
4.
As vacuum cannot exert pressure, Mercury in the tube provides a precise measure
of air pressure which is called atmospheric pressure.
5.
It is used in a laboratory or weather station.
3. How does an object’s density
determine whether the object will sink or float in water?
Answer:
l.
Whether an object sinks or floats is determined by density of the object
compared with density of liquid.
2.
If density of object is less than the density of the liquid, the object will
float, (e.g) less density object, wood will float on water.
3.
If density of object is more than the density of liquid, the object will sink.
(e.g)
more dense object, stone sinks into water.
4. Explain the construction and
working of a hydrometer with diagram.
Answer:
1.
Hydrometer consists of a cylindrical stem having a spherical bulb at its lower
end and a narrow tube at its upper end.
2.
The lower spherical bulb is partially filled with lead shots or mercury.
3.
This helps hydrometer to float or stand vertically in liquids.
4.
The narrow tube has markings so that relative density of a liquid can be read
directly.
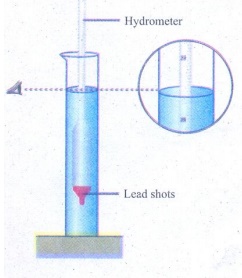
Lower end of
hydrometer:
A
cylindrical stem having a spherical bulb which partially filled with lead shots
or mercury which helps to float or stand vertical in liquids
Upper end of
hydrometer:
A
narrow tube has markings so that relative density of liquids can be read off
directly.
Working:
1.
Liquid to be tested is poured into the glass jar.
2.
The hydrometer is gently lowered into the liquid until it floats freely.
3.
The reading against the level touching the tube gives the relative density of
the liquid.
5. State the laws of flotation.
Answer:
Laws of flotation
1.
The weight of a floating body in a fluid is equal to the weight of the fluid
displaced by the body.
2.
The centre of gravity of the floating body and the centre of buoyancy are in
the same vertical line.
VII. Assertion and reason type questions:
Mark the correct
answer as:
(a)
If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of
assertion.
(b)
If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation
of assertion.
(c)
If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d)
If assertion is false but reason is true.
1. Assertion: To
float, body must displace liquid whose weight is equal to the actual weight.
Reason: The body
will experience no net downward force in that case.
[Ans: (a) Both assertion
and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion]
2. Assertion: Pascal’s
law is the working principle of a hydraulic lift.
Reason: Pressure
is thrust per unit area.
[Ans: (b) Both
assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of
assertion.]
Reason: Pascal's
law is the working principle of Hydraulic lift. In Hydraulic lift, applied
pressure is transmitted uniformly and
multiplied through out the system.
VIII. Numerical
Problems:
1. A block of wood of weight 200
g floats on the surface of water. If the volume of block is 300 cm3,
calculate the upthrust due to water.
Answer:
Weight
of wood block, m = 200 g
Volume
of the wood block, V = 300 cm3.
Upthrust
= Weight of the fluid displaced
= Volume of the wood block
Upthrust
= 300 cm3
2. Density of mercury is 13600 kg
m-3. Calculate the relative density.
Answer:
Density
of Mercury = 13600 kg m-3
Density
of water at 4°C = 1000 kg m-3
Relative
density = Density of mercury / Density of water at 4° C
= 13600 kg m−3 / 1000 kg m−3
Relative
Density = 13.6
3. The density of water is 1 g cm−3.
What is its density in S.I. units?
Answer: Density
of water in SI units = 1000 kg / m3.
4. Calculate the apparent weight
of wood floating on water if it weighs l00g in air.
Answer:
Mass
of wood = 100 g.
As
the wood floats on the water, water will not be displaced.
So,
actual weight of wood is equal to Apparent weight of wood.
IX. Higher Order Thinking Skills :
1. How high does the mercury
barometer stand on a day when atmospheric pressure is 98.6 kPa?
Answer:
Pressure
of Atmosphere Patm = 98.6 kPa.
Density
of Mercury , ρHg = 13.6 × 103 kg/cm3
Acceleration
due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Pressure,
Patm = h × ρHg ×
g
h = Patm
/ (ρHg×g)
=
98.6 kPa / (13.6 × 103 kg/cm3 × 9.8 m/s2)
=
98.6 × 103 Pa / (13.6 × 103 kg/cm3 × 9.8 m/s2)
Height
of Barometer, h = 0.7397 m = 739.7 mm
2. How does a fish manage to rise
up and move down in water?
