Term 3 Chapter 3 | 5th Science - Air | 5th Science : Term 3 Unit 3 : Air
Chapter: 5th Science : Term 3 Unit 3 : Air
Air
UNIT 3
AIR

Learning Objectives
After the completion of this lesson,
students will be able to:
* Know about different layers of
atmosphere.
* Understand the causes of air
pollution.
* List out the ways of reducing air
pollution.
* Know about the airborne diseases.
* Understand the importance of air in daily
life.
Introduction
Air is present everywhere around us.
Though we cannot see it we can feel it. Air is a mixture of gases like oxygen,
nitrogen, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. These gases act as an envelope around
the earth and form the atmosphere. It is the presence of atmosphere that makes
the earth a suitable place for living. In the recent years more number of
industries has been established and they release excess of harmful gases like
carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Because of this air is polluted more than
ever before. In this lesson we are going to study about different layers of
atmosphere, air pollution, air borne diseases and the measures to control air
pollution.
I. Atmosphere
The earth is surrounded by a layer of
gases which is called the atmosphere. It is composed mainly of nitrogen (78%)
and oxygen (21%). Other gases like carbon dioxide and argon comprise 1% of the
atmosphere by volume. The atmosphere is like a blanket that surrounds the
earth. It protects the Earth from getting too cold or too hot.
Atmosphere
is divided into five different layers. The layers from the bottom upwards are
called Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere.
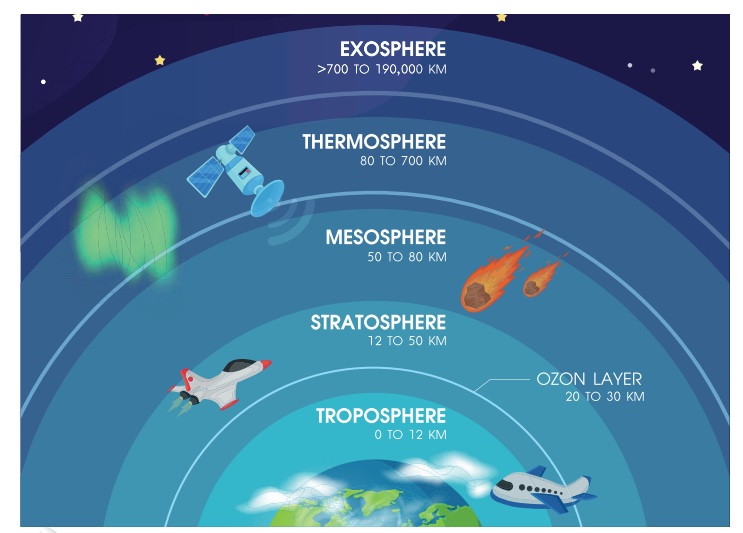
* Troposphere
The
troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. From the sea level it
extends upto about 10 km. It is the densest layer and almost 75% of the air in
the atmosphere is found in this layer. This layer also has water vapour. We
live in the troposphere and most of the weather - clouds, rain, snow - is found
in this layer. All weather changes also occur in this layer.
Activity 1
Read the weather news in a
daily news paper and note down the changes in the weather over a week. In which
layer these changes take place? Discuss in the classroom about these changes
and record your points.
* Stratosphere
It extends from the top of the troposphere to about 50 km above the ground. Ozone layer found in this layer absorbs harmful ultraviolet rays which can cause damage to our skin and eyes. There is no water vapor in this layer. The temperature in this layer is around −550 C.
* Mesosphere
The region above the stratosphere is
called the mesosphere. It extends upward to a height of about 85km from the
ground. The temperature in this layer decreases with height and it is −1100 C.
Most of the meteors found in the sky burn in this layer.
* Thermosphere
The layer of very rare air above the
mesosphere is called the thermosphere. It is found above the mesosphere.
* Exosphere
The outermost layer of the atmosphere is
called the exosphere. It lies between 400 - 1500 km above the earth.The air
here is extremely thin.
Do you know?
As the height increases
the amount of air in the atmosphere decreases and so the oxygen level will
decrease. That is why mountain climbers carry oxygen cylinders while climbing
mountains.

II. Importance of Air
Air is important for all the living
organisms. Without air no life can exist on the earth. We take in oxygen from
the air and release carbon dioxide. Plants in turn use carbon dioxide present
in the air to produce their food. The gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon
dioxide and hydrogen present in the air are important to us for many reasons.
Let us study about the importance of air in this section.
