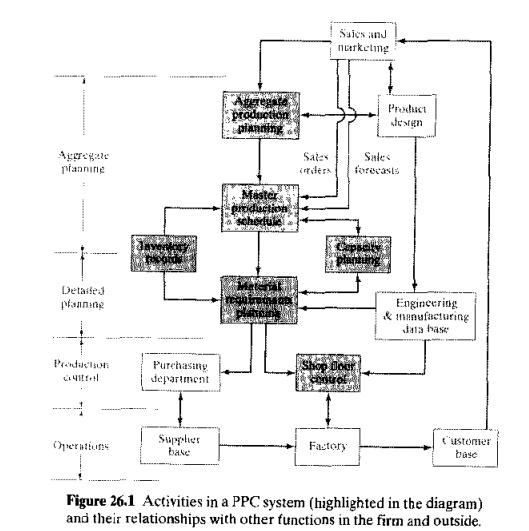
Chapter: Automation, Production Systems, and Computer Integrated Manufacturing : Production Planning and Control Systems
Aggregate Production Planning and the Master Production Schedule
AGGREGATE
PRODUCTION PLANNING AND
THE MASTER PRODUCTION SCHEDULE
Aggregate planning is a high-level corporate planning activity. The aggregate production pian indicates production output levels for the major product lines of the company. The aggregate plan must be coordinated with the plans of the sales and marketing departments. Because the aggregate production plan includes products that are currently in production, it must also consider the present and future inventory levels of those products and their component parts. Because new products currently being developed will also be included in the aggregate plan. the marketing plans and promotions for current products and new products must be reconciled against the total capacity resources available to the company.
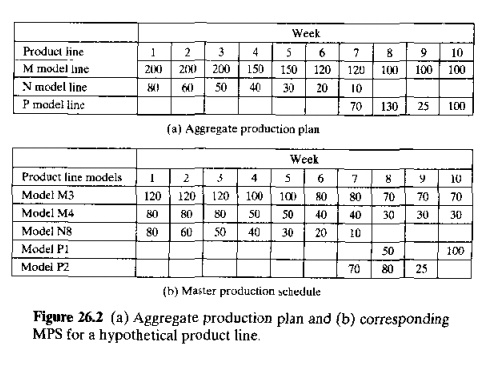
The
production quantities of the major product lines listed in the aggregate plan
must he converted into a very specific schedule of individual products, known
as the master production schedule (MPS).lt
is a list or the products to be manufactured, when they should be completed and delivered, and in what
quantities. A hypothetical MPS for a narrow product set is presented in Figure
26.2(0), showing how it is derived from the conesponding aggregate plan in
Figure 26.2(a). The master schedule must be based on an accurate estimate of
demand and a realistic assessment of the company's production capacity.
Products included in the MPS divide into three
categories: (1) firm customer orders, (2) forecasted demand, and (3) spare
parts. Proportions in each category vary for different companies, and in some
cases one or more categories are omitted. Companies producing assembled
products will generally have to handle all three types. In the case of customer
orders for specific products, the company is usually obligated to delivery the
item by a particular date that has been promised by the sales department. In
the second category. production output quantities are based on statistical forecasting techniques
applied to previous demand patterns, estimates by the sales staff. and other
sources. For many companies, forecasted demand constitutes the largest portion
of the master schedule. The third category consists of repair parts that will
either be stocked in the company's service department or sent directly to the
customer. Some companies exclude this third category from the master schedule
since it does not represent end products.
The MPS
is generally considered to be a medium-range plan since it must take into
account The lead times to order raw materials and components, produce parts in
the factory, and then assemble the end products. Depending on the product. the
lead times can
range
from several weeks 10 many months; in some cases. more than a year. The MPS is usually
considered to he fixed in the near term. This means that changes arc not
allowed within about a 6 week honzon because of the difficulty in adjusting
production schedules within such a short period. However. schedule adjustments
are allowed beyond 6 weeks to cope with changing demand patterns or the
introduction of new products.Accordingly, we should note that the aggregate
production plan is not the only input to the master schedule. Other inputs that
may came the master schedule to depart from the aggregate plan include new
customer orders and changes in sales forecast over the near term.
Related Topics