Introduction to Object Oriented Programming Techniques | Computer Science - Answer the following questions | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 13 : Introduction to Object Oriented Programming Techniques
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 13 : Introduction to Object Oriented Programming Techniques
Answer the following questions
Object Oriented Programming with C++
Introduction to Object Oriented Programming Techniques
Evaluation
PART II
Answer to all the questions (2 Marks):
1. How is modular programming different from procedural programming paradigm?
Answer: (i) Procedural means a list of instructions were given to the
computer to do something. Procedural programming aims more at procedures. This
emphasis on doing things.
(ii) Modular programming consist of a list of instructions that
instructs the computer to do something. But this Paradigm consits of multiple
modules, each module has a set of functions of related types. Data is hidden
under the modules. Arrangement of data can be changed only by modifying the
module.
2. Differentiate classes and objects.
Answer: (i) Class: A Class is a construct in C++ which is used to bind data and
its associated function together into a single unit using the encapsulation
concept. Class is a user defined data type. Class represents a group of similar
objects.
(ii) Objects : Represents data and its associated function together into a
single unit. Objects are the basic unit of oop. Basically an object is created
from a class. They are instances of class also called as class variables.
3. What is polymorphism?
Answer: Polymorphism is the ability of a message or function to be
displayed in more than one form.
4. How is encapsulation and abstraction are interrelated?
Answer: Classes use the concept of abstraction to define a list of
abstract attributes and function which operate on these attribute. They
encapsulate all the essential properties of the object that are to be created.
5. Write the disadvantages of OOP.
Answer: (i) Size : Object Oriented Programs are much larger than other programs.
(ii) Effort: Object Oriented Programs require a lot of work to create.
(iii) Speed: Object Oriented Programs are slower than other programs,
because of their size.
PART III
Answer to all the questions (3 Marks):
1. What is paradigm ?Mention the different types of paradigm.
Answer: Paradigm means organizing principle of a program. It is an
approach to programming. There are different approaches available for problem
solving using computer. They are Procedural programming, Modular Programming
and Object Oriented Programming.
2. Write a note on the features of procedural programming.
Answer:
(i) Programs are organized in the form of subroutines or sub
programs.
(ii) All data items are global.
(iii) Suitable for small sized software application.
(iv) Difficult to maintain and enhance the program code as any
change in data type needs to be propagated to all subroutines that use the same
data type. This is time consuming.
(v) Example: FORTRAN and COBAL.
3. List some of the features of modular programming
Answer:
(i) Emphasis on algorithm rather than data.
(ii) Programs are divided into individual modules.
(iii) Each modules are independent of each other and have their
own local data.
(iv) Modules can work with its own data as well as with the data
passed to it.
(v) Example: Pascal and C.
4. What do you mean by modularization and software reuse?
Answer:
(i) Modularisation: where the program can be decomposed into modules.
(ii) Software
re-use: where a program can be composed from existing
and new modules.
5. Define information hiding.
Answer: Encapsulation is the most striking feature of a class. The data
is not accessible to the outside world, and only those functions which are
wrapped in the class can access it. These functions provide the interface
between the object’s data and the program. This encapsulation of data from
direct access by the program is called data hiding or information hiding.
PART IV
Answer to all the questions (5 Marks):
1. Write the differences between Object Oriented Programming and procedural programming
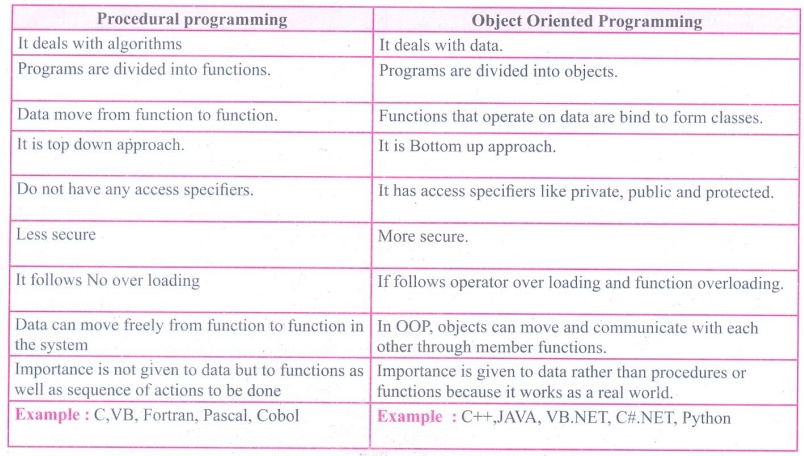
Procedural
programming
• It deals with algorithms.
• Programs are divided into functions.
• Data move from function to function.
• It is top down approach.
• Do not have any access specifiers.
• Less secure
• It follows No over loading
• Data can move freely from function to function in the system.
• Importance is not given to data but to functions as well as
sequence of actions to be done
• Example : C,VB,
Fortran, Pascal, Cobol
Object Oriented
Programming
• It deals with data.
• Programs are divided into objects.
• Functions that operate on data are bind to form classes.
• It is Bottom up approach.
• It has access specifiers like private, public and protected.
• More secure.
• If follows operator over loading and function overloading.
• In OOP, objects can move and communicate with each other
through member functions.
• Importance is given to data rather than procedures or
functions because it works as a real world.
• Example : C++, JAVA,
VB.NET, C#.NET, Python
2. What are the advanatges of OOPs?
Answer:
Advantages of OOP:
(i) Re-usability: "Write once and use it multiple times" you can
achieve this by using class.
(ii) Redundancy: Inheritance is the good feature for data redundancy. If you
need a same functionality in multiple class you can write a common class for
the same functionality and inherit that class to sub class.
(iii) Easy
Maintenance: It is easy to maintain and modify
existing code as new objects can be created with small difference to existing
ones.
(ii) Security: Using data hinding and abstraction only necessary data will be
provided thus maintains the security of data.
3. Write a note on the basic concepts that suppors OOPs?
Answer: Basic
Concepts of OOP : The Object Oriented Programing has
been developed to overcome the drawbacks of procedural and modular programming.
It is widely accepted that object-oriented programming is the most important
and powerful way of creating software.
The Object-Oriented Programming approach mainly encourages:
(i) Modularisation
: Where the program can be decomposed into modules.
(ii) Software
re-use: Where a program can be composed from existing
and new modules.
(iii) Main Features
of Object Oreitned Programming : Data Abstraction, Encapsulation, Modularity,
Inheritance, Polymorphism
(iv) Encapsulation
: The mechanism by which the data and functions are bound
together into a single unit is known as Encapsulation. It implements
abstraction.
Encapsulation is about binding the data variables and functions
together in class. It can also be called data binding.
Encapsulation is the most striking feature of a class. The data
is not accessible to the outside world, and only those functions which are
wrapped in the class can access it. These functions provide the interface
between the object's data and the program. This encapsulation of data from
direct access by the program is called data hiding or information hiding.
(v) Data
Abstraction : Abstraction refers to showing only
the essential features without revelaing background details. Classes use the
concept of abstraction to define a list of abstract attributes and function
which operate on these attributes. They encapsulate all the essential
properties of the object that are to be created. The attributes are called data
members because they hold information. The functions that operate on these data
are called methods or member function.
(vi) Modularity : Modularity is designing a system that is divided into a set of
functional units (named modules) that can be composed into a larger
application.
(vii) Inheritance : Inheritance is the technique of building new classes (derived
class) from an existing Class (base class). The most important advantage of
inheritance is code reusability
(viii) Polymorphism : Polymorphism is the ability of a message or function to be displayed in more than one form.
Related Topics