Chapter: Physics : Magnetic and Superconducting Materials
Solved Problems: Magnetic and Superconducting Materials
SOLVED PROBLEMS
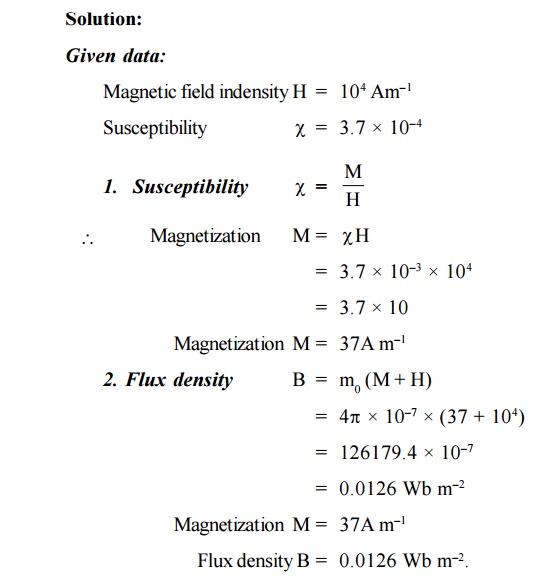
A paramagnetic material has a magnetic field
intensity of 104 Am–1. If the susceptibility of the
material at room temperature is 3.7 × 10–5. Calculate the
magnetization and flux density in the material.
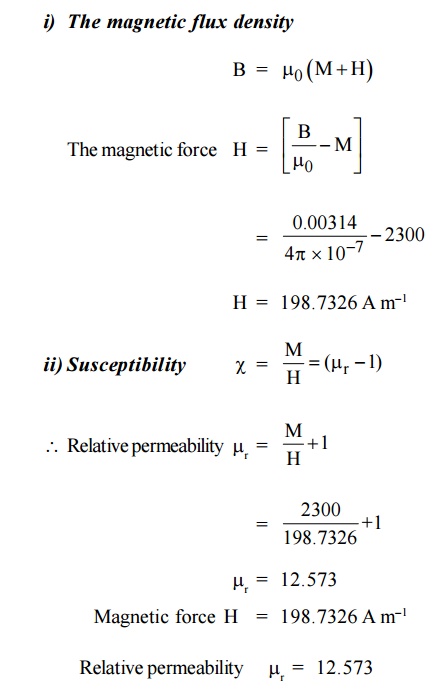
A
magnetic material has a magnetization of 2300 A m–1 and produces a
flux density of 0.00314 Wb m–2. Calculate the magnetizing force and
the relative permeability of the material.
Solution :
Given
data:
Magnetization
M = 2300 A m–1
Flux
density B = 0.00314 Web m–2.
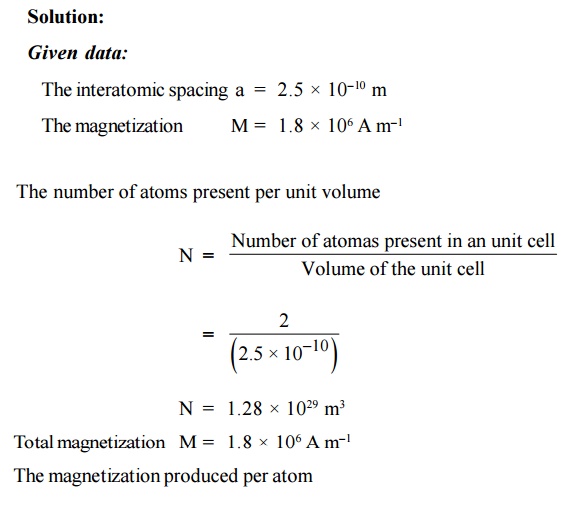
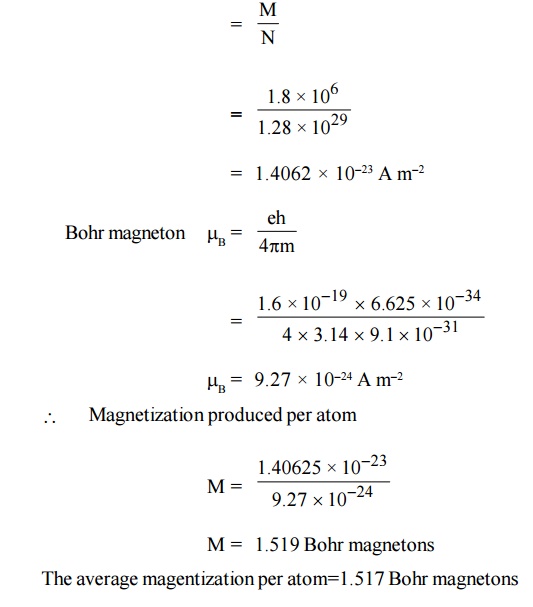
A paramagnetic material has FCC structure with a
cubic edge of 2.5 A°. If the saturation value of magnetization is 1.8 × 106
A m–1, Calculate the magnetization contributed per atom in Bohr
magnetrons.