Answer:
(i)
Fish manages to rise up in water by reducing its density by filling oxygen in
bladder via the gills. Thus volume will be increased to support its ascending
motion. ‘
(ii)
Fish moves down by decreasing its volume by releasing oxygen from bladder. Thus
volume will be decreased so it will sink in the water.
3. If you put one ice cube in a
glass of water and another in a glass of alcohol, what would you observe?
Explain your observations.
Answer:
Ice cube in water: As the
density of ice cube is less than water, the ice cube floats in water.
Ice cube in alcohol: As the
density of ice cube is greater than alcohol, the ice cube will sink in alcohol.
[Note: Density:
Water = 1.00, Ice cube = 0.917, Alcohol = 0.78]
4. Why does a boat with a hole in
the bottom would eventually sink?
Answer:
A
boat with a hole in the bottom eventually sinks due to:
(1)The
water entered through a hole will increase the weight of boat.
(2)
The boat becomes heavier so it cannot displace more water. So the boat sinks.
Intext Activity
ACTIVITY - 1
Stand on loose stand. Your feet
go deep into the sand. Now, lie down on the sand. What happens? You will find
that your body will not go that deep into the sand. Why?
Aim:
To
demonstrate the effect of thrust
Materials Required:
Sand
Procedure:
1.
First, you stand on the sand on your feet.
2.
Lie down on the sand with your whole body.
Observation:
1.
While standing on your feet on sand, your feet go deep into the sand.
2.
While lying down with your body on sand, your body will not go deep into the
sand.
Conclusion:
1.
Pressure depends upon the area on which it acts.
2.
The effect of thrust on sand is larger while standing than lying.
ACTIVITY-2
Take a transparent plastic pipe.
Also take a balloon and tie it tightly over one end of the plastic pipe. Pour
some water in the pipe from the top. What happens? The balloon tied at the
bottom stretches and bulges out. It shows that the water poured in the pipe
exerts a pressure on the bottom of its container.
Aim: To
demonstrate that water exerts pressure on the bottom of the container.
Materials Required: Plastic
pipe, Balloon, Water.
Procedure:
1.
Take a transparent plastic pipe and a balloon.
2.
Tie the balloon tightly over one end of plastic pipe.
3.
Keep the pipe with the closed end at the bottom.
4.
Pour some water in the pipe from the top.
Observation: The
balloon tied at the bottom stretches and bulges out.
Conclusion: Water
poured in the pipe exerts pressure on the bottom of its container.
ACTIVITY - 3
Take a large plastic can. Punch
holes with a nail in a vertical line on the side of the can as shown in figure.
Then fill the can with water. The water may just dribble out from the top hole,
but with increased speed at the bottom holes as depth causes the water to
squirt out with more pressure.
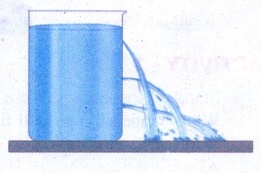
Aim:
To
demonstrate that pressure increases as depth increases.
Materials Required:
1.
Large plastic can.
2.
A sharp nail.
Procedure:
1.
Take a large plastic can.
2.
Punch holes with a nail in a vertical line up on the side of can every inch or
several centimetres.
Observation:
1.
Water dribbles out from top hole.
2.
Water from bottom hole flows with increased speed.
Conclusion:
Depth
causes water to squirt out with more pressure.
ACTIVITY - 4
Take two liquids of different
densities say water and oil to a same level in two plastic containers. Make
holes in the two containers at the same level. What do you see? It can be seen
that water is squirting out with more pressure than oil. This indicates that
pressure depends on density of the liquid.

Aim:
To
demonstrate pressure depends on density of the liquid.
Materials Required:
1.
Two plastic containers, 2.Water, 3. Oil (Both same volume), 4. Sharp nail
Procedure:
1.
Take a water and oil to a same level in two plastic containers.
2.
Make a hole at same level in two containers.
Observation:
Water
squirts out with more pressure than that of oil.
Conclusion:
Pressure
depends on density of the liquid.
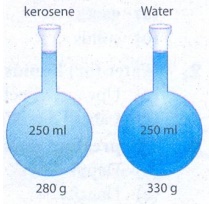
ACTIVITY - 5
Take two identical flasks and
fill one flask with water to 250 cm3 mark and the other with
kerosene to the same 250 cm3 mark. Measure them in a balance. The
flask filled with water will be heavier than the one filled with kerosene. Why?
The answer is in finding the mass per unit volume of kerosene and water in
respective flasks.
