Chapter: mathematics : Three Dimensional Analytical Geometry
Three Dimensional Analytical Geometry
THREE
DIMENSIONAL ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY
Formulae
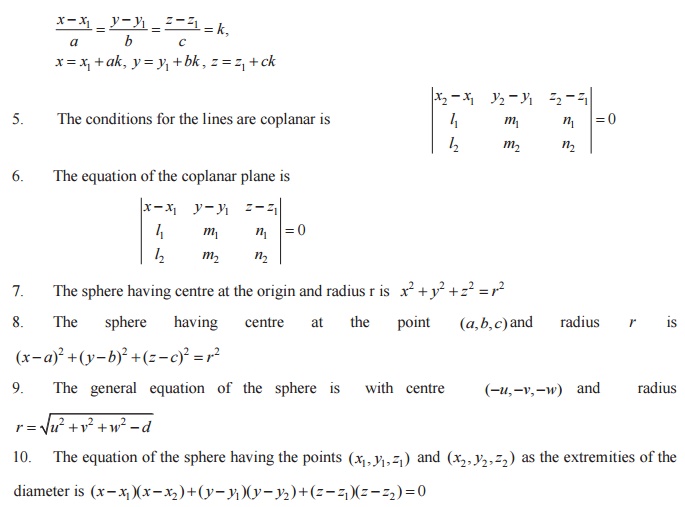
Cone
Right-Circular Cone
Cylinder
Right-Circular Cylinder
The Sphere
FORMULAE:
1. The equation of the straight line
through the point p(x1,y2,z1)
and having direction cosines
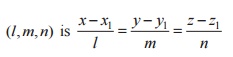
2. The equation of the straight line
through the point B(x2,y2,z2) and having
direction ratios
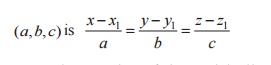
3. The equation of the straight line
passing through the points A(x1,y1,z1) and B(x2,y2,z2)
is
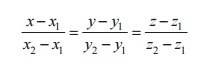
4. Angle between the straight lines:
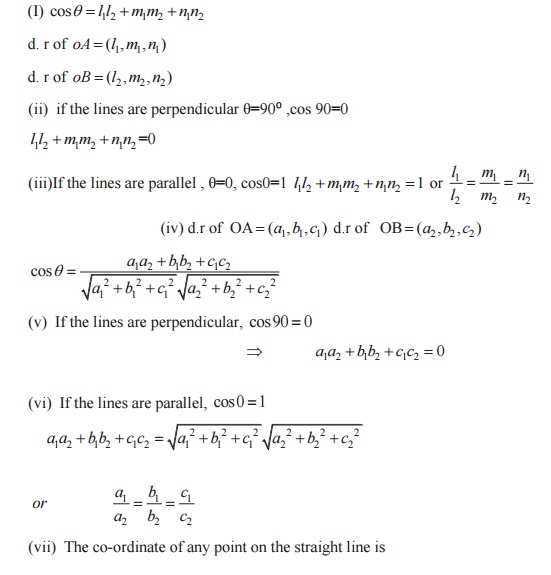
CONE
DEFINITION:
A cone is defined as a surface generated by a straight line which passes
through a fixed point and satisfies one or more conditioni.e.ie, it may
intersect a fixed curve.
Note:
1. The fixed point is said to be the
vertex of the cone
2. The fixed curve is said to be the
guiding curve of the cone
3. The straight line in any position is
called the generator of the cone.
FORMULA:
The equation of the cone with vertex (x1,y2,z1)
and whose generators intersect the guiding curve
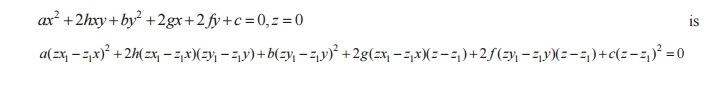
1.