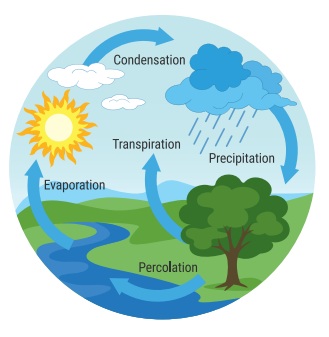
*Water Cycle
Water vapour present in the air is
important for the formation of water cycle. Water from the water bodies such as
rivers and oceans evaporates and becomes water vapour. This water vapour then
forms the clouds. These clouds move to the land and get cooled to give us the
rain. This movement of clouds is possible due to air.
* Supplies Energy
We breathe oxygen present in the air and
it is supplied to the cells in our body. Body cells burn the food molecules
with the help of oxygen and produce energy. With this energy we do all kinds of
works.
* Sound travels through air
We
hear many things from the surrounding and people hear what we speak. This is
possible due to air because sound needs a medium to travel. Sound travels from
the point of generation to the listener through air.
* Useful for plants
Nitrogen
present in the air is useful for plants. The nitrogen in the atmosphere is
converted into easily absorbable nitrates by plants with the help of some
microbes. It is known as nitrogen fixation. These nitrates are useful for the
growth of plants. Also air is helpful for the pollination of plants. Pollen
grains travel from one plant to another plant through air. Thus cross
pollination is achieved with the help of air.
* Transport
Movement
of air is called wind. This is helpful for the ships and boats to sail on the
water. Airplanes and helicopters travel though air.
* Sports
Paragliding
is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying. In this sports
pilot sits in a harness suspended below a fabric wing. Hang gliding is also an
air sport or recreational activity in which a pilot flies a light,
non-motorized foot – launched air craft called a hang glider. Paragliding and
hang gliding are possible with the help of air. Other sports like wind surfing,
kite surfing and sailing are also possible with the hep of air.

Do you know?
Bir billing in
Jogindernagar valley of Himachal Pradesh is known as para-gliding capital of
India. In Tamilnadu, Yelgiri is a good paragliding spot.
Activity 2
Find out the places where
wind energy is produced. Also discuss about the importance of wind energy in
the classroom and make a report on your discussion.
* Parachutes and Hot air balloons
Parachutes
and hot air balloons are used to land from above. In case of emergency, people
use parachutes and come down slowly and safely with the help of air.
* Wind energy
Air
flows from a region of high pressure to low pressure. This flow of air at high
speed is called wind. This wind is
used to generate electric power with the help of wind mills.
III. Air Pollution
The presence of harmful substances in
the air which can have an adverse effect on living beings and the environment
is called air pollution. When harmful substances including gases like carbon
dioxide, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide etc., and particles like dust and
aerosols are released into the earth’s atmosphere, air pollution occurs. These
substances are released into the atmosphere at a rate which exceeds the natural
capacity of the environment to absorb them. Air pollution may cause diseases,
allergies and even death to humans. It may also cause harm to other living
organisms such as plants and animals. It may damage the natural environment
also.
1. Causes of Air pollution
Air pollution is caused by both natural
and manmade activities. Air pollutants are released into the atmosphere through
human activities like burning of fuels, releasing industrial wastes, mining
etc. Natural events like volcanic eruption also cause air pollution. Let us see
about some of the causes of air pollution in detail.
* Industries
Many
industries have been established to manufacture things. Large amount of carbon
monoxide, hydrocarbons, organic compounds, and chemicals are released into the
air by these industries. Because of this pollutants quality of air is affected
very much.
Do you know?
The word pollution is
derived from the Latin word ‘polluere’ which means contamination or make dirty.
Activity 3
Organise a debate in your
class about the advantages and disadvantages of industries. Discuss in what way
industries are responsible for air pollution. Also discuss what measures can be
taken to minimise air pollution caused by industries.
* Burning of fuels
Combustion of fossil fuels like coal and
petroleum release sulphur dioxide which is an air pollutant. Major air
pollutants are released by the vehicles including bus, cars, trains and
airplanes. Improper or incomplete combustion of fuel release carbon monoxide.
Nitrogen oxides which are released by both natural and man-made processes, also
cause air pollution.
* Agricultural activities
Use of insecticides, pesticides, and
fertilizers in agricultural activities has increased in the modern days. They
emit harmful chemicals such as ammonia into the air causing air pollution.
Do you know?
Taj Mahal in Agra is built
entirely by white marbles. But it has become yellow in colour in the recent
years. It is because of air pollution. Industries located in these areas
release lot of pollutants into the air. Every day 2000 metric tons of waste is
being dumped into the city.

* Mining
Extraction of minerals from the earth is
called mining. Mining processes release dust and chemicals into the air causing
massive air pollution. This affects the health conditions of workers and the
people living in the surrounding areas.
* Household activities
Air is polluted through household
activities also. While cleaning and painting we use lot of chemicals. These
chemicals pollute the environment.

