Chapter: Business Science : Merchant Banking and Financial Services : Leasing
Hire Purchase
HIRE PURCHASE
According to the Hire Purchase Act of
1972, the term hire purchase is defined as, an agreement under which goods are
let on hire and under which the hirer has an option to purchase them in
accordance with the terms of the agreement, and includes an agreement under
which a. Possession of goods is delivered by the owner thereof to a person on
the condition that such person pays the agreed amount in periodic payments b.
The property of the goods is to pass to such a person on the payment of the
last of such installment c. Such a person has a right to terminate the
agreement any time before the companies are controlled by the Hire Purchase
Act, 1972. A Hire purchase transaction has two elements, Bailment which is
governed by the Indian Contract Act, 1872 and Sale under the Sale of Goods Act,
1930.
1 Hire Purchase Agreement
A Hire Purchase
Agreement is an agreement between the seller and the buyer, where the ownership
of goods does not pass to the buyer until he pays the last installment. There
are two parties to the hire purchase agreement. The hire vendor, who is the
seller and other, is the hire purchaser, the buyer. The purchaser has to make a
down payment of 20 to 25% of the cost and the remaining amount has to be paid
in equal monthly installments. In the case of a Deposit linked plan, the hire
purchaser has to invest a fixed amount as fixed deposits in the finance company
which is returned together with interest after the payment of the last
installment.
Parties to the Hire Purchase Contract:
There
are two parties in a hire purchase contract 1. The intending seller 2.
The intending
purchaser or the hirer.
Tripartite agreement 1.
Seller 2. Financier 3. Hirer/Purchaser
Difference between Hire Purchase and
Leasing:
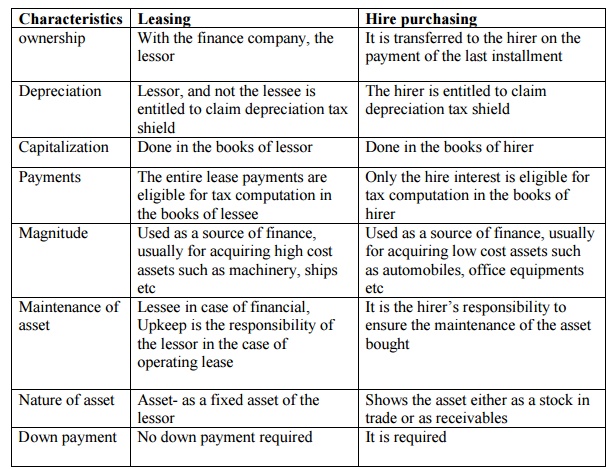
Characteristics
Ownership:
Leasing: With the finance company, the lessor
Hire purchasing: It is transferred to the hirer on
the payment of the last installment
Depreciation:
Leasing: Lessor, and not the lessee is entitled to claim depreciation tax shield
Hire purchasing: The hirer is entitled to claim
depreciation tax shield
Capitalization
Leasing: Done in the books of lessor
Hire purchasing: Done in the books of hirer
Payments
Leasing: The entire lease payments are eligible for
tax computation in the books of lessee
Hire purchasing: Only the hire interest is eligible
for tax computation in the books of hirer
Magnitude
Leasing: Used as a source of finance, usually for
acquiring high cost assets such as machinery, ships etc
Hire purchasing: Used as a source of finance,
usually for acquiring low cost assets such as automobiles, office equipments
etc
Maintenance
of asset
Leasing: Lessee in case of financial, Upkeep is the
responsibility of the lessor in the case of operating lease
Hire purchasing: It is the hirer‘s responsibility to
ensure the maintenance of the asset bought
Nature
of asset
Leasing: Asset- as a fixed asset of the lessor
Hire purchasing:
Shows the asset either as a stock in trade or as receivables
Down
payment
Leasing: No down payment required
Hire purchasing: It is required
Financial Evaluation:
It is an evaluation by
the hirer of the desirability for lease and hire purchase. The hirer makes
decision based on the Present Value of Net Cash Outflow. The decision is
considered favorable when the PV of Net Cash Outflow under Hire Purchase is
less than the PV of Net cash Outflow under leasing. Following are the steps
involved.
Step 1 Calculate
annual interest amount
Step 2 Find
the principal amount outstanding at the beginning of the each year = Total outstanding
principal –principal paid in the previous year.
Step 3 Find
principal paid in the previous year = Annual installment amount –Annual
Interest
Step 4 Find
Annual ITS = Annual Interest x Tax rate
Step 5 Find
Annual Depreciation
Step 6 Find
Annual DTS = Annual depreciation x Tax rate
Step 7 Find
Total TS = Step 4 + Step 6
Step 8 Find
Annual installment amount = Total HP amount + (HP amount x flat rate of
interest) / No. of HP years
Step 9 Find
PV of salvage value of assets = SV x PVF
Step 10 Find
Net Cash Outflow of HP = Step 8 –Step 7
HIRE PURCHASE LEASING
1. It
is a tripartite agreement, involving the seller, finance company and the
purchaser/hirer
2. Depreciation
is claimed by the purchaser/hirer
3.
The agreement is entered for the
transfer of ownership after a fixed period. 1. It is a bipartite agreement
involving lessor and lessee. 2. Depreciation is claimed by the lessor in the
lease agreement. 3. In finance lease the ownership will get transferred. While
in operating lease, the ownership is not transferred.
Step 11 Find
PV of net cash outflow of HP at the appropriate discount rate.
Step 12 Find
Total PV net cash outflow of HP = Step 11 –Step 9.
Step 13 Find
Tax shield on annual ease rentals = Annual Lease rental x Tax rate.
Step 14 Find
Net cash outflow of Leasing = Annual lease rental –Step 13.
Step 15 Find
Total PV of net cash outflow of Leasing at the approp. Discount rate = Net cash
outflow of Leasing x PVAF.
Step 16 Make
a decision: HP is desirable if total PV of net cash flow of HP is Less than
that of leasing.
Related Topics