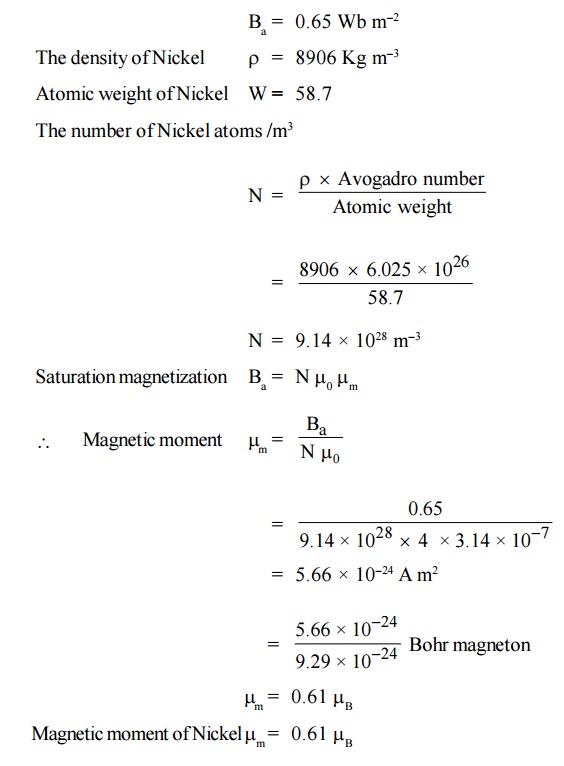
The saturation magnetic induction of Nickel is 0.65
Wb m–2. If the density of Nickel is 8906 kg m–3 and its
atomic weight is 58.7, calculate the magnetic moment of the Nickel atom in Bohr
magnetron.
Solution:
Given
data:
Saturation
magnetic induction of Nickel
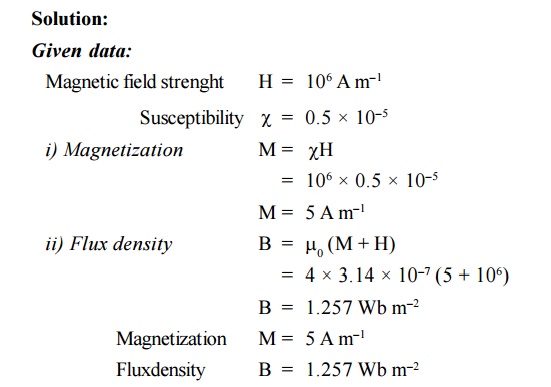
In a magnetic material the field strength is found
to be 106 A m–1. If the magnetic susceptibility of the
material is 0.5 × 10–5, calculate the intensity of magnetization and
flux density in the material.
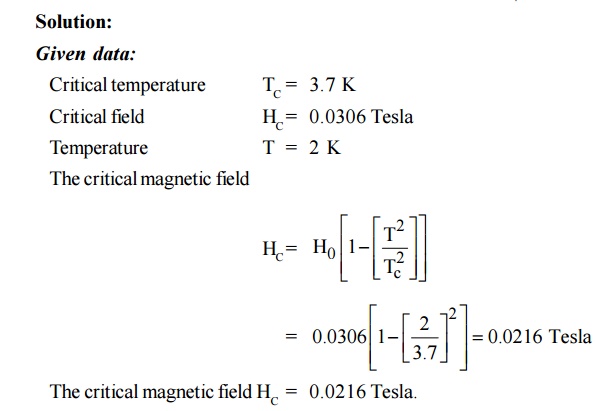
A superconducting tin has a critical temperature of
3.7 K at zero magnetic field and a critical field of 0.0306 Tesla at 0 K. Find
the critical field at 2 K.