2. Effects of Air pollution
Air pollution affects all living
organisms including man. It causes serious health problems to human beings and
affects both plants and animals. It brings about lot of changes in the climate
and environment also. In this section let us learn about some of the effects of
air pollution.
* Diseases
Air pollution causes several respiratory
and heart problems. Many people have died due to air pollution. Air pollutants
cause pneumonia and asthma in children.
* Global warming
Air pollution results in the
accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. When gases like carbon
dioxide are present in the atmosphere in large amount, they increase the
atmospheric temperature. With increased temperatures, melting of ice and
icebergs in polar regions and increase in sea levels are taking place. It
affects the living organisms living there.

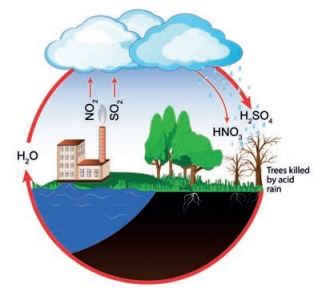
* Acid rain
As we saw earlier harmful gases like
nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides are released into the atmosphere while
burning fossil fuels. When it rains, the water droplets combine with these
gases and fall on the ground in the form of acid rain. Acid rain affects human,
animals, and crops.
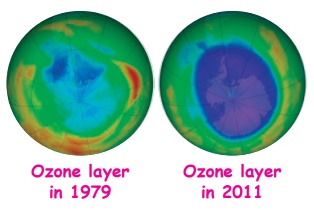
* Depletion of ozone layer
Ozone molecules are present in the
Earth’s stratosphere and they are responsible for protecting humans from
harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. Chlorofluorocarbons, released into the
atmosphere by human activities deplete the ozone layer. As the ozone layer is
depleted, UV rays reach the earth and they cause skin and eye related problems
to us.
* Marine life
Large amount of nitrogen present in some
fertilisers is washed into the water bodies. They cause the growth of green
algae in the seas. This is called Eutrophication. This adversely affects fish,
plants and animal species.
* Effect on wildlife
Harmful substances present in the air
affect wild animals. Wild animals move to a new place when the air is polluted.
When their habitat is changed they face extinction.
Do you know?
Chemicals like
chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) which are used in refrigerators, spray cans and fire
extinguishers, have reduced the amount of ozone in the stratosphere. It has
resulted in the depletion of ozone layer in the Antarctic region.
3. Prevention of Air pollution
If the air pollution increases at this
rate, then there will be no life on the earth in the future. Future generation
will be affected very badly. So we need to take some measures to avoid air
pollution. Some of them are discussed below.
* Major pollutants which cause air
pollution come from automobiles. Using public modes of transport can reduce the
rate of pollution. We also should encourage others to use public transport.
* By reducing the usage of fossil fuels
for burning we can save the environment.
* Using non-renewable energy resources
like solar energy and wind energy instead of conventional energy can reduce air
pollution.
* We need to reduce our usage. We can
reuse or recycle few items.
* Switch off fans and lights when you
are not using them.
* CFL bulbs consume less electricity. By
using these bulbs we can save energy.
* Planting more trees can reduce the
amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Activity 4
Find out the common air
pollutants present in your area. Discuss about the effects of these pollutants.
Record your observations in your note book.
IV. Airborne Diseases
Diseases which are caused by
microorganisms and communicated through air are called airborne diseases. When
we breathe in air there are chances for the microorganisms present in the air
to get into our body. The microorganisms which cause airborne diseases are
bacteria, virus and fungi. These microorganisms are transmitted through
droplets caused by coughing or sneezing, breathing and talking. Let us study
about some of the airborne diseases here.
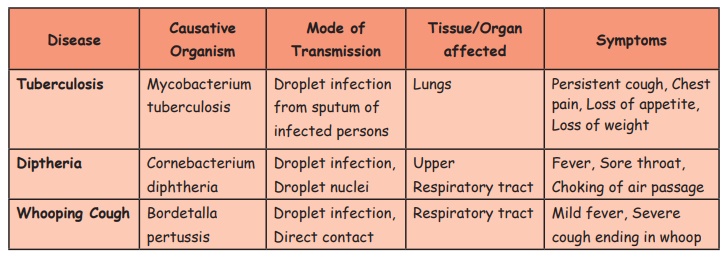
1. Diseases caused by bacteria
Diphtheria,
Whooping Cough and Tuberclosis are some of the common airborne diseases caused
by bacteria.
* Diphtheria
It
is caused by the bacteria, Cornebacterium diphtheria. It generally affects the
upper respiratory tract (nose and throat) and causes fever, sore throat and
chocking of air passage.
* Whooping Cough
Whooping
cough is caused by Bordetalla pertusis. It also affects the respiratory tract
and causes mild fever, severe cough ending in whoop.
