Chapter: Clinical Cases in Anesthesia : Mitral Stenosis
How should preload, afterload, heart rate, and contractility be managed in a patient with mitral stenosis?
How
should preload, afterload, heart rate, and contractility be managed in a
patient with mitral stenosis?
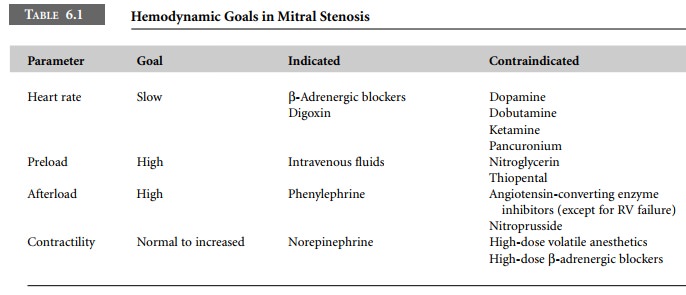
It is useful to consider the goals for preload, afterload, heart
rate, and contractility as the major principles guiding intraoperative
management in patients with mitral stenosis.
Left atrial pressure should remain high to
maintain preload. Thus, hypovolemia and venodilating drugs should be avoided.
Afterload (systemic vascular resistance) should be kept high to maintain
perfusion pressure in the face of a relatively fixed cardiac output. Heart rate
should be kept slow to maximize diastolic filling of the left ventricle.
Contractility should not be diminished because the cardiac output is already
low in these patients. The hemodynamic goals in mitral stenosis are summarized
in Table 6.1.
Related Topics