Aim:
To
prove that density of a substance is the mass per unit volume of given
substance.
Materials Required:
1.
Two identical flasks.
2.
Water
3.
Kerosene (same volume as water)
Procedure:
1.
Take two identical flasks.
2.
Fill one flask with water to 250 cm3 mark.
3.
Fill the other flask with kerosene to same 250 cm3 mark.
4.
Measure both flasks in balance separately.
Observation:
The
flask filled with water will be heavier than that of the flask filled with
kerosene.
Conclusion:
In
the above activity, we know that
1.
Both water and kerosene have same volume (i.e.) 250 cm3.
2.
The density of the water lg / cm3 and density of kerosene is 0.8g /
cm3
3.
Density = (mass/ volume) , therefore mass = Density × volume.
Hence
mass of water = lg / cm3 × 250 cm3 = 250g
mass
of kerosene = 0.8 g / cm3 × 250 cm3 = 200g
4.
Even though, water and kerosene have same volume, they have different
densities. So water and kerosene have different masses.
5.
Water has more mass than kerosene.
Hence,
we proved that density of the substance is the mass per unit volume of the
substance.
VIII. Numerical Problems:
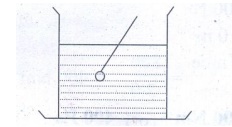
1. A vessel with water is placed
on a weighing pan and it reads 600 g. Now a ball of mass 40 g and density is
0.80g / cm3 is sunk into the water with a pin of negligible volume
as shown in figure. The weighing pan will show the reading of….?
Solution:
Weight
of vessel with water = 600g
Mass of ball = 40g
Density of ball = 0.80 g /cm3
Volume
of the ball = ( mass / density ) = (40/0.80 )= 50g
So,
weight of vessel + volume of ball = 600 + 50 g
The
weighing pan will show = 650 g
The
weighing pan will show = 650 g
2. The reading of a spring
balance when a block is suspended from it in air is 60 newton. This reading is
changed to 40 newton when the block is submerged in water. Calculate the
specific gravity of block.
Solution:
Weight of block in air = 60 newton
Loss
of weight of block in water = 60 - 40 = 20 newton
Relative
density (or) specific gravity = (Weight of block in air / Loss of weight in
water)
= (60 newton / 20 newton)
Specific
gravity of block = 3
3. The mass of a body is 4 kg and
its volume is 500 cm3. Find its relative density.
Solution:
Mass of the body m = 4 kg = 4000 g
Volume of the body v =500 cm3
∴
Density of the body = Mass (m) / Volume (v)
= 4000 / 500
∴ The relative density of
the body = 8 g cm-3
= (Density of substance / Density of water)
= (8 g/cm3 ) / (1 g/cm3)
=8
Relative
density of the body = 8
4. Calculate the pressure
produced by a force of 800 N acting on an area of 2.0m2.
Solution:
Force =
800 N
Area = 2.0m2
Pressure, P = (Force / Area) = (800 / 2.0) =
400Nm-2
Pressure,
P = 400Nm-2 (or) 400 Pa
5. A swimming pool of width 9.0 m
and length 24.0 m is filled with water of depth 3.0 m. Calculate the pressure
on the bottom of the pool due to the water.
Solution:
Width
of the pool, b = 9.0m
Length
of the pool, l = 24.0 m
Depth
of the pool, h = 3.0m
Density
of water, ρ = 1000 kg/m3
Pressure
due to column of Fluid,p = ρhg
Acceleration
due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Substituting
the values, p = ρhg
P = (1000kgm−3) × (3.0m) × (9.8ms-2)
Pressure P
= 2940 kgm-1s-2 ∴ 1pa = 1kgm-1 s-2
∴
P
= 29400Nm-2 (or) 29400pa
6. A body of volume 100 cc is
immersed completely in water contained in a jar. The weight of water and the
jar before immersion of the body was 700 g. Calculate the weight of water and
jar after immersion.
Solution:
Volume
of body completely immersed in water V = 100cc.
Weight
of water and jar before Immersion = 700g.
Volume
of jar immersed in water = Volume of water displace
=
100cc.
Density
of water = 1g/cm3
Mass
of water displaced = Apparent weight loss
Mass
of water displaced = Volume × Density.
=
100cc × 1 g/cm3.
Apparent
weight loss of body = 100g
Weight of
jar and water after immersion = Weight of water and jar before immersion −
Apparent weight loss
= 700g − 100g
= 600g
Related Topics