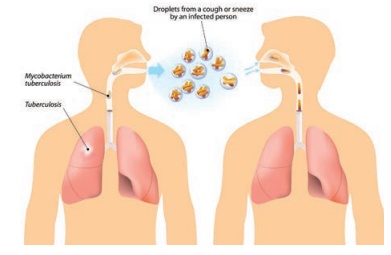
* Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
is caused by the bacteria, Microbacterium tuberculosis. When we breathe, the
bacteria present in the air gets into the lungs and affect it. Infected person
has to be treated with anti-tubercular drugs for a period of 6 months to one
year.
Do you know?
National TB Control Programme was started in 1962. World Tuberculosis Day is observed on 24th March.
2. Diseases caused by Virus
Some diseases are caused by the virus
present in the air. Common cold, influenza, measles, mumps and chickenpox are
some of the diseases caused by virus.
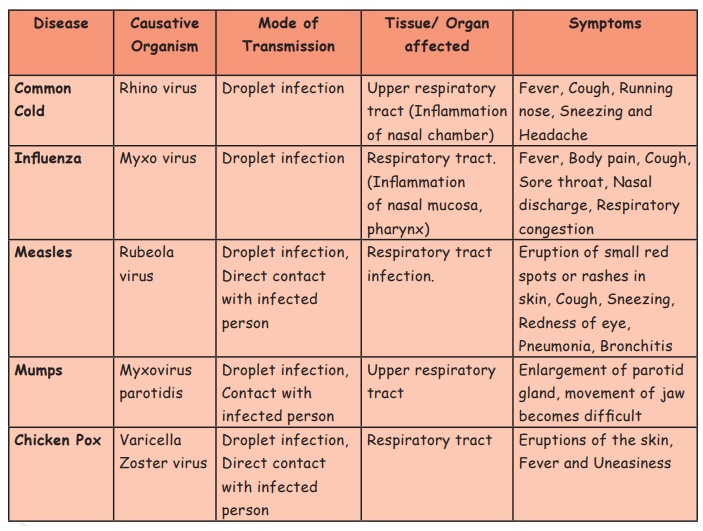
* Common cold
Common cold is an infectious disease
which affects the upper respiratory system like nose and throat and it is
easily spread. Symptoms of common cold include cough, painful throat, running
nose and sometimes fever. Though many viruses can cause this, it is generally
caused by Rhinovirus.
* Influenza
Influenza is commonly found during
childhood. It is caused by the virus, Myxo virus and results in inflammation of
nasal mucosa and pharynx. It is also known as flu.
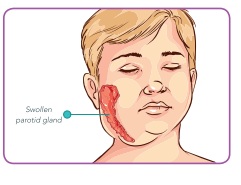
* Mumps
It is caused by Myxovirus parotidis and
it affects the upper respiratory tract. Some of the common symptoms of mumps
include fever, headaches, sore throat and swelling of parotoid glands which
makes the jaw movement difficult.
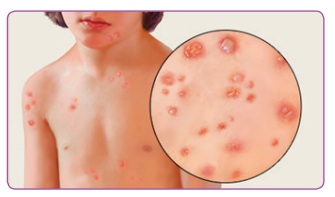
* Chickenpox
It is common among children but adults
also may get it. Affected people will have blisters or spots in the body and
face along with fever. Those blisters with fluid will drain but sometimes it
may leave scars.
* Measles
Measles is caused by Rubeola virus and
it is easily caught by people from other infected people. Symptoms of measles
include eruption of small rashes in skin, cough, sneezing, redness of eye,
pneumonia and bronchitis. There is no cure for this disease. Yet people can
recover from this by proper rest and diet.
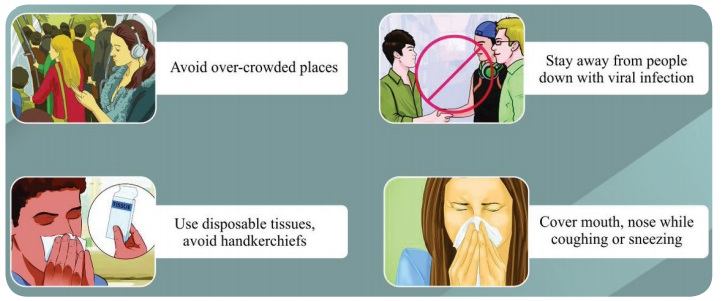
3. Prevention
Prevention is better than cure. Airborne
diseases can be prevented if we take certain measures.
* Avoid close contact with people who
have active symptoms of disease.
* Maintain personal hygiene.
* Keep the patient in complete
isolation.
* Cover nose and mouth while sneezing or
coughing.
* Avoid touching the face or other
people with unwashed hands.
* Wash your hands thoroughly.
* Timely vaccination can prevent the
diseases.
Activity 5
Divide the students in the
class into different groups and discuss how airborne diseases can be prevented.