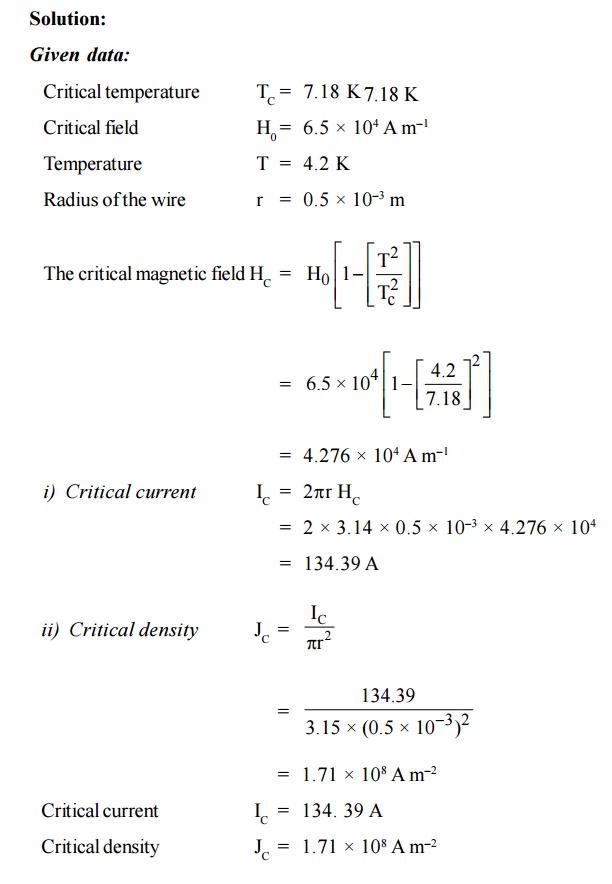
7. Calculate the critical current and current
density for a wire of a lead having a diameter of 1 mm at 4.2 K. The critical
temperature for lead is 7.18 K and H = 6.5 × 104 A m–1.
Prove
that susceptibility of superconductor is -1 and relative permeability is zero.

Find the
critical current which can pass through a long thin superconducting wire of
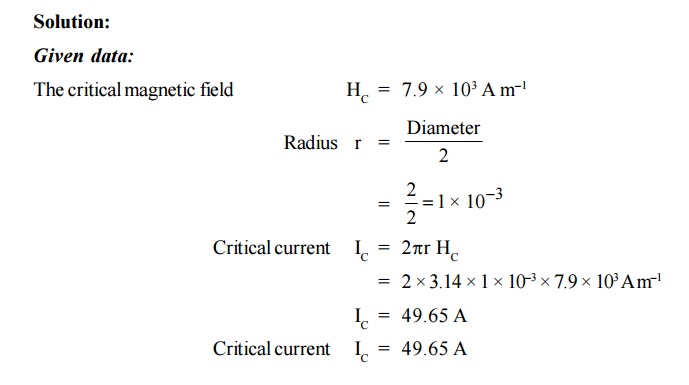
aluminum of diameter 2 mm, the critical magnetic field for aluminum is 7.9 × 103
A m–1.
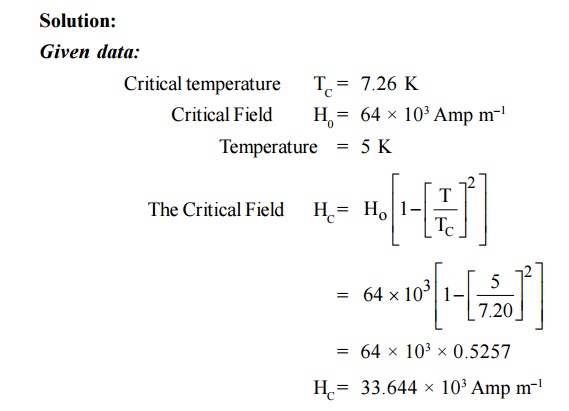
The superconducting transistion temperature of Lead
is 7.26 K. The initial field at 0 K is 64 × 103 Amp m–1.
Calculate the critical field at 5 K.
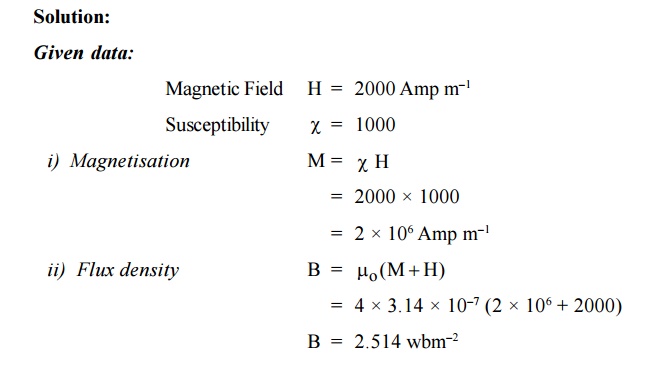
A magnetic field of 2000 Amp m–1 is
applied to a material which has a susceptibility of 1000. Calculate the (i)
Intensity and (ii) Flux density.