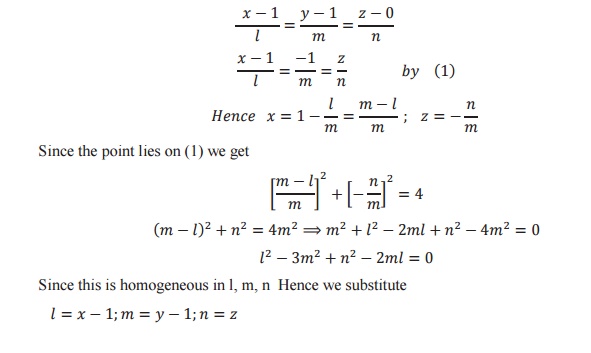
Find the equation of the cone with vertex at (1,1,1) and which passes through
the curve given by




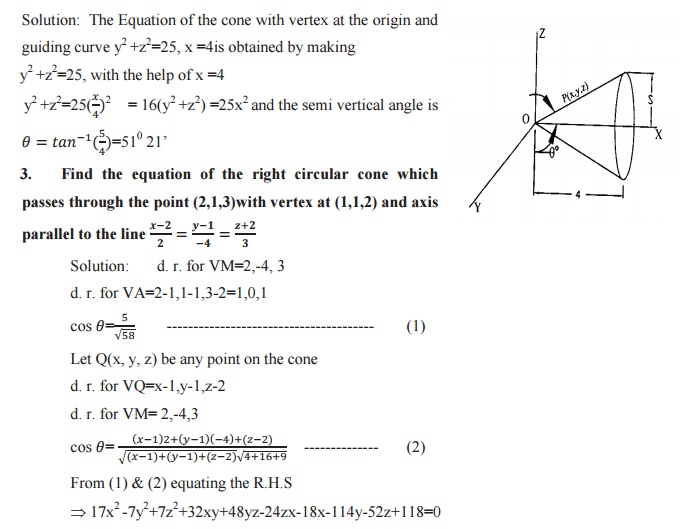
RIGHT-CIRCULAR CONE
DEFINITION:
A right circular cone is a surface generated by a straight line which passes
through a fixed point and makes a constant angle with a fixed line through the
fixed point. The equation of right
circular cone vertex is (x1,y1,z1) ,the semi
vertical angle a and axis the line



CYLINDER
DEFINITION:
A cylinder is a surface generated by a straight line which is parallel to a
fixed line and it has to intersect a given fixed curve. The straight line is
any position called a generator and the fixed point is called the guiding curve
of the cylinder.
The equation of cylinders whose generators are parallel to the line
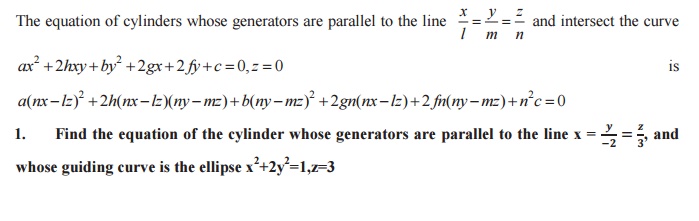
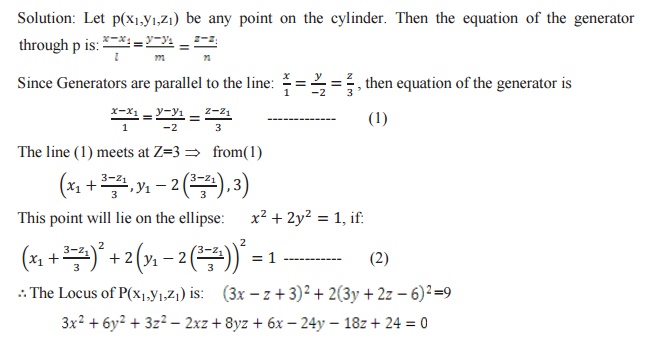
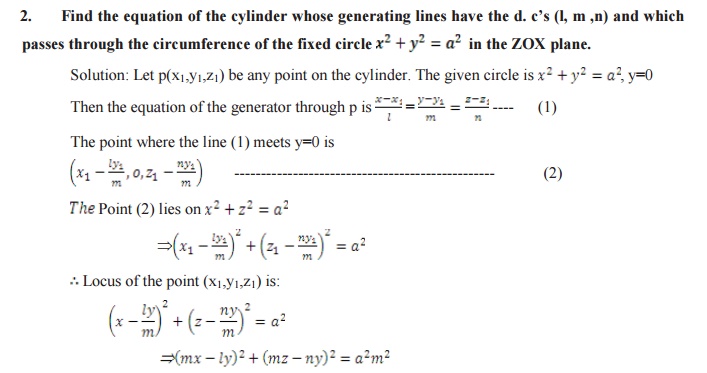
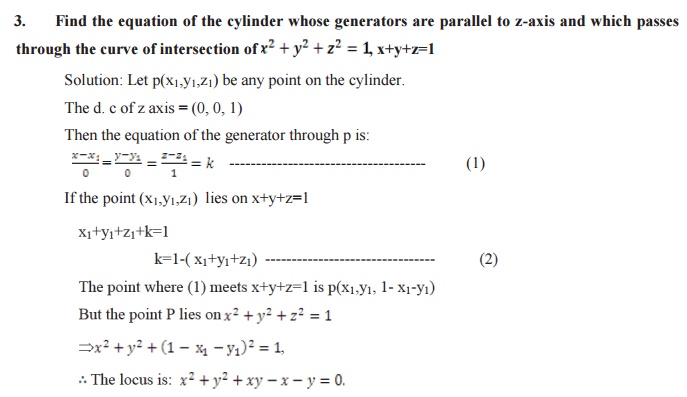
RIGHT CIRCULAR
CYLINDER
DEINITION: Right circular cylinder is a
surace generated by a straight line which is parallel to a fixed line is at a
contant distance it or whose guiding
curve is a circle.
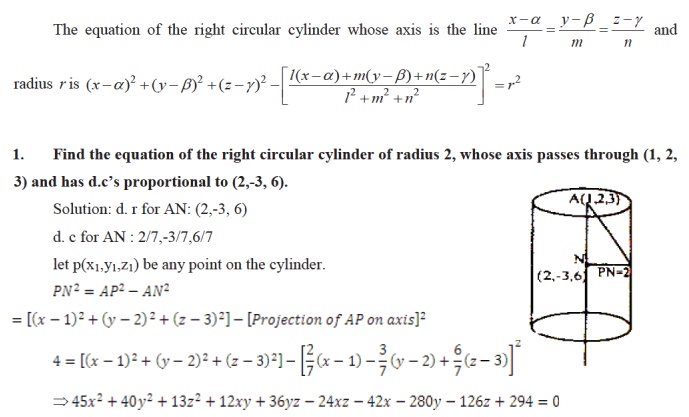
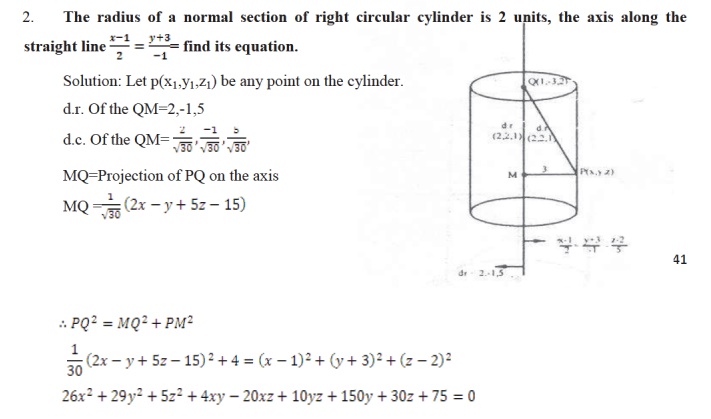
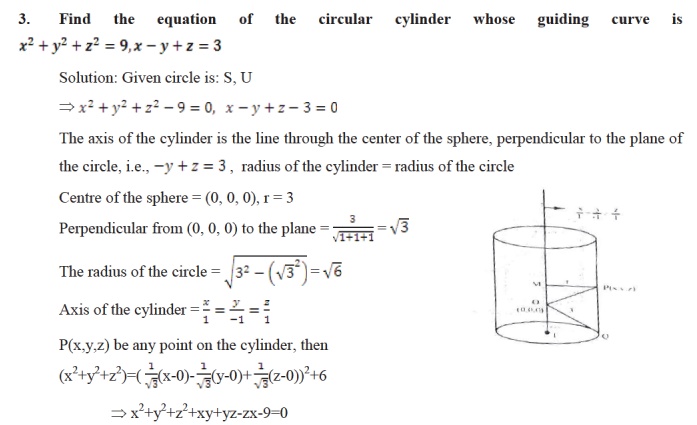
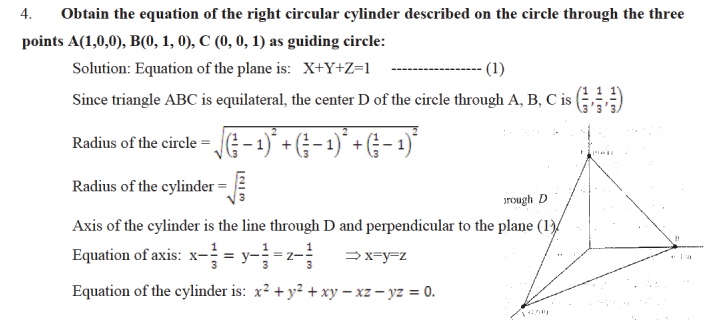

THE
SPHERE
DEFINITION:
A sphere is the locus of a point moving at a constant distance form a fixed
point. The constant distance is the
radius and the fixed point is the centre of the sphere.