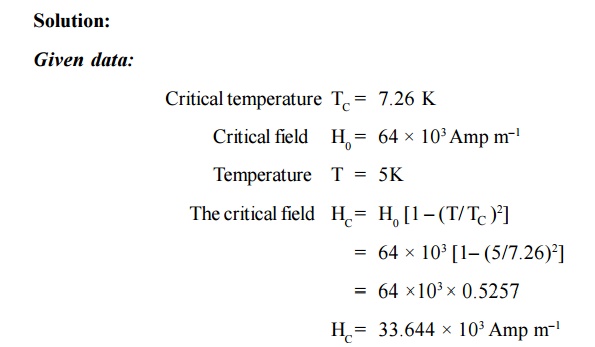
The superconducting transition temperature of lead
of 7.26 K. The initial field at 0 K is 64 × 103 Amp m–1.
Calculate the critical field at 5 K.
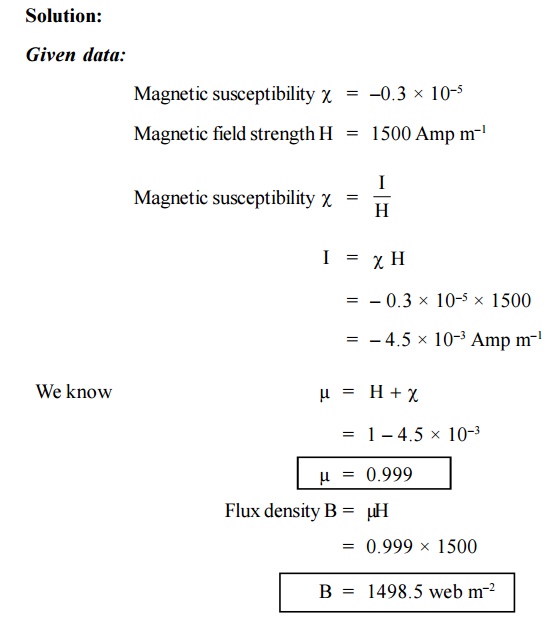
The magnetic field strength of Silicon is 1500 Amp
m–1. If the magnetic susceptibility is (–0.3 × 10–5),
calculate the magnetization and flux density in Silicon.
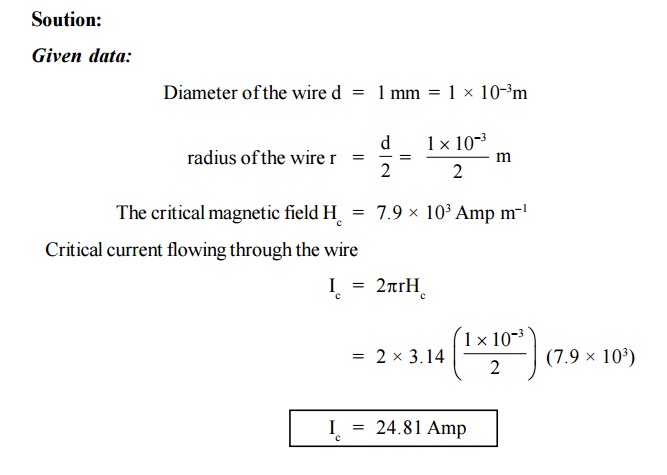
14. Calculate the critical current which can flow
through a long thin super conducting wire of diameter 1 mm. The critical
magnetic field is 7.9 × 103 Amp m–1.
ASSIGNMENT
PROBLEMS
1.The
saturation value of magnetization of iron is 1.76 × 106 A m–1.
Iron had body centered cubic structure with an elementary edge of 2.86
Å.Calculate the average number of Bohr magnetrons contributed to the
magnetization per atom.
(Ans: 2.2 Bohr magnetron per
atom)
2.The
magnetic field intensity of a ferric oxide piece is 106 A m–1.
If the susceptibility of the material at room temperature is 10.5 × 10–3,
calculate the flux density and magnetization of the material.
(Ans: B = 1.259 T and M = 1500 A
m–1 )
3. A magnetic material has a magnetization of 3000 A m–1
and flux density of 0.044 Wb m–2. Calculate the magnetic force and
the relative permeability of the
material. (Ans: M = 203 and r = 17.26)
Calculate the magnetic filed in the lead at 5 K, if
it’s critical magnetic field at 0 K H0 = 8 × 105 A m–1,
and transition temperature TC = 7.26 K
(Ans: 4.2 × 105 A m–1)
The critical temperature TC for mercury
with isotopic mass 199.5 is 4.185 K. Calculate its critical Temperature, when
it’s isotopic masses changes to 203.4.
(Ans: 4.139 K)
Calculate
the critical current which can flow though a long thin superconducting wire of
aluminum of diameter 1 mm. The critical magnetic field for aluminum is 7.9 × 103
A m–1.
Related Topics