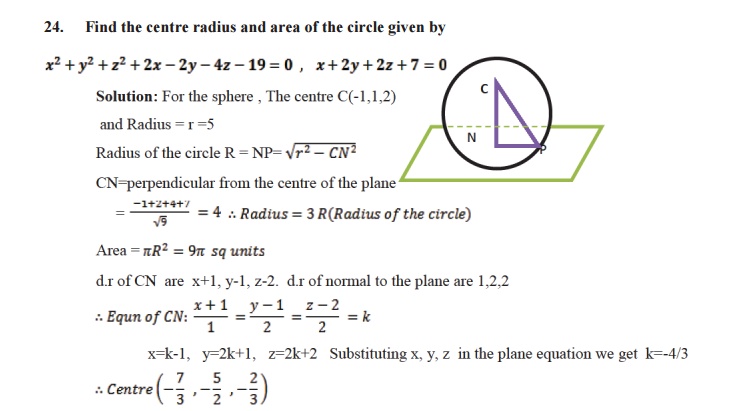
PLANE
SECTION OF A SPHERE:
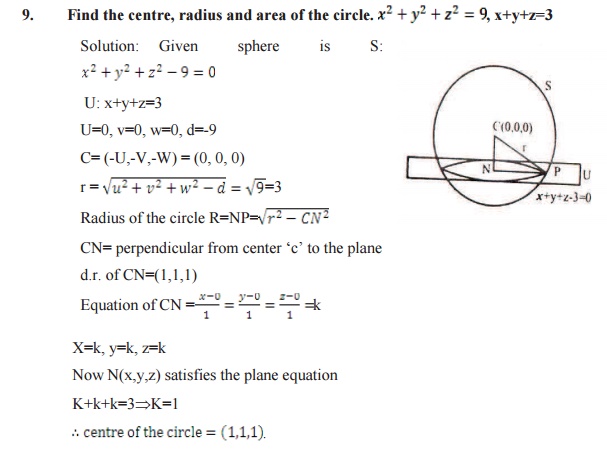
A
plane section of a sphere is a circle sphere S: x2+y2+z2+2ux+2vy+2wz+d=0
plane U: ax+by+cz+d1= 0 the combined equation (S,U) is a circle.
The equation of the sphere through the circle
a (S, U ) is S1=S+KU
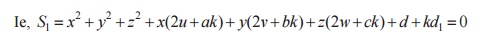
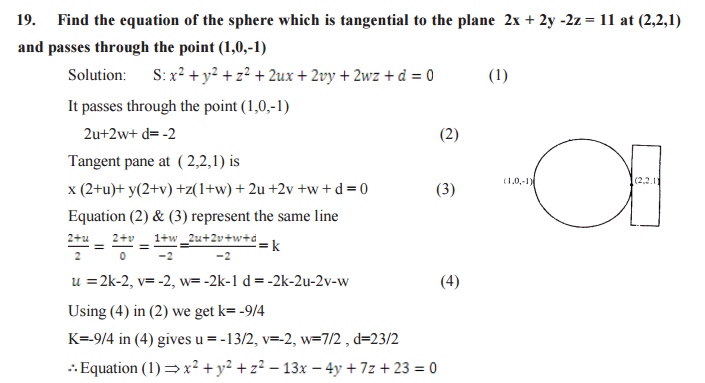
EQUATION
OF THE TANGENT PLANE
The sphere is x2+y2+z2+2ux+2vy+2wz+d=0
and the point of contact is (x1,y1,z1)
then
Equation of the Tangent plane is xx1+yy1+zz1+
u(x+x1)+v(y+y1)+w(z+z1) +d=0
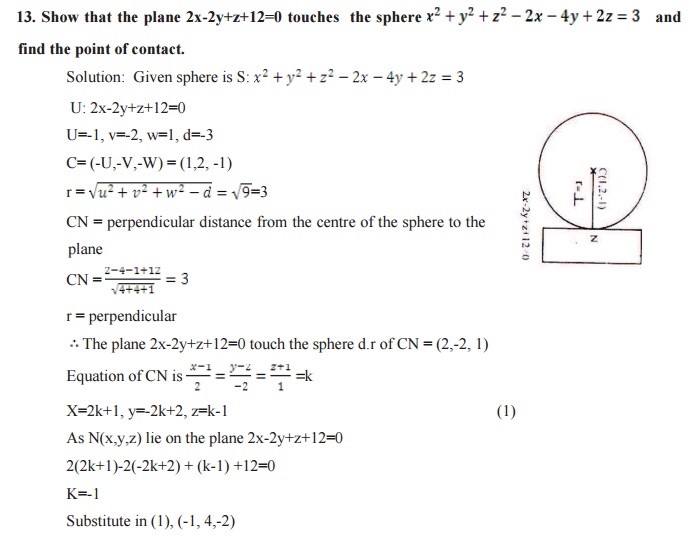
CONDITION
FOR TANGENCY:
Condition for tangency is perpendicular from
centre to the plane = radius
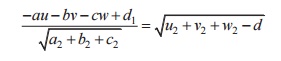
CONDITION
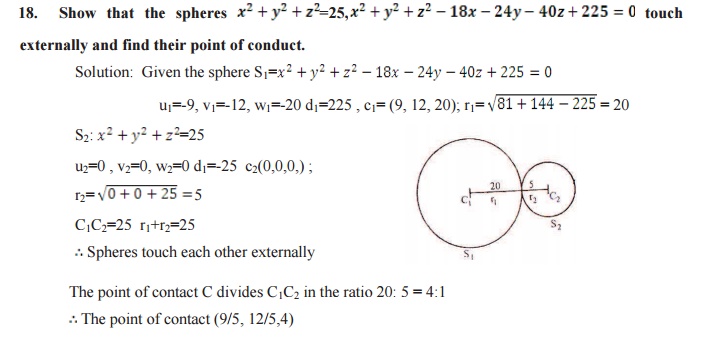
FOR ORTHOGONALITY OF TWO SPHERES:
The condition for orthogonality of two spheres
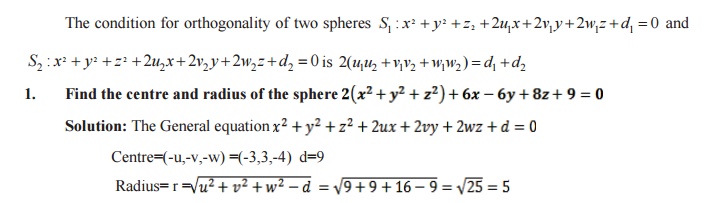
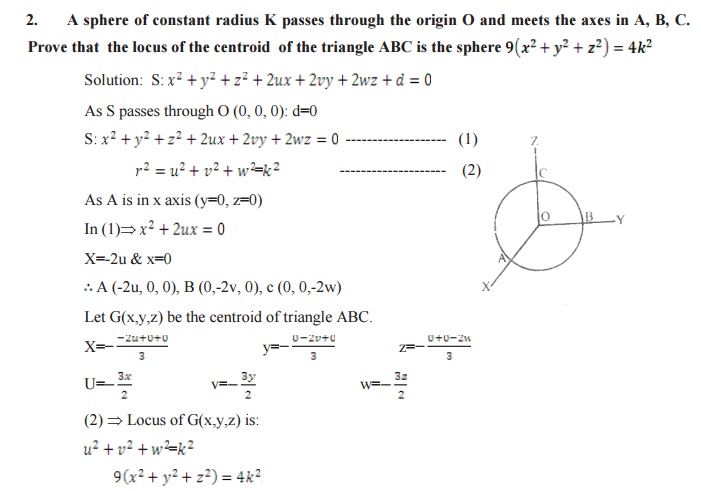








Related Topics